Original publish date: October 31, 2019
It was Saturday, October 31, 1903. The college football season was half over as the Purdue Boilermakers geared up for their annual in-state rivalry game against Indiana University. (The “Old Oaken Bucket” trophy was still 20 years in the future.) The rivalry had started a dozen years before in 1891 and for awhile it looked like a clean sweep for the Purdue squad with the Boilers taking the first 6 games outscoring the boys from Bloomington 227 to 6. Then I.U. reeled off 3 in a row to shock the West Lafayette faithful before Purdue took the 1902 contest by once again swamping the cream & crimson 39-0.
The competition for gridiron glory between these two in-state titans was so hot and intense that, for the 1903 contest, both schools agreed that games should be held on neutral ground to quell “potential hooliganism” on the part of the students and fans. To this point eight games had been played in West Lafayette and two in Bloomington. In the spirit of fair play, officials from both schools decided to play the 11th contest on a neutral field at Washington Park in Indianapolis. Washington Park was located at 3001 East Washington Street where it meets Gray Street (in the southwest corner of that intersection). The ballpark, built in 1900 just a stone’s throw from Irvington, was home to the 1902 defending American Association champion Indianapolis Indians.

To get to the new state capital location, both teams joined what seemed like the entire student body as they piled into separate special service trains to travel to the game from north and south of the city. Two special trains, operated by the “Big Four Railroad” (the Cleveland, Cincinnati, Chicago and St. Louis Railway), were chartered to carry over 1,500 passengers from Lafayette to Indianapolis for the annual rivalry game. Purdue’s team train was cobbled together like a patchwork quilt and included modern steel streamliner coaches coupled to older wooden coaches. The Boilermakers football team rode in the wooden cars at the front of the train procession.
 The train was traveling on what would have been the 101st birthday of school founder and namesake John Purdue (born October 31, 1802). Purdue, a wealthy landowner, politician, educator and merchant, was the primary benefactor of the University. In 1903, if you wanted to get to Indianapolis from either school, you had three choices: ride a horse and buggy, walk or take the train. Since these were the days before automobile travel was popular, train travel was the most widely accepted form of transportation.
The train was traveling on what would have been the 101st birthday of school founder and namesake John Purdue (born October 31, 1802). Purdue, a wealthy landowner, politician, educator and merchant, was the primary benefactor of the University. In 1903, if you wanted to get to Indianapolis from either school, you had three choices: ride a horse and buggy, walk or take the train. Since these were the days before automobile travel was popular, train travel was the most widely accepted form of transportation.
It was Halloween in 1903; late October in the Hoosier Heartland. It is hard for our modern sensibilities to imagine those pre-electricity rural landscapes dotted by farmhouses scattered in a wide swath like checkers on a checkerboard. In this era, Hoosiers generally lived in small communities and held tight to their neighbors. News traveled slowly and so did the traffic. As the Gilded age of Mark Twain collided with the Progressive Era of Teddy Roosevelt, it became apparent that something’s gotta give. Safety was an issue in this gargantuan game of rock, paper, scissors where iron and steel trumped wood every time.

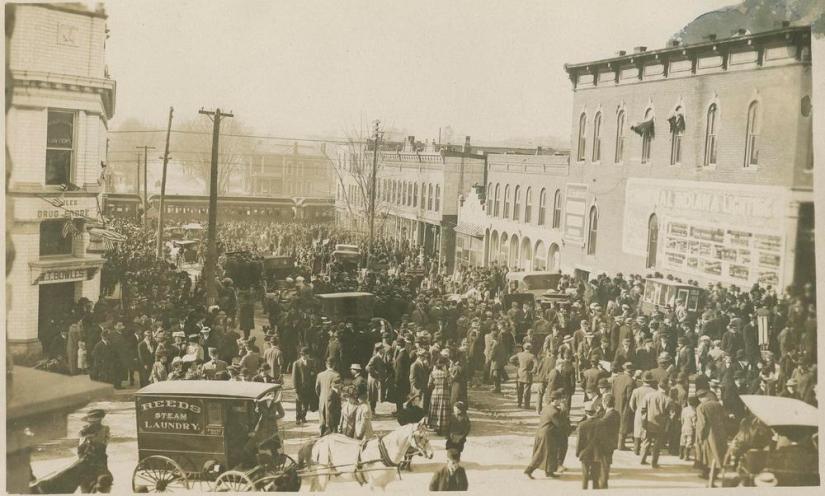
In West Lafayette, it was a festive atmosphere and the town was buzzingly, excited for the match up against the Hoosiers. Like I.U.’s Bloomington, West Lafayette draws so much of its identity from their University and the entire community was looking forward to the weekend. Purdue was 4-2 on the season with a big win over rival Wabash College, but losses to Chicago and Illinois. Purdue enjoyed a 7-3 overall advantage in the series against I.U. and was feeling confident. Running at the rate of thirty miles an hour, the John Purdue Big Four special was carrying 954 students and spectators, including the football team, University President and star fullback and team captain Harry “Skillet” Leslie.
 Unlike the raucous fans traveling in the 13 plush, modern streamliner train coaches behind them, the Boilermakers team traveled in relative silence, focusing on the task at hand, mentally preparing for their upcoming rivalry game in the cozy confines of an older wooden train car. Unfortunately, the athletes had no idea that a minor mistake would lead to a major disaster. Railroad protocol specified that “Special” trains operate independent of the regular schedule. Timing was everything in the railroad game.
Unlike the raucous fans traveling in the 13 plush, modern streamliner train coaches behind them, the Boilermakers team traveled in relative silence, focusing on the task at hand, mentally preparing for their upcoming rivalry game in the cozy confines of an older wooden train car. Unfortunately, the athletes had no idea that a minor mistake would lead to a major disaster. Railroad protocol specified that “Special” trains operate independent of the regular schedule. Timing was everything in the railroad game.
In the early 1900s, the rail service depended on many human components: conductors and their assistants, dining car stewards, ticket collectors, train baggage men, brakemen, and train flagmen on the vehicle itself and yardmasters, yard conductors, switch tenders, foremen, flagmen, brakemen, switchmen, car tenders, operators, hump riders, and car operators on the ground. In 1903, railroad track “switches” were manually operated by lantern carrying tenders fluent in the language of railway lantern semaphore, which, strictly defined, means the act of waving a lantern as a warning.
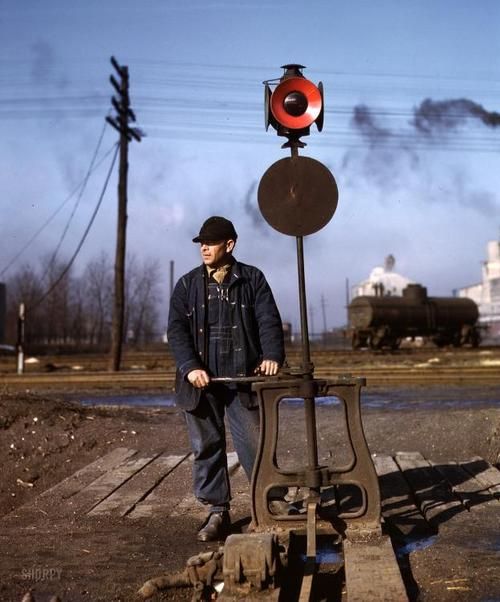

Switch tenders communicated with brakemen who most often stood atop boxcars waving happily at his railyard cohorts and locals as the train glided past. As the train traveled down the rails, some of these daredevils ran along the top of the cars, adjusting the brake wheels sticking up from each car as they went. The complexities of switching, congestion, and rearranging cars made freight yards a far more perilous workplace and working on a moving train could be downright treacherous. One railyard superintendent, when talking about his workers, once famously said, “Men are cheaper than shingles. . . There’s a dozen waiting when one drops out.”
