Original Publish Date September 21, 2023.
https://weeklyview.net/2023/09/21/21-top-grossing-songs-of-all-time/

So, I’m down in Florida celebrating my 34th wedding anniversary with my bride, Rhonda, who is still the prettiest girl I’ve ever seen. Down here, I’m a thousand miles away from cutting the lawn, watering the flowers, and a honey-do list as long as my arm. So what better time to write about music? I wondered what a list of the top twenty-one money-making songs of all time would look like. Not best-selling albums. Not best-selling song catalogs. Not even best-selling singles. Rather, what songs have made the most money? So, here’s a list for you to ponder. There will be obvious titles, obscure titles, and some surprises, and by the end, I’ll throw some sand in the Vaseline. Only then will you understand what put the thought in my mind.

Many songs have made over $10 million including The Village People “YMCA,” Gene Autry’s “Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer,” The Beatles “I Want to Hold Your Hand,” and, should you consult that black hole that is the Internet, names like Taylor Swift, Justin Bieber, Ed Sheehan, and a liturgy of mysterious electronic dance will muddy the issue. But for the purposes of this article, I have consulted more reputable sources for the numbers: Billboard, Music Grotto, Rolling Stone, and the Guinness Book of World Records.

Number 21: “You’re The One That I Want,” by John Travolta and Olivia Newton-John from the 1978 film Grease. Estimated earnings: $15 million. The song featuring Travolta’s greaser Danny Zuko and Olivia’s good girl temporarily gone bad, Sandy Dombrowski, propelled the film into one of the highest-grossing musical films of all time and the soundtrack became a worldwide hit. Fun fact, Richard Gere and Barry Bostwick portrayed the Travolta character on Broadway in 1972/1973.

Number 20: “(Everything I Do) I Do It For You” by Bryan Adams (1991). Estimated earnings: $15 million. The song appeared on the soundtrack for the film Robin Hood: Prince of Thieves and on the Canadian singer’s sixth studio album, Waking Up the Neighbours.

Number 19: “All I Want For Christmas Is You” by Mariah Carey (1994). Estimated earnings: $16 million. This holiday standard (or earworm depending on your point of view) is the most loved and hated song on the list by a longshot. Every holiday season it returns to the number one spot on the Billboard charts, much to the dismay of seasonal retail workers. Love it or hate it, you gotta give Mariah a tip of the cap for her skimpy Santa suit: an homage to Ronnie Spector and the Ronettes.

Number 18: “My Heart Will Go On” by Céline Dion (1997). Estimated earnings: $18 million. Better known as the theme song for the film Titanic, it has become Dion’s signature song and is the second-best-selling single by a woman in music history.

Number 17: “The Christmas Song” by Mel Torme (1944). Estimated earnings: $19 million. While the title may not ring a bell, when you hear Torme (a.k.a. “The Velvet Fog”) croon “chestnuts roasting on an open fire,” you know what time it is. The song is ironic in a couple of different ways. First Torme is Jewish. Second, Torme wrote the Christmas song “Jack Frost Nipping at Your Nose” in 45 minutes on a blistering hot California day.

Number 16: “If I Didn’t Care” by The Ink Spots (1939). Estimated earnings: $19.75 million. The Ink Spots were one of the first all-black bands to be widely accepted in both the white and black communities. The group traces its origin to Indianapolis and in 1989 they were inducted into the Rock ‘n Roll Hall of Fame.

Number 15: “Oh Pretty Woman” by Roy Orbison and Bill Dees (1964). Estimated earnings: $19.75 million. Most movies form the song but this song formed the movie. The song was released as a single in August 1964 and the movie didn’t come along until 1980. The Richard Gere and Julia Roberts movie was originally intended to be a dark cautionary tale about class and prostitution in Los Angeles but the film was re-imagined as a romantic comedy and was mostly shot at Walt Disney studios. As for Orbison’s original song? It was inspired when his wife, Claudette, interrupted a conversation to announce she was going out. When Orbison asked if she had enough cash, his co-writer Bill Dees interjected, “A pretty woman never needs any money.”

