Original Publish Date March 6, 2025.
https://weeklyview.net/2025/03/06/osborn-h-oldroyds-greatest-fear/
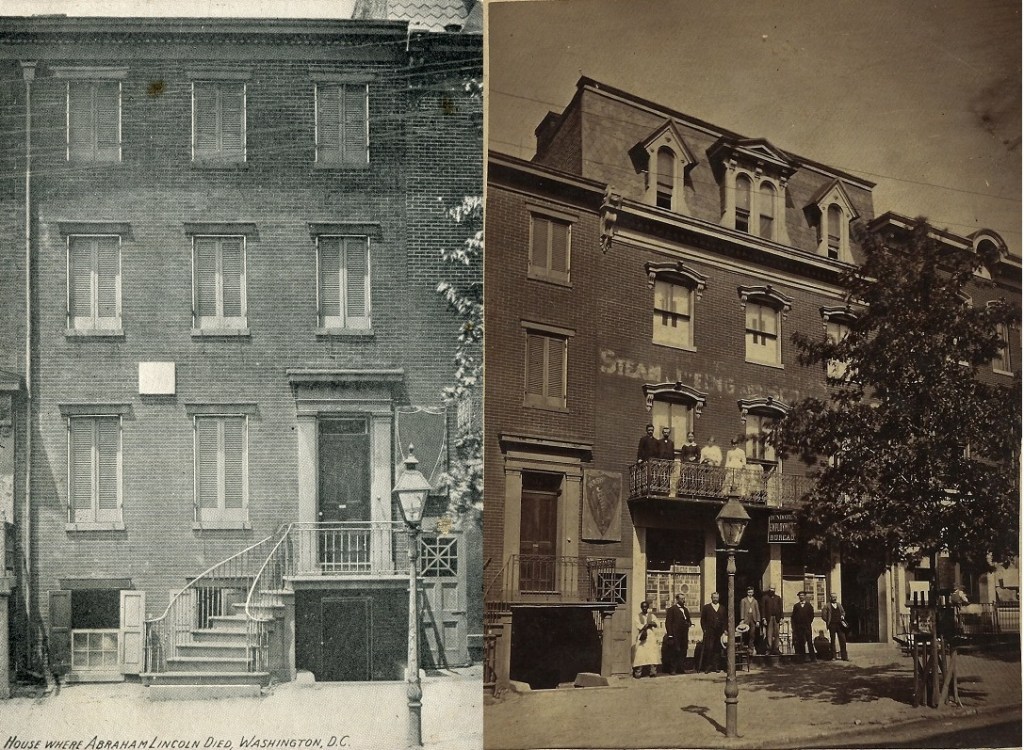

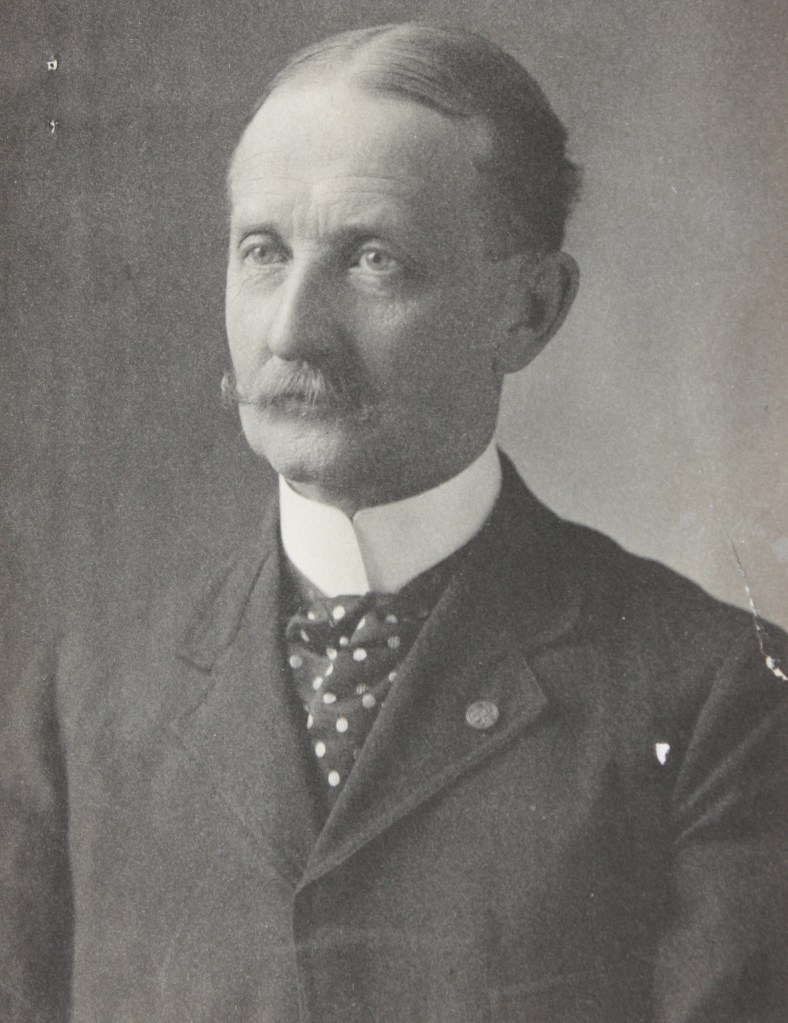
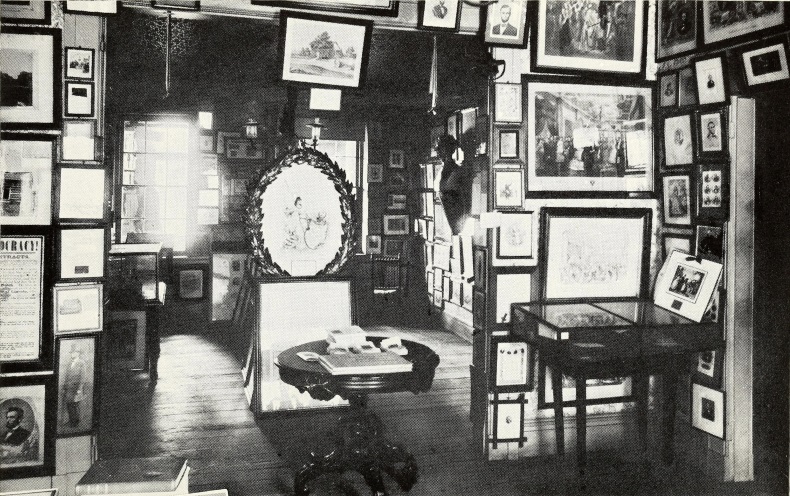
My wife and I recently traveled to Springfield, Illinois for a book release event (actually two books). One book on Springfield’s greatest living Lincoln historian, Dr. Wayne C. “Doc” Temple, and the other on my muse for the past fifteen years, Osborn H. Oldroyd. I have fairly worn out my family, friends, and readers with the exploits of Oldroyd over the years. He has been the subject of two of my books and a bevy of my articles. Oldroyd was the first great Lincoln collector. He exhibited his collection in Lincoln’s Springfield home and then in the House Where Lincoln Died in Washington DC from 1883 to 1926. Oldroyd’s collection survives and forms much of the objects in Ford’s Theatre today.