The trouble was, this apparent dispensability of railway workers could cause havoc in areas where tracks needed to be switched to avoid collisions. As the Purdue Special steamed towards the Circle City at over 30 miles per hour, a clerk up the line from Lafayette failed to inform the yardmaster near 18th Street in Indianapolis that the trains were coming. The first train, carrying the team, rounded a curve at the Mill Street Power House and saw a coal train being pushed back on the tracks. The engineer immediately slammed the engine in reverse, locked the emergency brake, and leapt off the moving train.
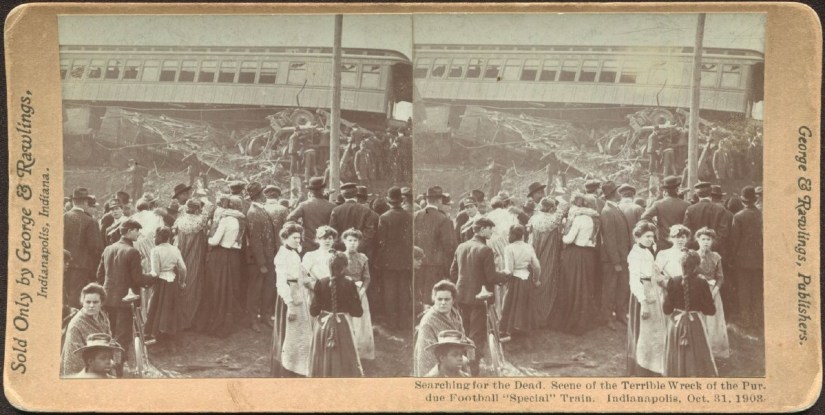 The Boilermakers never knew what hit ’em. The engine slammed into the coal car, splintering apart the first few cars while folding like an accordion. When the two trains collided, the lead car hit the debris, causing it to shoot into the air. This gave the full impact to the second train car, causing all the deaths. The wooden train cars splintered like kindling and were destroyed, and the adjacent cars careened violently off the elevated tracks, tumbling to the ground below like jack straws.
The Boilermakers never knew what hit ’em. The engine slammed into the coal car, splintering apart the first few cars while folding like an accordion. When the two trains collided, the lead car hit the debris, causing it to shoot into the air. This gave the full impact to the second train car, causing all the deaths. The wooden train cars splintered like kindling and were destroyed, and the adjacent cars careened violently off the elevated tracks, tumbling to the ground below like jack straws.
 The Indianapolis star reported, “The trains came together with a great crash, which wrecked three of the passenger coaches, in addition to the engine and tender of the special train and two or three of the coal cars. The first coach on the special train was reduced to splinters. The second coach was thrown down a fifteen-foot embankment into the gravel pit and the third coach was thrown from the track to the west-side and badly wrecked. The coal cars plowed their way into the engine and demolished it completely. The coal tender was tossed to the side and turned over. A wild effort on the part of the imprisoned passengers to escape from the wrecked car followed the crash. Immediately following the wreck the students and the others turned their attention to the work of rescuing the injured, and by the time the first ambulances arrived many of the dead and suffering young men had been carried out and placed on the grass on both sides of the track.”
The Indianapolis star reported, “The trains came together with a great crash, which wrecked three of the passenger coaches, in addition to the engine and tender of the special train and two or three of the coal cars. The first coach on the special train was reduced to splinters. The second coach was thrown down a fifteen-foot embankment into the gravel pit and the third coach was thrown from the track to the west-side and badly wrecked. The coal cars plowed their way into the engine and demolished it completely. The coal tender was tossed to the side and turned over. A wild effort on the part of the imprisoned passengers to escape from the wrecked car followed the crash. Immediately following the wreck the students and the others turned their attention to the work of rescuing the injured, and by the time the first ambulances arrived many of the dead and suffering young men had been carried out and placed on the grass on both sides of the track.”
 The fans at the rear of the train were unaware of what happened and only felt a slight jolt as the train came to a sudden stop. These rearmost passengers wasted no time in coming to the assistance of the victims up ahead. The erstwhile revelers skidded to a stop at the scene of carnage and were horrified at the devastation before them. Acts of unselfish action made heroes out of athletes and ordinary people alike.
The fans at the rear of the train were unaware of what happened and only felt a slight jolt as the train came to a sudden stop. These rearmost passengers wasted no time in coming to the assistance of the victims up ahead. The erstwhile revelers skidded to a stop at the scene of carnage and were horrified at the devastation before them. Acts of unselfish action made heroes out of athletes and ordinary people alike.
According to Purdue student Joseph Bradfield who was riding in the procession, “We began carrying the people out, the injured ones. There was a line of horse-and-buggies along the whole stretch there for half a mile. We didn’t stop for ceremony; we simply loaded the injured people into the buggies and sent the buggies into town, got them to a hospital…There was no ambulance, no cars…”
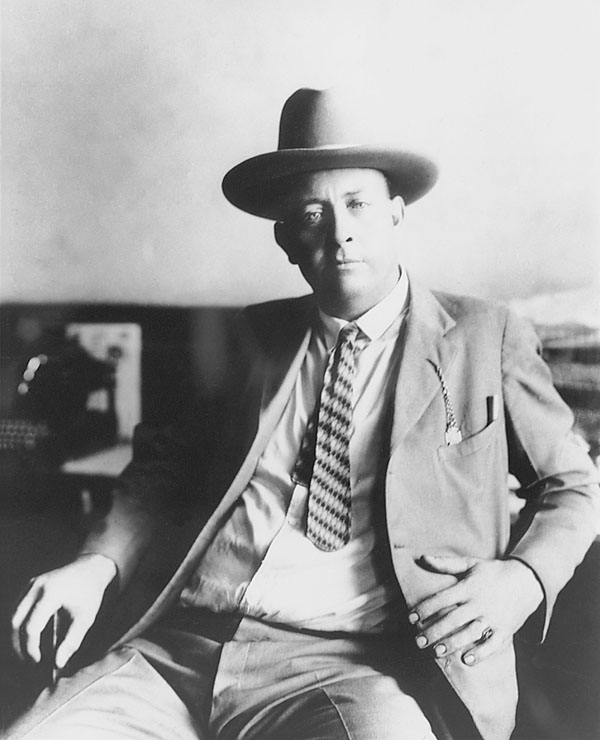
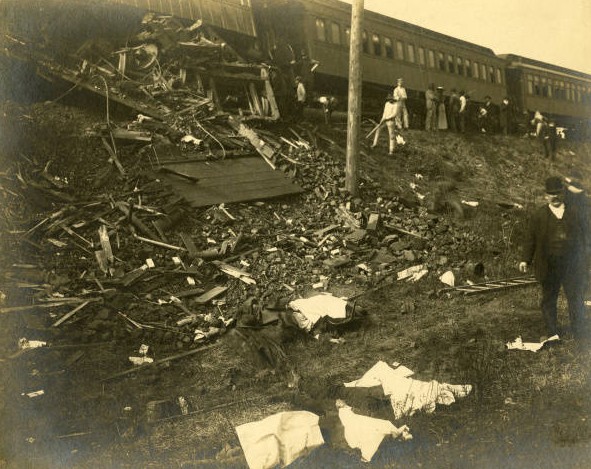 Seventeen passengers in the first coach were killed. Thirteen of the dead were members of the Purdue football team. Walter Bailey, a reserve player from New Richmond, although grievously injured, refused aid so that others could be helped. Team Captain Skeets Leslie was covered up for dead, his body transported to the morgue with the others. It was the first catastrophe to hit a major college sports team in the history of this country. The affects would be felt for decades to come and one of those players would rise from the dead, shake off accusations of association with Irvington KKK leader D.C. Stephenson, and lead his state and country through the Great Depression.
Seventeen passengers in the first coach were killed. Thirteen of the dead were members of the Purdue football team. Walter Bailey, a reserve player from New Richmond, although grievously injured, refused aid so that others could be helped. Team Captain Skeets Leslie was covered up for dead, his body transported to the morgue with the others. It was the first catastrophe to hit a major college sports team in the history of this country. The affects would be felt for decades to come and one of those players would rise from the dead, shake off accusations of association with Irvington KKK leader D.C. Stephenson, and lead his state and country through the Great Depression.