Number 14: “I Will Always Love You” by Dolly Parton (1972). Estimated earnings: $20.5 million. Dolly wrote the song to honor her early mentor, Porter Wagoner. The song helped Dolly win CMA’s Female Vocalist of the Year in 1975 but had its biggest impact in 1992 when Whitney Houston covered it for her 1992 movie, The Bodyguard. Houston’s version is the best-selling single by a woman in music history. The song has earned Dolly over $10 million which she famously donated to charities serving black communities.

Number 13: “We Are The World” by USA For Africa (1985). Estimated earnings: $20.5 million. This charity single was written by Michael Jackson and Lionel Richie. The song featured some of the biggest musicians of the time, including Stevie Wonder, Billy Joel, Paul Simon, Kenny Rogers, Tina Turner, Diana Ross, Willie Nelson, Bruce Springsteen, Kenny Loggins, Steve Perry, Daryl Hall, Huey Lewis, Cyndi Lauper, Ray Charles, and Bob Dylan (who, when chastised by Producer Quincy Jones for singing “off-key”, responded, “That’s my style, man.”) .The chorus was equally notable: Dan Aykroyd, Harry Belafonte, Lindsey Buckingham, Sheila E., Waylon Jennings, Bette Midler, Smokey Robinson, the Pointer Sisters, and the other 4 members of the Jackson Five. The album raised a whopping $63 million in relief funds.

Number 12: “Every Breath You Take” by Sting (1983). Estimated earnings: $20.5 million. Although officially a song by The Police, it has become Sting’s signature song and was, for many years, a popular wedding song until it was revealed to be about a stalker with an unhealthy obsession. In 2010, Sting’s former business manager claimed that the song “is responsible for more than 1/4 of all the singer’s lifetime publishing income and today still produces $2,000 a day ($730,000 per year) in royalties income for Sting.” The songwriting for “Every Breath You Take” is credited 100% to Sting (AKA Gordon Sumner).

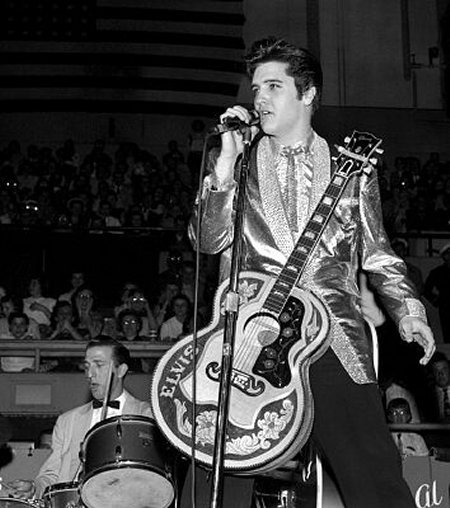
Number 11: “It’s Now Or Never” by Elvis Presley (1960). Estimated earnings: $22 million. I know, I know, why THIS Elvis song in particular? Elvis had so many great ones. When Presley wrote the song, he was serving in the military, stationed in Germany. When he returned to the States after his stint, “Now or Never” became one of his first releases, so fans raided the record stores by the millions in search of it.

Number 10: “Rock Around The Clock” by Bill Haley & His Comets (1954). Estimated earnings: $25 million. Most of us remember it as the theme song for the Happy Days TV show, “Rock Around the Clock” was one of the earliest successful mainstream records of the rock ‘n roll era. It was the first rock and roll record to hit number one on the U.S. pop charts. Here’s a mind-bender for you: “Rock Around The Clock” was written to the tune of Hank Williams’ “Move It On Over.”

Number 9: “Santa Claus Is Coming To Town” by Haven Gillespie And Fred J. Coots (1934). Estimated earnings: $27 million. Another head-scratcher, but as they say, timing is everything. Although the original artist who recorded it is long forgotten (Harry Reser and His Band), in November 1934 when it was covered by Eddie Cantor on his radio show, within 24 hours, 500,000 copies of sheet music and more than 30,000 records were sold and it just kept selling. The song has been recorded by over 200 artists including Bing Crosby, Neil Diamond, Fred Astaire, Bruce Springsteen, Mariah Carey, Frank Sinatra, the Temptations, the Carpenters, and the Jackson 5.