For this trip, we traveled up from the south to Springfield through parts of northwest Kentucky and southeast Missouri. What struck us most were the conditions of the small towns we drove through. Today many of these little burgs and boroughs are in sad shape, littered by once majestic brick buildings featuring the names of the merchants that built them above the doorways, eaves, and peaks of their frontispieces in a valiant last stand. Most had boarded-up windows and doors and some with ghost signs of products and services that disappeared generations ago.
They are tightly packed and many share common walls. We were amazed how many of them have caved-in or worse, burnt down. The caved-in buildings are the work of Father Time and Mother Nature, but the burnt ones look as if the fires were extinguished just recently. My wife deduces that these are likely the result of the many meth labs that blight these long-forgotten, empty buildings. Indeed, a little research reveals that these rural areas do lead the league in these hastily constructed, outlaw drug factories.
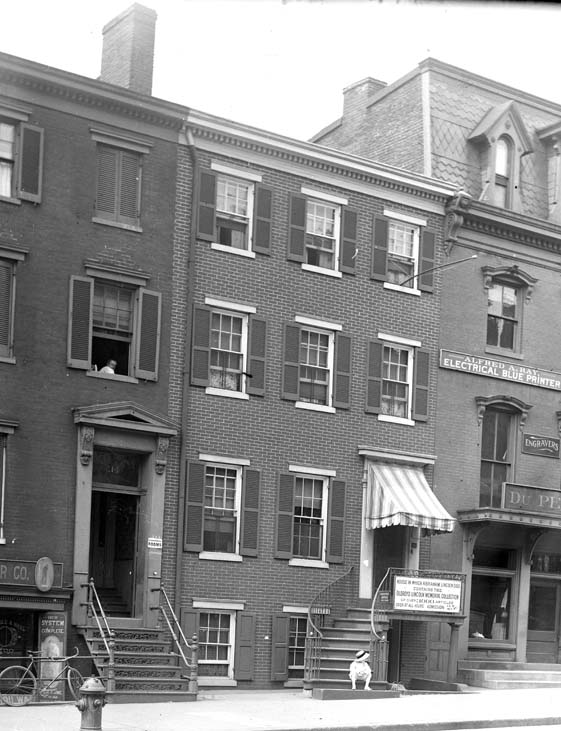

Of course, that got me thinking about Oldroyd’s museum. Oldroyd lobbied for decades to have his collection purchased by the U.S. government and preserved for future generations to explore. The Feds eventually purchased it in 1926 for $50,000 (around $900,000 today). For over half a century while assembling his collection, Oldroyd had one great fear: Fire. Visiting the House Where Lincoln Died today, the building remains unique in size and architecture compared to those around it. In Oldroyd’s day, smoking cigars, pipes, and cigarettes indoors was as prevalent as carrying cell phones and water bottles are today. The threat of fire was very real for Oldroyd.

The March 20, 1903, Huntington Indiana Weekly Herald ran an article titled “A Visit to the Lincoln Museum in Washington City.” After describing the relics in the collection, columnist H.S. Butler states, “It is hoped the next Congress will purchase this collection and care for it. Mr. Oldroyd is not a man of means such as would enable him to do all he would like, and it seems to me a little short of criminal to expose such valuable relics, impossible to replace, to the great risk of fire. I understand Congressman [Charles] Landis, of Indiana, is trying to get the collection stored in the new Congressional Library, in itself the handsomest structure, interiorly, in Washington. I hope that his brother, the congressman from the Eleventh District [Frederick Landis], will lend his influence to Senators [Charles] Fairbanks and [Albert] Beveridge to urge forward the same end.”