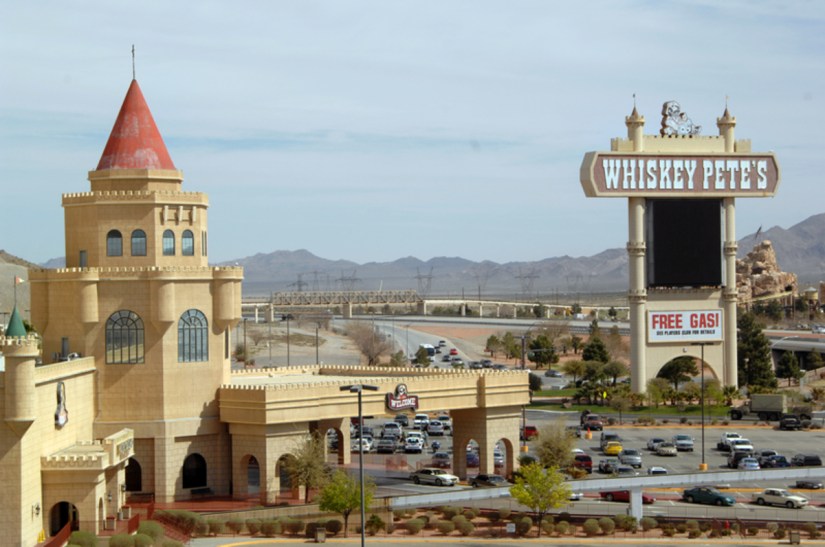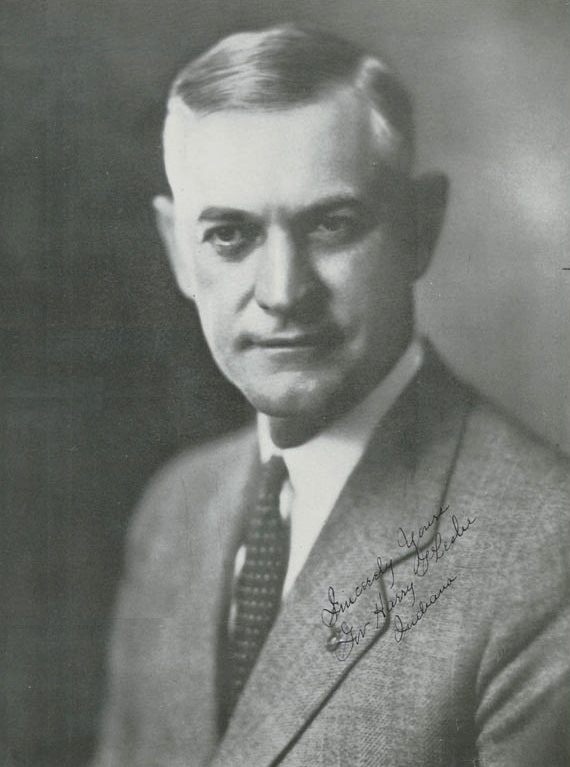



 One of those “must see” old timey casinos is located about 30 miles southwest of the Vegas strip in a desert town called Primm, Nevada not far from the California border. Known as “Whiskey Pete’s”, the casino covers 35,000 square feet, has 777 rooms, a large swimming pool, gift shop and four restaurants. The casino is named after gas station owner Pete MacIntyre. “Whiskey Pete” had a difficult time making ends meet selling gas, so he resorted to bootlegging and an idea was born. When Whiskey Pete died in 1933, he was secretly buried standing up with a bottle of whiskey in his hands so he could watch over the area. Decades later, his unmarked grave was accidentally exhumed by workers building a connecting bridge from Whiskey Pete’s to Buffalo Bill’s (on the other side of I-15). According to legend, the body was reburied in one of the caves where Pete once cooked up his moonshine.
One of those “must see” old timey casinos is located about 30 miles southwest of the Vegas strip in a desert town called Primm, Nevada not far from the California border. Known as “Whiskey Pete’s”, the casino covers 35,000 square feet, has 777 rooms, a large swimming pool, gift shop and four restaurants. The casino is named after gas station owner Pete MacIntyre. “Whiskey Pete” had a difficult time making ends meet selling gas, so he resorted to bootlegging and an idea was born. When Whiskey Pete died in 1933, he was secretly buried standing up with a bottle of whiskey in his hands so he could watch over the area. Decades later, his unmarked grave was accidentally exhumed by workers building a connecting bridge from Whiskey Pete’s to Buffalo Bill’s (on the other side of I-15). According to legend, the body was reburied in one of the caves where Pete once cooked up his moonshine. Oh, I forgot to mention that Whiskey Pete’s is also home to the Bonnie and Clyde death car. As detailed in part III of this series, the car has had a long strange trip to Primm. The bullet-ridden car toured carnivals, amusement parks, flea markets, and state fairs for decades before being permanently parked on the plush carpet between the main cashier cage and a lifesize caged effigy of Whiskey Pete himself. According to the “Roadside America” website, “For a time it was in the Museum of Antique Autos in Princeton, Massachusetts, then in the 1970s it was at a Nevada race track where people could sit in it for a dollar. A decade later it was in a Las Vegas car museum; a decade after that it was in a casino near the California / Nevada state line. It was then moved to a different casino on the other side of the freeway, then it went on tour to other casinos in Iowa, Missouri, and northern Nevada.
Oh, I forgot to mention that Whiskey Pete’s is also home to the Bonnie and Clyde death car. As detailed in part III of this series, the car has had a long strange trip to Primm. The bullet-ridden car toured carnivals, amusement parks, flea markets, and state fairs for decades before being permanently parked on the plush carpet between the main cashier cage and a lifesize caged effigy of Whiskey Pete himself. According to the “Roadside America” website, “For a time it was in the Museum of Antique Autos in Princeton, Massachusetts, then in the 1970s it was at a Nevada race track where people could sit in it for a dollar. A decade later it was in a Las Vegas car museum; a decade after that it was in a casino near the California / Nevada state line. It was then moved to a different casino on the other side of the freeway, then it went on tour to other casinos in Iowa, Missouri, and northern Nevada.  Complicating matters was the existence of at least a half-dozen fake Death Cars and the Death Car from the 1967 Bonnie and Clyde movie (which was in Louisiana and then Washington, DC, but now is in Tennessee).” Just in case of any remaining confusion, the Primm car is accompanied by a bullet riddled sign reading: “Yes, this is the original, authentic Bonnie and Clyde death car” (in all caps for emphasis).
Complicating matters was the existence of at least a half-dozen fake Death Cars and the Death Car from the 1967 Bonnie and Clyde movie (which was in Louisiana and then Washington, DC, but now is in Tennessee).” Just in case of any remaining confusion, the Primm car is accompanied by a bullet riddled sign reading: “Yes, this is the original, authentic Bonnie and Clyde death car” (in all caps for emphasis).