Number 8: “Stand By Me” by Ben E. King, Jerry Leiber, and Mike Stoller (1961). Estimated earnings: $27 million. According to King, the title was inspired by a spiritual written by Sam Cooke and J. W. Alexander called “Stand by Me Father.” “Stand By Me” was successful on its own, but it shot to prominence when it was used in the Stephen King blockbuster movie of the same name twenty years later and found itself at the top of the charts in 1986. In March of 1974, John Lennon recorded two takes of the song with former Beatles bandmate Paul McCartney on the drums and Lennon on guitar. The unreleased recordings would eventually be included in a bootleg album A Toot and a Snore in ‘74.

Number 7: “Unchained Melody” by Alex North And Hy Zaret (1955). Estimated earnings: $27.5 million. The song was written for a movie, Unchained, which was not a success and is remembered ONLY for starring football Hall of Famer Elroy “Crazylegs” Hirsch, Perry Mason’s Barabara Hale and Dick Van Dyke’s dentist neighbor Jerry Paris. However, the song would go on to be one of the most covered songs in recorded history; more than 650 artists at last count. The 1965 version by the Righteous Brothers is the most famous version, but the song re-emerged after it was used in the 1990 Oscar-winning movie Ghost starring Demi Moore and Patrick Swayze.

Number 6: “In The Summertime” by Mungo Jerry (1970). Estimated earnings: $30 million. I guess we should think of this as the seasonal song for summer. Just like Christmas, summer comes around every year. Impressive when you consider it was Mungo Jerry’s debut single and that lead singer Ray Dorset said it only took him 10 minutes to write. Dorset later recalled writing it “on a second-hand Fender Stratocaster while I was on break from my day job, working in a lab for Timex.” Initially, the song was only two minutes long; to make it longer, the sound of a motorcycle was added in the middle. But they didn’t have a motorcycle, so “the engineer had a Triumph sports car, which he drove past the studio microphone. So he got the stereo effects from left to right or right to left, whatever. And that was it.” That scene is made even more comical when you watch the music video for the song (one of the earliest such videos you’re likely to find) and see one of the musicians pretend to create the sound by blowing into a water jug.

Number 5: “Yesterday” by John Lennon and Paul McCartney (1965). Estimated earnings: $30 million. Although Paul McCartney was 100% responsible for the writing and singing of the song, the songwriting credit goes to both men. From the start the duo agreed to share equal credit for their songs, no matter how much either of them contributed to the song. “Yesterday” would become the second-most-played song in the history of radio. It has been covered by more than 2200 different artists. Yoko Ono, John Lennon’s sole heir, has received millions in royalties from the song. BMI asserts that it was performed over seven million times in the 20th century.

Number 4: “You’ve Lost That Feeling” by Barry Mann, Cynthia Weil, and Phil Spector (1964). Estimated earnings: $32 million. Notable as the ONLY song to crack the top 21 that was written by a convicted murderer: Phil Spector. Ironically, Spector’s sole contribution to the songwriting was the line, “and he is gone, gone, gone, Whoa, whoa, whoa.” This Spector-produced song is cited by music critics as the ultimate example of his Wall of Sound recording technique. The song became a massive hit after it was recorded by The Righteous Brothers but resurfaced in a big way in 1986 after it was included in the soundtrack for Top Gun, starring Tom Cruise. The song has been covered by over 2200 different artists and went on to become one of the most-played songs in radio history.

Number 3: “Candle In The Wind” by Elton John and Bernie Taupin (1973). Estimated earnings: $32 million. The song was originally written about the death of Marilyn Monroe, but, in 1997, Elton did a rewrite as a memorial for his close friend Princess Diana. The rewritten version had greater success than the original version. During a concert on April 7, 1990, at Farm Aid IV, Elton dedicated the song to Cicero, Indiana AIDS patient Ryan White, who died of AIDS complications the next day.