Fifteen years later, the Topeka State Journal described an event that fueled Oldroyd’s concern. “May 21 [1918]-a few days ago the Negro cook in the kitchen of a dairy lunch spilled some fat on the fire and the resulting blaze was extinguished with some difficulty. The unique feature of this trifling accident was that, had the blaze gotten beyond control, it would probably have destroyed a neighboring house in which is the greatest collection in the world of relics, manuscripts, and books bearing upon the life and death of Abraham Lincoln…Sixty feet away from the room in which Lincoln died are three kitchens of restaurants and a hotel. More than one recent fire scare has caused alarm over the danger that threatens these relics.”

The February 11, 1922, Dearborn [Michigan] Independent reported, “A vagrant spark, a carelessly tossed cigarette or cigar stub, an exposed electric wire might at any time mean the destruction of the collection and the building which, of course, is itself a sacred bit of Lincolniana.” The January 21, 1924, Daily Advocate of Belleville, Ill. reported “The collection is contained in a small and overcrowded room of the house opposite Ford’s Theatre, with two restaurants across a narrow alleyway constituting a constant fire menace…it is likely that the U.S. Government will request that the Illinois Historical Society return the bed in which Lincoln died, that it may again be placed in the room it occupied on that fateful night and the entire setting restored.” Due to that unresolved fire threat the bed was never returned and is today on display at the Chicago History Museum. A 1924 Christmas day article in the Washington Standard 1924 described, “There are a number of restaurants in the block at the rear, and once an oil supply house did business close at hand. On two occasions there have been fires in the neighborhood.”

The July 6, 1926, Indianapolis News speculated, “The government will add to the collection the high silk hat Lincoln wore to the theatre that fatal night, the chair in which he sat in the presidential box, and the flag in which Booth’s foot caught. The flag now hangs in the treasury, while the hat and chair are in storage. These articles formerly were in the Oldroyd collection, but after a fire in the neighborhood some years ago, officials of the government took them back, fearing that they might be destroyed.” The February 18, 1927, Greenfield [Indiana] Reporter stated, “The plan proposed by Senator Watson, of Indiana, and Rep. Rathbone of Illinois, is to remodel the building to protect it against the danger of fire and the ravages of age. They would…place in it the famous Oldroyd collection of Lincoln relics.” Fire remained a nightmare for Oldroyd right up to the day he died on October 8, 1930.

Ironically, after that book signing I found myself browsing the bookstore. I found there a 2 1/2” x 4” business card from the New Lincoln Cafe in the adjoining building to the north of Oldroyd’s Museum (at 516 10th St. NW). Putting aside the fact that I have a personal affinity for old business cards, the item called out to me and made me wonder about the businesses that had been neighbors to this hallowed spot over the generations.

The card reads: “Chinese and American New Lincoln Cafe. Located at 518 10th St., N.W. Phone EX. 1468. We Specialize In Spaghetti-Home Made Fresh Daily. Your Favorite Mixed Drinks And Cocktails. President Lincoln Was Assassinated In Ford’s Theatre On Night Of April 14th, 1865, And Died Following Morning At Seven-Thirty.” A check of the records indicates that this restaurant remained next to the museum from the late 1930s to the early 1960s. This was just one of the businesses to call that space home over the generations.

Located in the Penn Quarter section of DC, the building was built sometime between 1865 to 1873. It envelopes the entire north side and part of the northwest back of the HWLD. It is 4 stories tall and features 11,904 square feet of retail space. One of the earliest storefronts to appear there was Dundore’s Employment Bureau which served D.C. during the 1870-90s. Ironically, when Dundore’s moved three blocks south to 717 M Street NW, the agency regularly advertised jobs at businesses occupying their old address for generations to come. Above the Dundore agency was Mrs. A. Whiting’s Millinery, which created specialty hats for women. The Washington Evening Star touted Mrs. Whiting’s “Millinery Steam Dyeing and Scouring” business for their “Imported Hats and Bonnets”. A 3rd-floor hand-painted sign on the bricks of the building advertising Whiting’s remained for years after the business vacated the premises, creating a “ghost sign” visible for many years as it slowly faded from view.
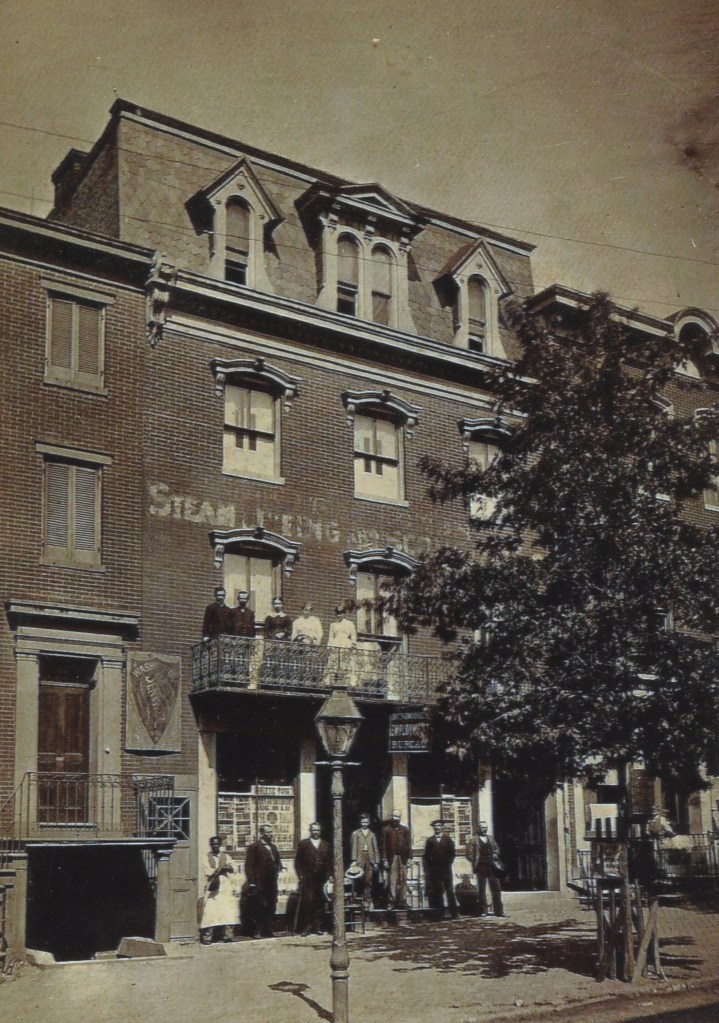