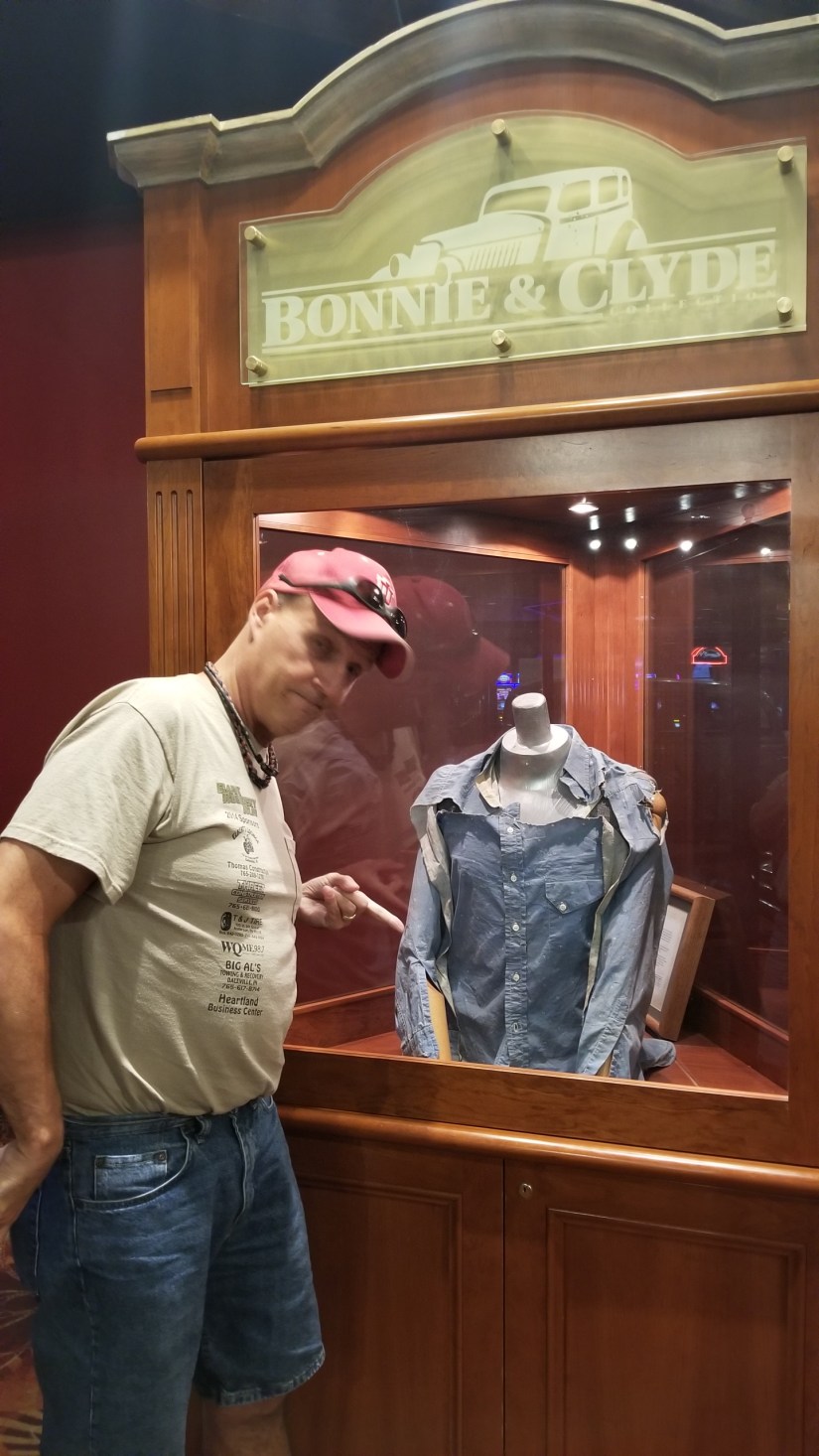
 The walls surrounding the death car are festooned with authentic newspapers detailing the outlaw lover’s demise and letters vouching to the vehicle’s authenticity. Cases contain other Bonnie and Clyde relics like a belt given by Clyde to his sister and classic candid photos of the star-crossed lovers and their families.
The walls surrounding the death car are festooned with authentic newspapers detailing the outlaw lover’s demise and letters vouching to the vehicle’s authenticity. Cases contain other Bonnie and Clyde relics like a belt given by Clyde to his sister and classic candid photos of the star-crossed lovers and their families.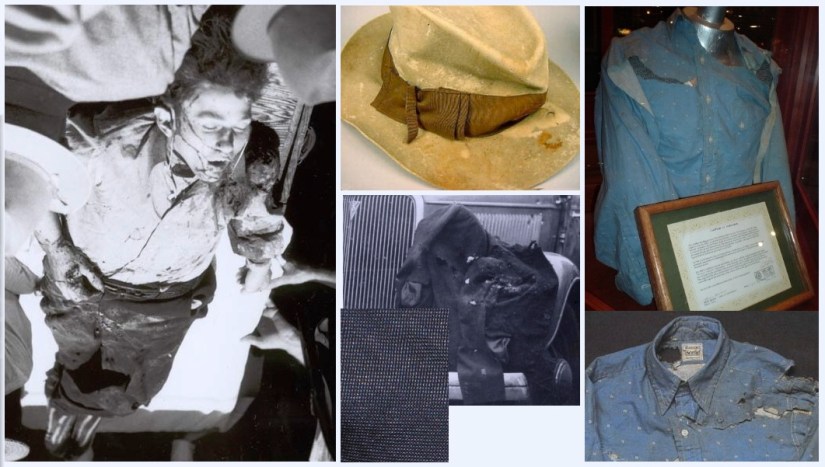 A movie, obviously created many years ago, recreates the event using newsreel footage, landscape photography and contemporary interviews with family members and eyewitnesses. Here, it is revealed that the shirt was found, decades after the outlaw’s death, secreted away in a sealed metal box along with Clyde’s hat. The film itself has become a piece of Americana and the images of Bonnie’s torn and tattered body left twitching in the car, resting silently mere yards away, are equally breathtaking. Nearby, although not nearly as shocking as the Bonnie and Clyde death car, another bullet-scarred automobile is on display. This one first belonged to gangster Dutch Schultz and later, Al Capone. Signs around the car proclaim that the doors are filled with lead and, judging by the pockmarks of the bullets denting the exterior, it is true. Although, like every casino, Whiskey Pete’s job remains separating gamblers from their money, both cars are on display 24 hours a day for free.
A movie, obviously created many years ago, recreates the event using newsreel footage, landscape photography and contemporary interviews with family members and eyewitnesses. Here, it is revealed that the shirt was found, decades after the outlaw’s death, secreted away in a sealed metal box along with Clyde’s hat. The film itself has become a piece of Americana and the images of Bonnie’s torn and tattered body left twitching in the car, resting silently mere yards away, are equally breathtaking. Nearby, although not nearly as shocking as the Bonnie and Clyde death car, another bullet-scarred automobile is on display. This one first belonged to gangster Dutch Schultz and later, Al Capone. Signs around the car proclaim that the doors are filled with lead and, judging by the pockmarks of the bullets denting the exterior, it is true. Although, like every casino, Whiskey Pete’s job remains separating gamblers from their money, both cars are on display 24 hours a day for free.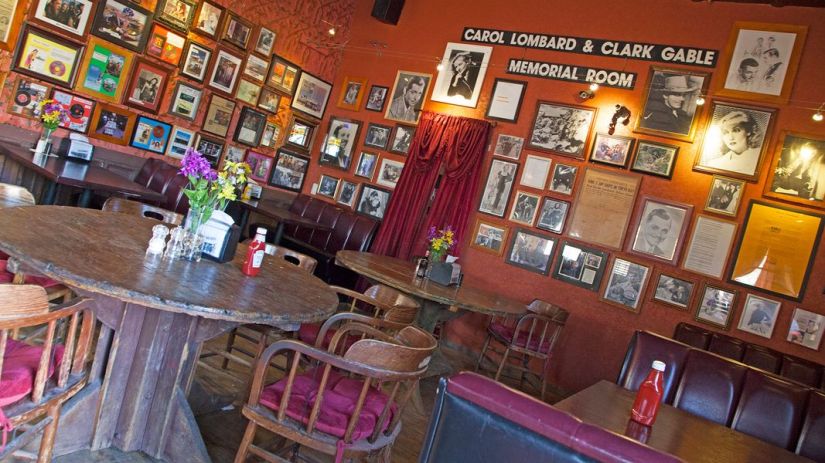 The interior of the Pioneer Saloon remains unchanged. It is easy to imagine Gone with the Wind star Gable drowning his sorrows at a rickety table or bracing himself against the cowboy bar and it’s brass boot rail. Ask and the bartender will point out the cigarette burn holes in the bar caused by Gable when he passed out from a mixture of grief and alcohol during his somber vigil. The tin ceiling remains as do the ancient celing fans (it gets HOT in the desert) and the walls are peppered with bullet holes left by cowboys who rode off into the sunset generations ago. The bar’s backroom is a shrine to the Lombard / Gable tragedy but sadly most of the relics on display there are modern photocopies and recreations. Locals claim that Carole Lombard’s ghost haunts the saloon in a desperate attempt to contact her grieving husband. The saloon is also reportedly haunted by the ghost of an old “Miner 49er” who appears drinking alone at the far end of the bar before vanishing into thin air. Millennials flock to the bar as the birthplace of the game “Fallout: New Vegas” which also has a small shrine located there.