Number 2: “White Christmas” by Irving Berlin (1940). Estimated earnings: $36 million. Ironically, this standard of all Christmas songs was written by a Jewish immigrant from Russia: Irving Berlin. Though the song has been covered by countless artists, the most famous version will always be Bing Crosby’s version which sold over 100 million copies worldwide. According to Crosby’s nephew, Howard Crosby, “I once asked Uncle Bing about the most difficult thing he ever had to do during his entertainment career…He said in December 1944, he was in an outdoor USO show in northern France… he had to stand there and sing ‘White Christmas’ with 100,000 G.I.s in tears without breaking down himself. Of course, a lot of those boys were killed in the Battle of the Bulge a few days later.” Think of that the next time you hear this song.

Number 1: “Happy Birthday” by The Hill Sisters (1893). Estimated earnings: $50 million. The ONLY song on the list that has been sung by every generation of your family you ever knew. You know the song, but do you know the story? Mildred Jane Hill was a musicologist from Louisville, Kentucky. Born two years before the start of the Civil War in 1859, Mildred studied music, teaching, composing, and performing, specializing in the study of Negro spirituals. Hill and her sister Patty were honored at the 1893 Chicago World’s Fair for their work in the progressive education program at the experimental Louisville Experimental Kindergarten School. Her progressive 1892 article, “Negro Music,” suggested that the existing body of black music would be the basis of a distinctive American musical style in the years to come. In 1893, the Hill sisters found themselves in need of a song for their kindergarten class to sing on birthdays. 130 years later, we are still singing the Hill sisters song. Today, “Happy Birthday” brings in a reported $5,000 a day, and $2 million a year in royalties. The cost of using the song in a movie or on TV is $25,000. It is actually against the law to sing “Happy Birthday” in a large group of unrelated people, but good luck trying to enforce that one.

There you have it. Those numbers will change in the years to come. No doubt, by scanning the list, you have deduced that all it takes for a song to make (or jump up on) the list is for a movie or TV show to pick it up as a theme song. But, as I told you earlier, I am in Florida as I write this, and for that reason, I would like to submit a song that is not on anyone’s list. Governor DeSantis of Florida has ordered that flags be lowered to half-staff from Thursday, Sept. 7, to Friday, Sept. 8th to commemorate the ‘life and legacy’ of Jimmy Buffett, the “Margaritaville” singer who died on Sept. 1st.

Buffet’s 1977 “Margaritaville” song was on his album Changes in Latitudes, Changes in Attitudes. Buffet claimed that the lyrics were taken directly from a bad day at the beach and that he really lost a flip-flop, stepped on a pop top, and cut his heel on the way back home. And, oh yes, he lost his salt shaker that day too. The song has a “lost verse” which he sometimes added when performing in concert but was cut from the original song. “Old men in tank tops, Cruisin’ the gift shops, Checkin’ out chiquitas, down by the shore. They dream about weight loss, Wish they could be their own boss, Those three-day vacations can become such a bore.” Although Buffet’s Margaritaville earned him millions, by itself, it never could have cracked the top 21.

However, Buffet’s song about life in this euphoric place has morphed into a global brand that has earned more than $4.8 billion and sees $1.5 billion in annual sales. Buffet’s Margaritaville Holdings company began in 1985 with the opening of a string of Margaritaville-themed stores and restaurants, the first of which was a store in Key West, Florida, that was followed in 1987 with the first Margaritaville Café nearby. Over the course of the next two decades, several more of each opened throughout Florida, New Orleans, and California. In 2002, Buffet partnered with Outback Steakhouse to develop the first Cheeseburger in Paradise Restaurant in Southport, Indiana. Margaritaville resorts by Wyndham have sprouted up all over the place and most recently, a plan to develop Latitude Margaritaville: new active adult communities for those “55 and better.” At the time of his death, Buffet had amassed a personal fortune of $1 billion. That’s BILLION with a “B”, a figure that cannot be surpassed, even if you added all of the top 21 together. Apparently, Margaritaville was a pretty good place to be.