The Forsyth Cafe seems to have been the first bistro to pop up next to the Oldroyd Museum. In late February/March 1885 (in the leadup to Grover Cleveland’s first Presidential Inauguration), DC’s Critic and Record newspaper’s ad for the cafe decries, “Yes, One Dollar is cheap for the Inauguration supper, but what about those excellent meals at the Forsythe Cafe for 15 Cents?” The Forsyth continued to advertise their meals from 15 to 50 cents but by late 1886, they were gone, replaced by the Logan Cafe. The Logan offered 15 and 25-cent breakfasts, “Big” 10-cent lunches, and elaborate 4-course dinners of Roast beef, stuffed veal, lamb stew, & oysters. Proprietor W.E. Logan’s claim to fame was “the best coffee to be had in the city, made in French-drip Glass-Lined Urn” and “Special Dining Rooms for Ladies-Polite waiters in attendance” and his menus warned “No Liquors” served.

The June 4, 1887, Critic and Record reported on a “friendly scuffle” at the Logan between two “colored” employees when cook Charles Sail tripped waiter William Butler who hit his head on the edge of a table and died the next morning at Freedman’s Hospital. The men were described as best friends and the death was deemed an accident. By late 1887, the Logan disappears from the newspapers. From 1897 to 1897, the building was home to the Yale Laundry. The Jan. 7, 1897, DC Times Herald reported on an event that likely added to Oldroyd’s anxiety. The article, titled “Laundry is Looted” details a break-in next door to the museum during which a couple of safecrackers got away with $85 cash including an 1883 $5 gold piece.
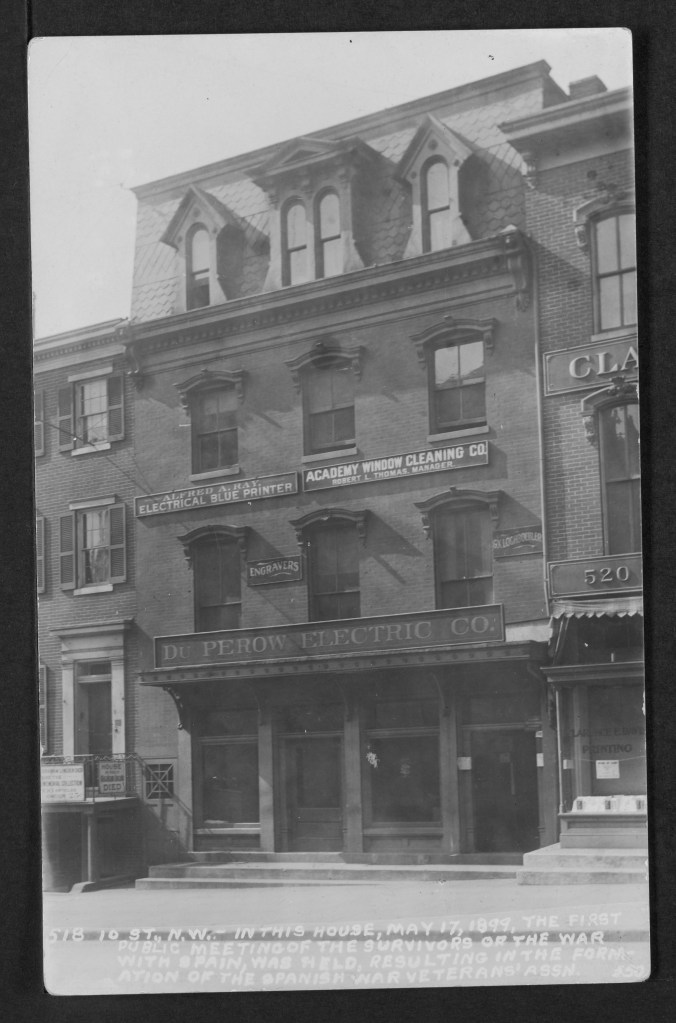