The interior of the Pioneer Saloon remains unchanged. It is easy to imagine Gone with the Wind star Gable drowning his sorrows at a rickety table or bracing himself against the cowboy bar and it’s brass boot rail. Ask and the bartender will point out the cigarette burn holes in the bar caused by Gable when he passed out from a mixture of grief and alcohol during his somber vigil. The tin ceiling remains as do the ancient celing fans (it gets HOT in the desert) and the walls are peppered with bullet holes left by cowboys who rode off into the sunset generations ago. The bar’s backroom is a shrine to the Lombard / Gable tragedy but sadly most of the relics on display there are modern photocopies and recreations. Locals claim that Carole Lombard’s ghost haunts the saloon in a desperate attempt to contact her grieving husband. The saloon is also reportedly haunted by the ghost of an old “Miner 49er” who appears drinking alone at the far end of the bar before vanishing into thin air. Millennials flock to the bar as the birthplace of the game “Fallout: New Vegas” which also has a small shrine located there.
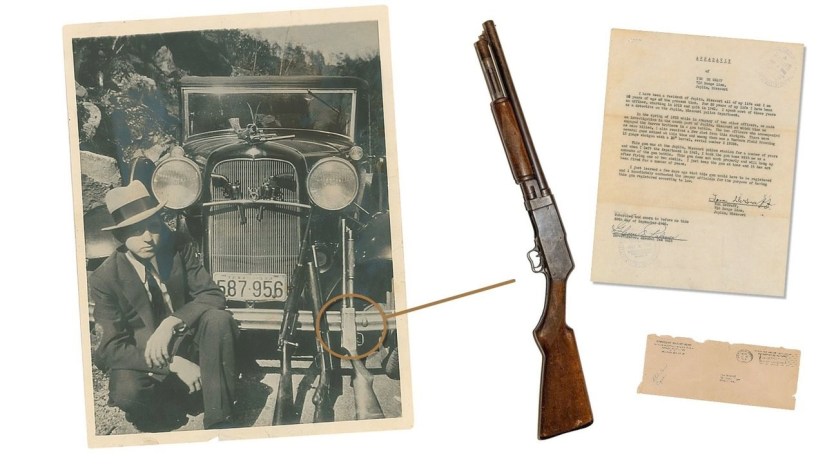








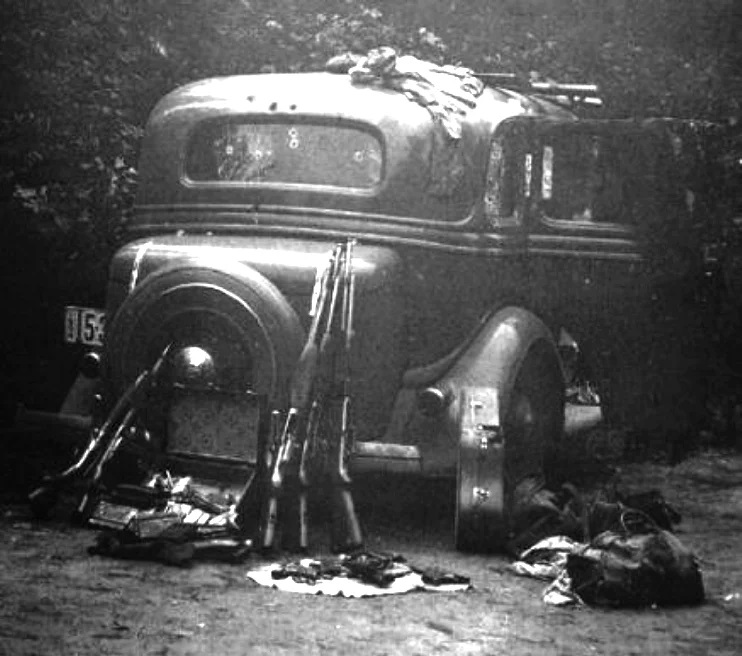
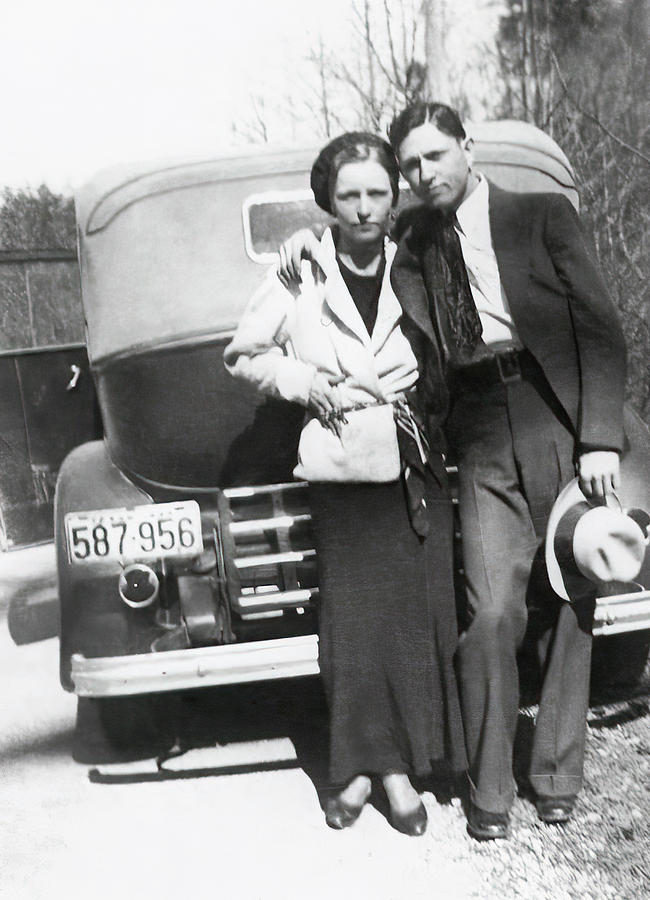
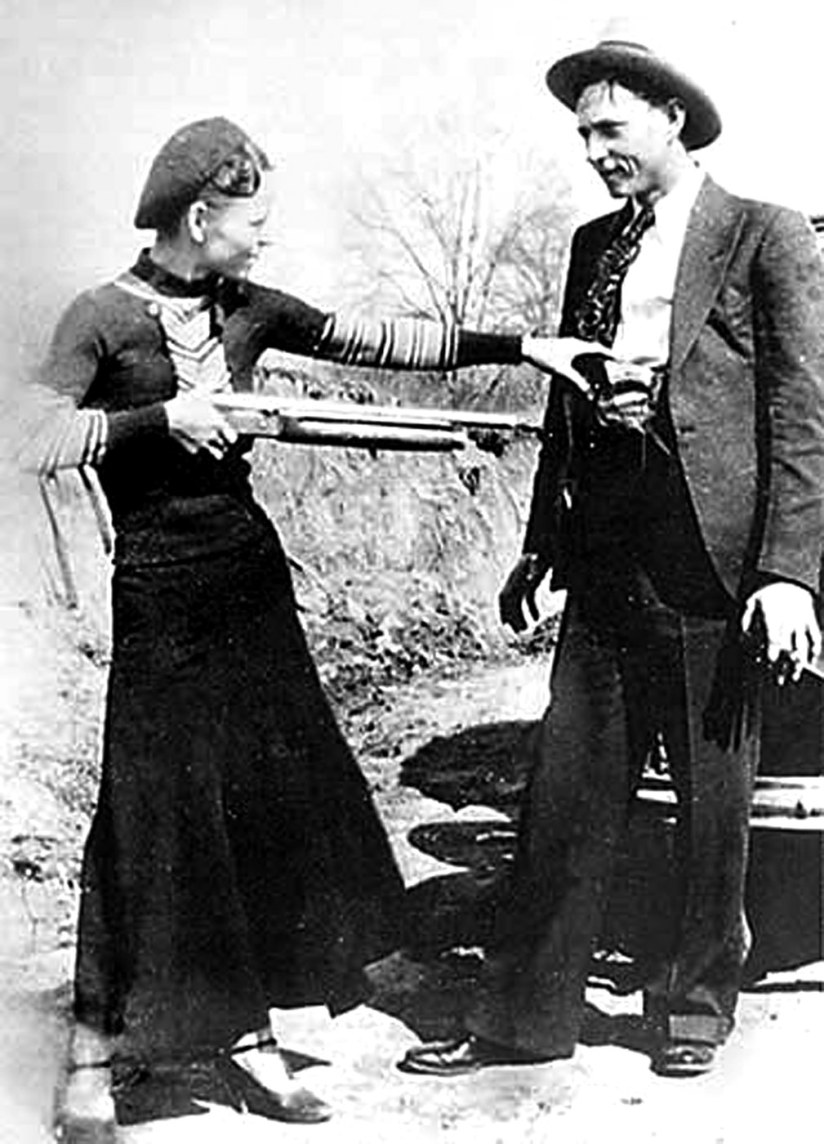
 During the Great Depression, some viewed the duo as near folk heroes, like Robin Hood and Maid Marian. And, although Hoosier outlaw John Dillinger reportedly once told a reporter that Bonnie and Clyde were “a couple of punks”, he and his fellow gang member Pretty Boy Floyd reportedly sent flowers to their funeral homes. The Barrow gang killed a total of 13 people, including nine police officers. They finally met their match on May 23, 1934, when six police officers ambushed them and shot some 130 rounds into the car. Dillinger outlasted Bonnie and Clyde by about two months – he met his maker on July 22, 1934. Truth is, proceeds from auctions of items associated with these outlaws over the past two decades (which number in the millions of dollars) far outdistance the proceeds of all of their robberies combined.