A real photo postcard in the collection of the District of Columbia Public Library pictures the building during Yale Laundry’s tenure captioned, “In this house the first public meeting of the survivors of the war with Spain, was held on May 17, 1899, resulting in the formation of the Spanish War Veterans’ Association.” The Dec. 1, 1900, Washington Star notes the addition of Harry Clemons Miller’s “Teacher of Piano” Studio and by 1903, the “Yale Steam Laundry” appeared in the DC newspapers at the address.
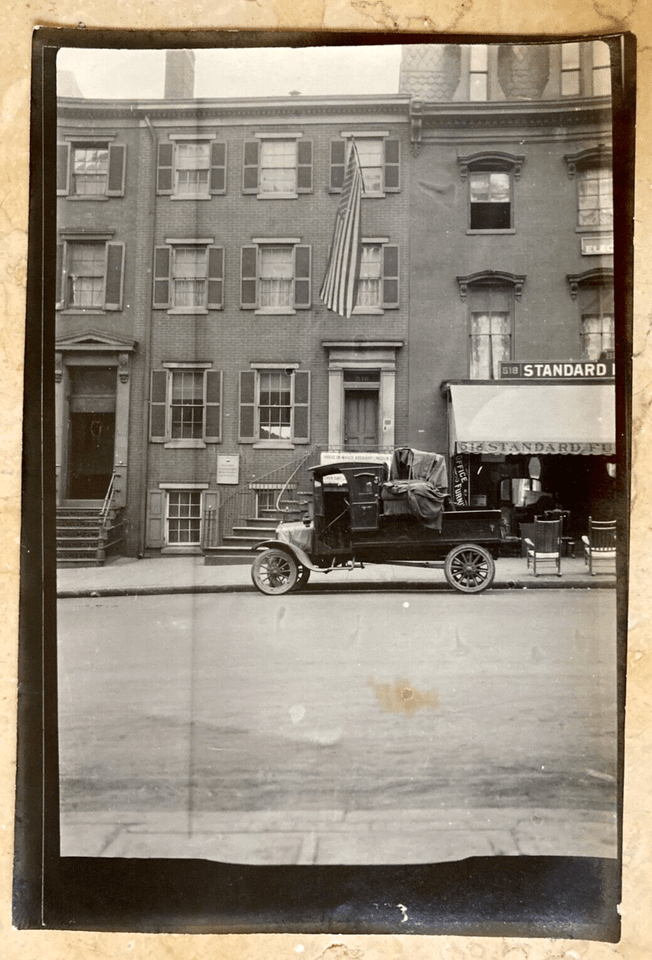
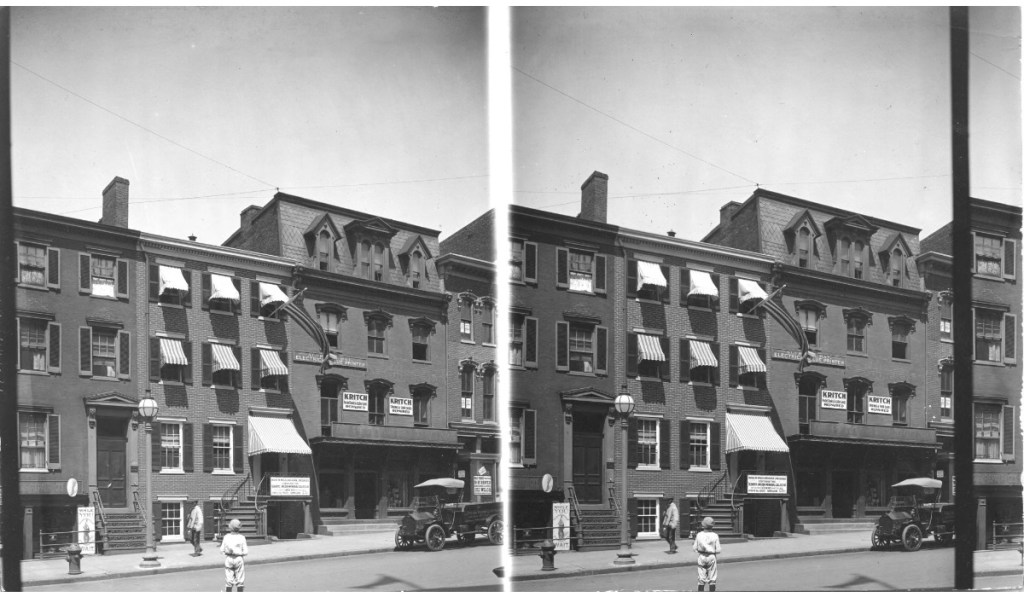
In 1909, Du Perow Electric Co. (AKA as “Du Pe”) and partner Alfred A. Ray “Electrical Blueprints” occupied the building. A window cleaning company occupied room # 9 and a leather goods store was located there during this same period. By 1912, the storefront was occupied by the Standard Furniture Co. At least one photo survives presenting an amusing scene of a furniture truck blocking the entrance to Oldroyd’s museum. Amusing to the viewer today but most assuredly not to the museum curator back in the day. Eventually, the restaurants, bars, and cafes that worried Oldroyd began to come and go, among them, the Lincoln Cafe & Cocktail Lounge, whose sign was dominated by the words “Beer Wine.” It appears that during the 1920-50s, a Pontiac, DeSoto, Plymouth Motor Car dealer known as “News & Company” kept an office in the building, with the car lot and gas station across the street.
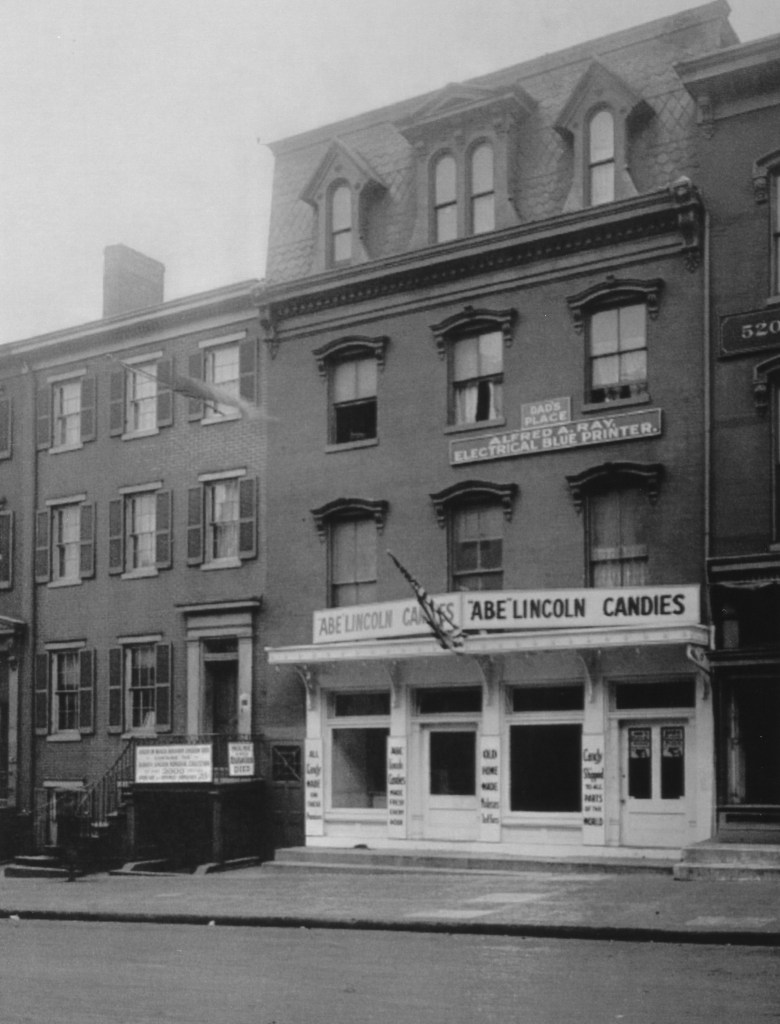


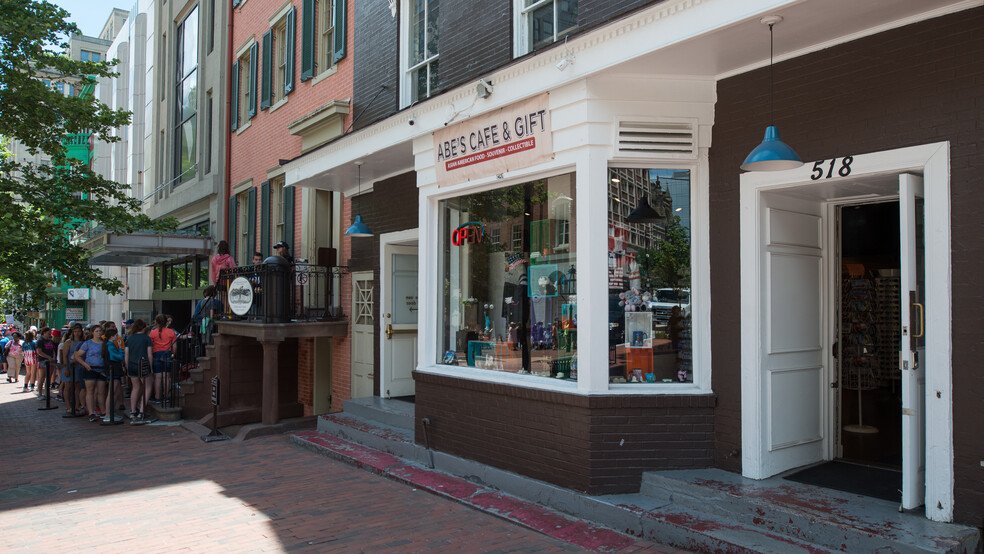
Old-timers remember a long-term tenant known as “Abe Lincoln Candies” that occupied the space from the 1950-70s. Other recent tenants included Abe’s Cafe & Gift Shop, Bistro d’Oc and Wine Bar, Jemal’s 10th Street Bistro, Mike Baker’s 10th St Grill, and the I Love DC gift store, and last year, The Inauguration-Make America Great Again Store, who one Yelp reviewer complained was crowded with outdated, sketchy clothing and that “they make u give them a good review before they give u a refund kinda scummy.”
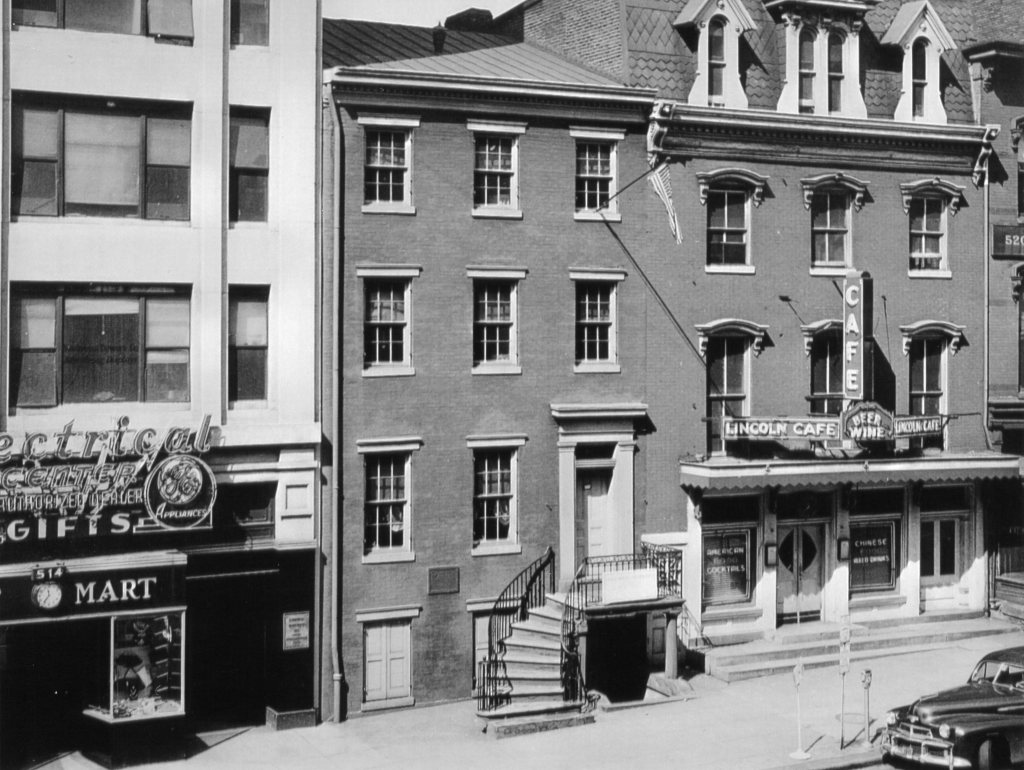