During the Great Depression, some viewed the duo as near folk heroes, like Robin Hood and Maid Marian. And, although Hoosier outlaw John Dillinger reportedly once told a reporter that Bonnie and Clyde were “a couple of punks”, he and his fellow gang member Pretty Boy Floyd reportedly sent flowers to their funeral homes. The Barrow gang killed a total of 13 people, including nine police officers. They finally met their match on May 23, 1934, when six police officers ambushed them and shot some 130 rounds into the car. Dillinger outlasted Bonnie and Clyde by about two months – he met his maker on July 22, 1934. Truth is, proceeds from auctions of items associated with these outlaws over the past two decades (which number in the millions of dollars) far outdistance the proceeds of all of their robberies combined. For my part, when we told our 25-year-old son about our anniversary trip to Las Vegas, he remained nonplussed by saying, “I would only want to go out there to see a town called Primm.” To which we said “been there, done that.” His reply, “I’d also like to go to a little town called Good Springs.” We answered, “Been there too.” He concluded by saying he’d like to see an old dive bar named the “Pioneer Saloon.” He was shocked when we said we went there too. Of course, the reason he wants to venture out there is video game related, not history related. Nonetheless, he was chagrined by our answers. I guess we old folks aren’t so square after all.
For my part, when we told our 25-year-old son about our anniversary trip to Las Vegas, he remained nonplussed by saying, “I would only want to go out there to see a town called Primm.” To which we said “been there, done that.” His reply, “I’d also like to go to a little town called Good Springs.” We answered, “Been there too.” He concluded by saying he’d like to see an old dive bar named the “Pioneer Saloon.” He was shocked when we said we went there too. Of course, the reason he wants to venture out there is video game related, not history related. Nonetheless, he was chagrined by our answers. I guess we old folks aren’t so square after all.
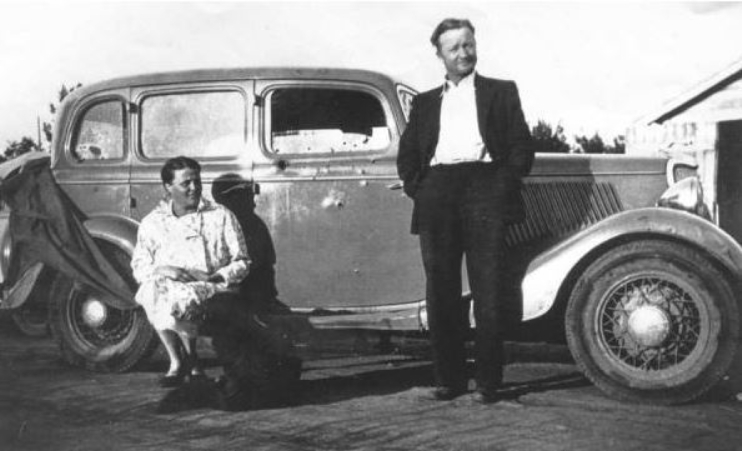





 She called the police and reported the car as stolen. According to the police report, shortly after one o’clock, neighbors saw a man and a woman circling the block in a Plymouth coupe. Later the mystery couple returned, this time with a man riding on the right running board. He jumped off, climbed into the Warren’s car, started it, backed out of the driveway, and sped away. The Warrens wouldn’t see their new Ford for three months.
She called the police and reported the car as stolen. According to the police report, shortly after one o’clock, neighbors saw a man and a woman circling the block in a Plymouth coupe. Later the mystery couple returned, this time with a man riding on the right running board. He jumped off, climbed into the Warren’s car, started it, backed out of the driveway, and sped away. The Warrens wouldn’t see their new Ford for three months.
 Ruth then rented the death car to carnival operator Charles Stanley, who exhibited it on the Hennies Brothers Midways in his 1939 crime show. Stanley displayed the car outside of his tent and charged admission to see the film of the actual ambush on the inside. Eventually, multiple bullet-riddled 1934 Ford Fordor sedans began appearing on the county fair and carnival circuit over the next few years, all claiming to be the actual death car. The various owners sometimes vigorously defended their claims, too, casting doubt on the authenticity of the real death car. Aside from the damage to historical accuracy, the frauds cut into the revenue generated by Ruth Warren as the death car toured the country.
Ruth then rented the death car to carnival operator Charles Stanley, who exhibited it on the Hennies Brothers Midways in his 1939 crime show. Stanley displayed the car outside of his tent and charged admission to see the film of the actual ambush on the inside. Eventually, multiple bullet-riddled 1934 Ford Fordor sedans began appearing on the county fair and carnival circuit over the next few years, all claiming to be the actual death car. The various owners sometimes vigorously defended their claims, too, casting doubt on the authenticity of the real death car. Aside from the damage to historical accuracy, the frauds cut into the revenue generated by Ruth Warren as the death car toured the country. After Ruth divorced her husband Jesse, she kept the title to the car and sold it to Stanley for $3,500.The car was then exhibited at Coney Island amusement park in Cincinnati from 1940-1960. After World War II, memories faded and interest waned in the “Public Enemies” Era, pushing the car further-and-further into obscurity. In a 1960 issue of Billboard magazine, Stanley offered the Bonnie and Clyde Death Car for sale. Ted Toddy purchased the car in 1960 for $14,500. The car then sat in a warehouse for years until the popularity of the 1967 movie “Bonnie & Clyde” brought it out of retirement.
After Ruth divorced her husband Jesse, she kept the title to the car and sold it to Stanley for $3,500.The car was then exhibited at Coney Island amusement park in Cincinnati from 1940-1960. After World War II, memories faded and interest waned in the “Public Enemies” Era, pushing the car further-and-further into obscurity. In a 1960 issue of Billboard magazine, Stanley offered the Bonnie and Clyde Death Car for sale. Ted Toddy purchased the car in 1960 for $14,500. The car then sat in a warehouse for years until the popularity of the 1967 movie “Bonnie & Clyde” brought it out of retirement. 