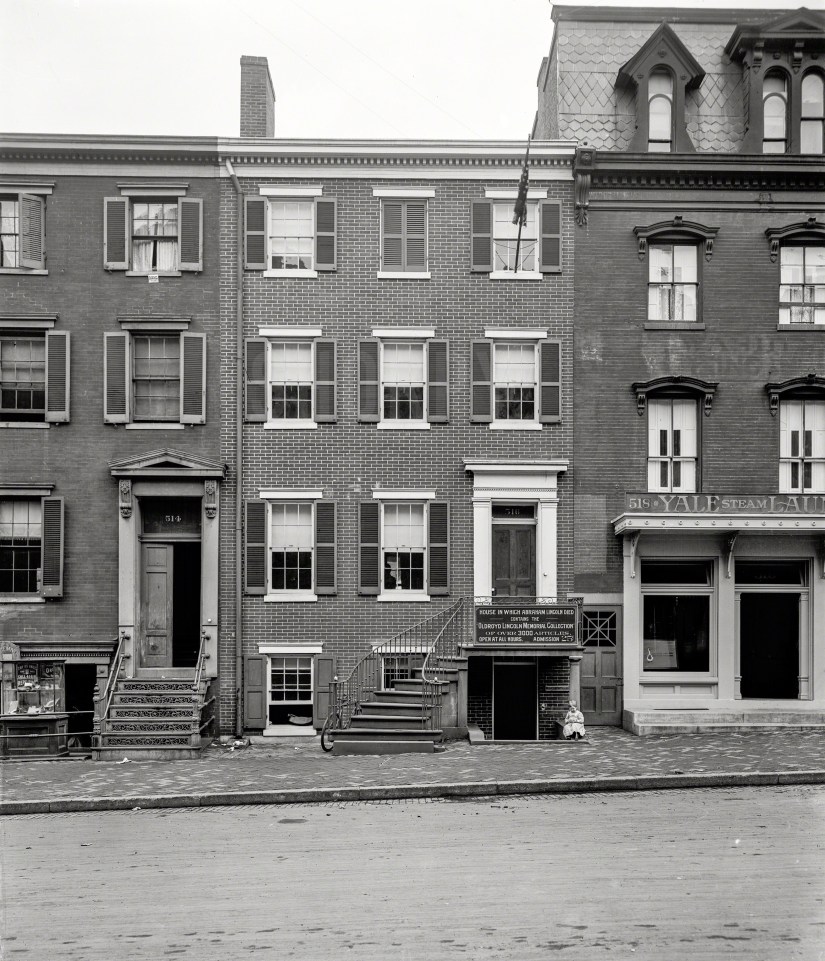
As for the building on the opposite side of Oldroyd’s museum at 514 Tenth St. NW, it remained a residence until 1922 when a $55,000, 10-story concrete & steel building with steam heat and a flat slag roof was built. Designed by architect Charles Gregg and built by Joseph Gant, the sky-scraper, known as the Lincoln Building, dwarfed the Oldroyd Museum. It was home to several businesses, including the Electrical Center (selling General Electric TVs, radios, and appliances) and the Garrison Toy & Novelty Co, its modern construction alleviated any concern of fire.

It must be noted that many great collections of Lincolniana fell victim to fire in the century and a half after Lincoln’s death. The Great Chicago Fire of 1871 consumed many Lincoln objects, documents, and personal furniture that had been removed from the Springfield home after the President’s departure to Washington DC. On June 15, 1906, Major William Harrison Lambert (1842-1912), recipient of the Congressional Medal of Honor and one of the Lincoln “Big Five” collectors, lost much of his collection in a fire at his West Johnson St. home in Germantown, Pa. Among the items lost were a bookcase, table, and chair from Lincoln’s Springfield law office and the chairs from Lincoln’s White House library. The threat of fire was a constant waking nightmare in Oldroyd’s life. While he did his best to control what went on inside his museum, he had no control over what happened outside. His life’s work of collecting precious Lincoln objects, over 3,500 at last count, could be gone in the flash of a pan.
ADDITIONAL IMAGES.


