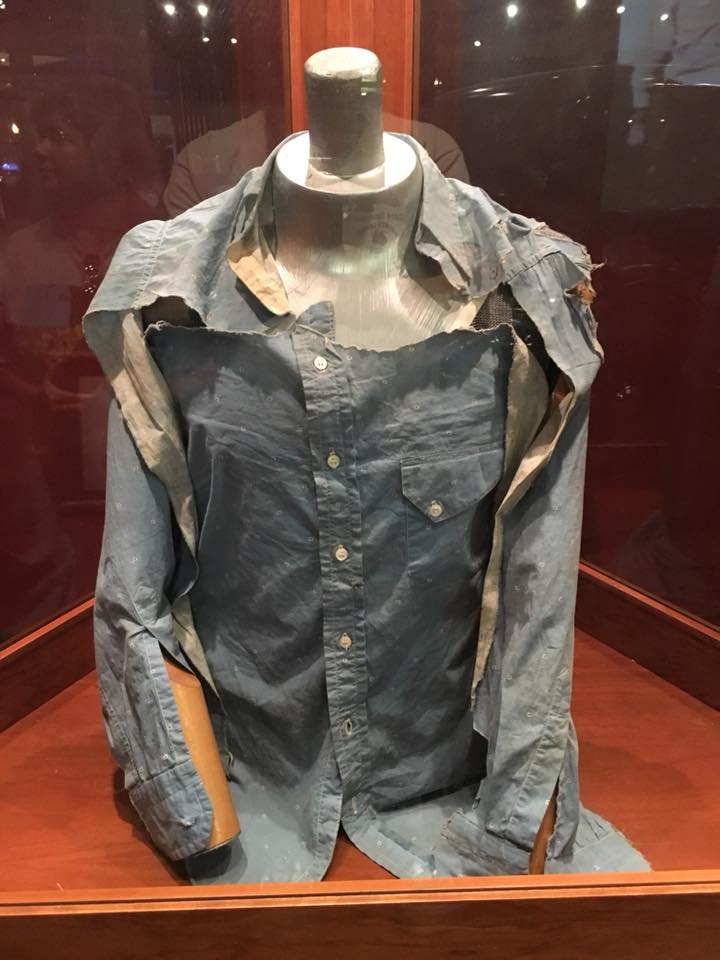
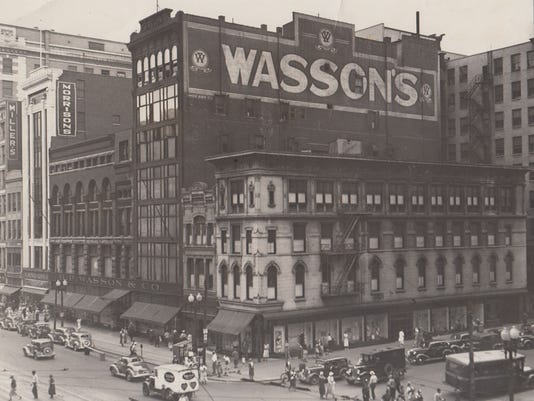








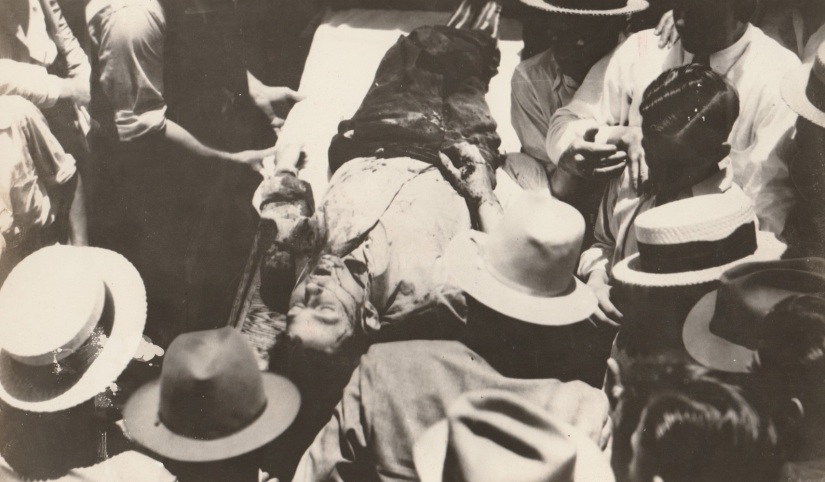
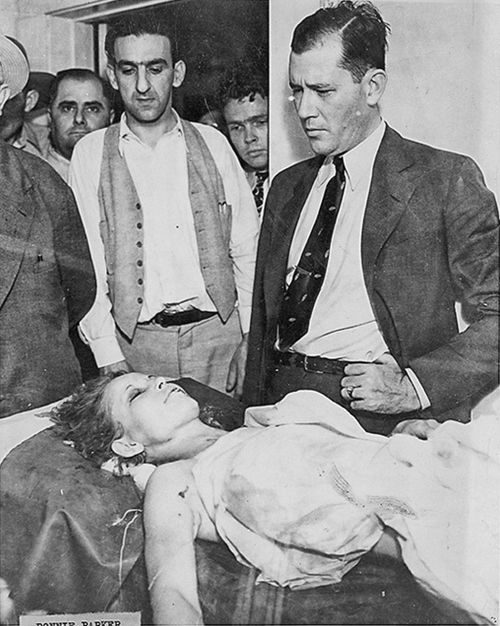
 Clyde was wearing a size 14-32 western style shirt of light blue cotton print with “one patch pocket and pearl buttons” when he was shot to death near Gibsland, Louisiana. The neck label on the shirt reads: “Wasson V Towne shirt/Indianapolis”. The shirt was removed from Clyde Barrow’s body by the coroner who performed the autopsy. Hit by over twenty rounds (Including buckshot), Clyde’s bullet-riddled body slumped against the shattered steering wheel, his 12-gauge shotgun, damaged by the gun fire, slid to the floorboard beside him. Bonnie, with a half-eaten sandwich and magazine at her side, was also struck over twenty times. Both of the star crossed lovers died instantly.
Clyde was wearing a size 14-32 western style shirt of light blue cotton print with “one patch pocket and pearl buttons” when he was shot to death near Gibsland, Louisiana. The neck label on the shirt reads: “Wasson V Towne shirt/Indianapolis”. The shirt was removed from Clyde Barrow’s body by the coroner who performed the autopsy. Hit by over twenty rounds (Including buckshot), Clyde’s bullet-riddled body slumped against the shattered steering wheel, his 12-gauge shotgun, damaged by the gun fire, slid to the floorboard beside him. Bonnie, with a half-eaten sandwich and magazine at her side, was also struck over twenty times. Both of the star crossed lovers died instantly.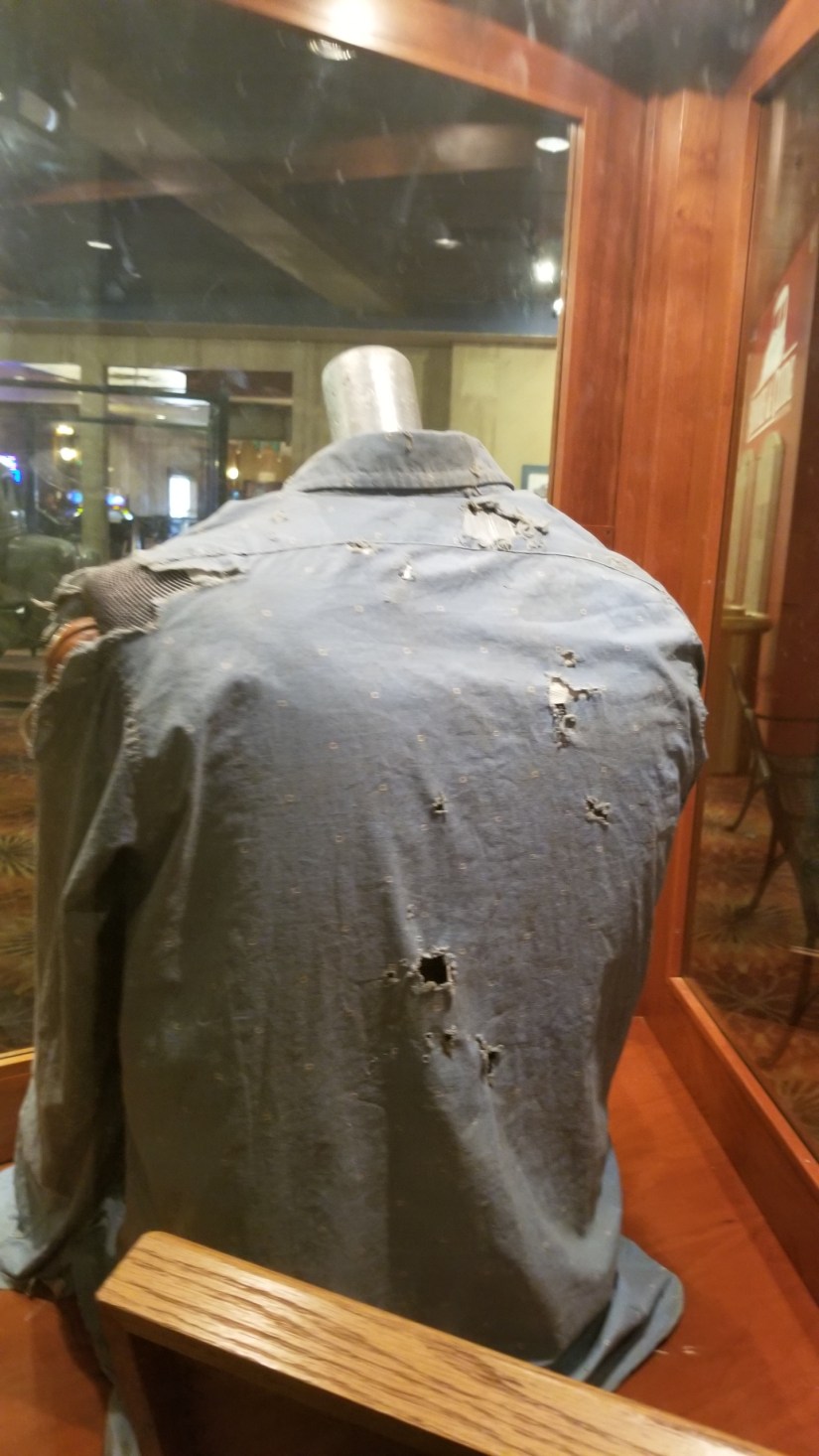
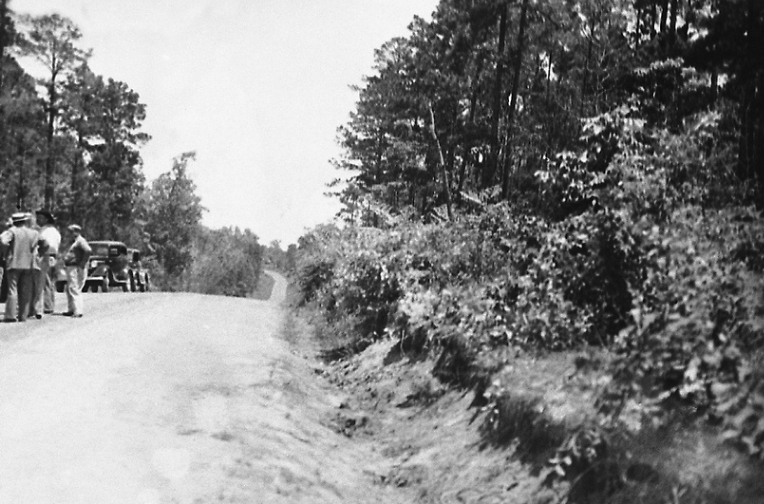





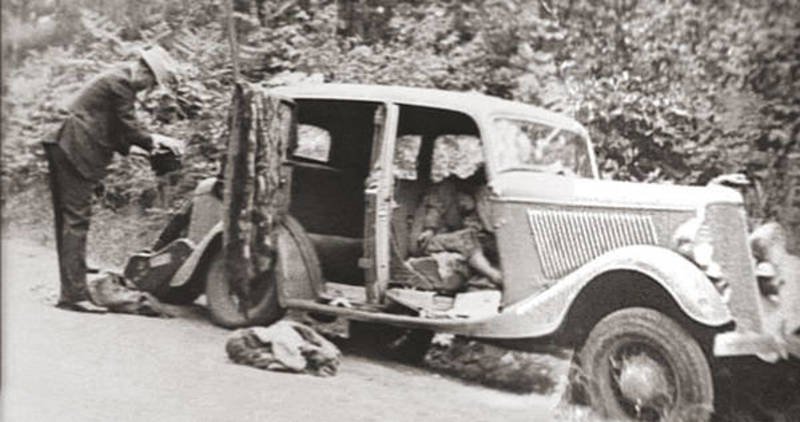
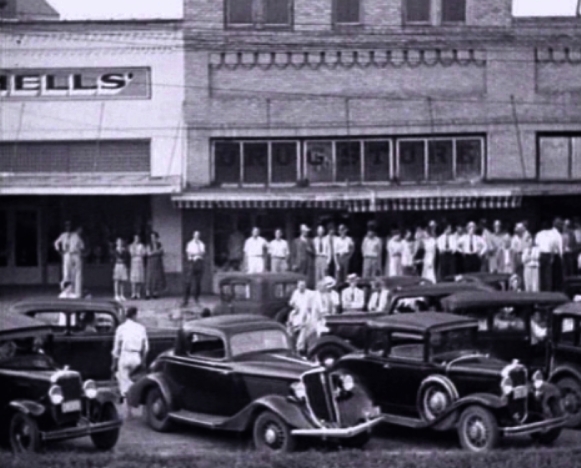
 Word of the ambush quickly spread after the officers drove into town to telephone their respective bosses. A raucous crowd soon flooded the death scene and the car that was still resting there. Two members of the posse were left to guard the bodies, but they quickly lost control of the bloodthirsty souvenir hunters. Locals pushed and shoved their way to the death car; one woman cut off bloody locks of Bonnie’s hair and pieces from her dress. She was later seen back in town selling them as grisly souvenirs. Hinton returned just in time to keep a man from cutting off Clyde’s trigger finger. Arriving at the scene, the coroner observed the following: “nearly everyone had begun collecting souvenirs such as shell casings, slivers of glass from the shattered car windows, and bloody pieces of clothing from the garments of Bonnie and Clyde. One eager man had opened his pocket knife, and was reaching into the car to cut off Clyde’s left ear.” The coroner enlisted Hamer for help in controlling the “circus-like atmosphere” and Clyde’s ear remained intact.
Word of the ambush quickly spread after the officers drove into town to telephone their respective bosses. A raucous crowd soon flooded the death scene and the car that was still resting there. Two members of the posse were left to guard the bodies, but they quickly lost control of the bloodthirsty souvenir hunters. Locals pushed and shoved their way to the death car; one woman cut off bloody locks of Bonnie’s hair and pieces from her dress. She was later seen back in town selling them as grisly souvenirs. Hinton returned just in time to keep a man from cutting off Clyde’s trigger finger. Arriving at the scene, the coroner observed the following: “nearly everyone had begun collecting souvenirs such as shell casings, slivers of glass from the shattered car windows, and bloody pieces of clothing from the garments of Bonnie and Clyde. One eager man had opened his pocket knife, and was reaching into the car to cut off Clyde’s left ear.” The coroner enlisted Hamer for help in controlling the “circus-like atmosphere” and Clyde’s ear remained intact.