 When animals huddle together in open fields…when ants travel in straight lines (or are unusually active)…when the “Northern Lights” are visible in the sky…when bats cry much, or attempt to fly into the house…when more bees enter than leave the hive (every notice that bees never get caught in a shower?)…when distant bells sound close…when birds skim close to the ground…when boiling water evaporates more rapidly than usual…when dead branches fall to the ground in calm weather…when bubbles rise from marshy ground or appear on pools of stagnant water…
When animals huddle together in open fields…when ants travel in straight lines (or are unusually active)…when the “Northern Lights” are visible in the sky…when bats cry much, or attempt to fly into the house…when more bees enter than leave the hive (every notice that bees never get caught in a shower?)…when distant bells sound close…when birds skim close to the ground…when boiling water evaporates more rapidly than usual…when dead branches fall to the ground in calm weather…when bubbles rise from marshy ground or appear on pools of stagnant water… If coffee bubbles cling to the cup instead of floating in the center…when corns are more painful than usual… when cottonwood trees turn the undersides of their leaves upward…when a cow thumps its ribs, or attempts to scratch its ear, with its tail…when crabs leave the water and remain on land… when cream or milk sours during the night…an old adage states that a new (crescent) moon with horns tilting downward can’t hold water so…when crickets chirp loudly and more persistently than usual… when crows caw loudly and continuously or when a crow is seen flying alone… when curly hair becomes more unruly than usual…
If coffee bubbles cling to the cup instead of floating in the center…when corns are more painful than usual… when cottonwood trees turn the undersides of their leaves upward…when a cow thumps its ribs, or attempts to scratch its ear, with its tail…when crabs leave the water and remain on land… when cream or milk sours during the night…an old adage states that a new (crescent) moon with horns tilting downward can’t hold water so…when crickets chirp loudly and more persistently than usual… when crows caw loudly and continuously or when a crow is seen flying alone… when curly hair becomes more unruly than usual… When grate fires crackle and throw sparks to a greater degree than usual…when fish jump from the water, or swim close to the surface…when oiled floors “sweat”…when flowers stay open all night (and some say when the fragrance is stronger)… when frogs assume a brownish hue and croak louder and longer…when there are two full moons in a single month…when geese are particularly noisy…when glow worms shine brighter…when goats bleat a great deal…
When grate fires crackle and throw sparks to a greater degree than usual…when fish jump from the water, or swim close to the surface…when oiled floors “sweat”…when flowers stay open all night (and some say when the fragrance is stronger)… when frogs assume a brownish hue and croak louder and longer…when there are two full moons in a single month…when geese are particularly noisy…when glow worms shine brighter…when goats bleat a great deal… And lastly, when ordinary salt begins to lump, cake and clog the saltcellar, get ready for rain. According to Morton’s, their salt is not made this way because, “When it rains it pours.” Morton’s explanation: “Because of its unique cube shaped crystals, which tumble off one another in damp weather instead of sticking together like the flake crystals of ordinary salt…every grain is usable-there are no wasteful lumps to throw away. If you have children between 6 and 18, be sure to use the iodized variety and thus protect them simple goiter.” Goiter is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. Before iodized salt hit the grocery shelves on May 1, 1924, iodine deficiency was the main cause of goiter in the U.S. and even though it has nothing to do with rain, I couldn’t resist throwing that last part in. So much information packed into such a little brochure.
And lastly, when ordinary salt begins to lump, cake and clog the saltcellar, get ready for rain. According to Morton’s, their salt is not made this way because, “When it rains it pours.” Morton’s explanation: “Because of its unique cube shaped crystals, which tumble off one another in damp weather instead of sticking together like the flake crystals of ordinary salt…every grain is usable-there are no wasteful lumps to throw away. If you have children between 6 and 18, be sure to use the iodized variety and thus protect them simple goiter.” Goiter is a swelling in the neck resulting from an enlarged thyroid gland. Before iodized salt hit the grocery shelves on May 1, 1924, iodine deficiency was the main cause of goiter in the U.S. and even though it has nothing to do with rain, I couldn’t resist throwing that last part in. So much information packed into such a little brochure.
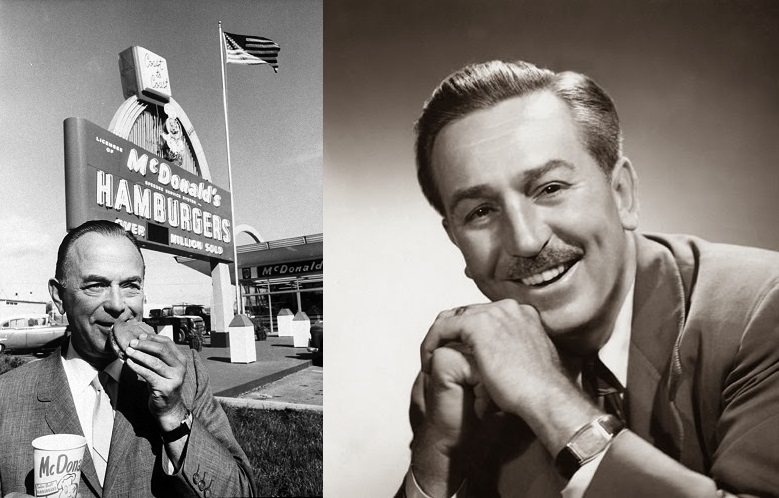
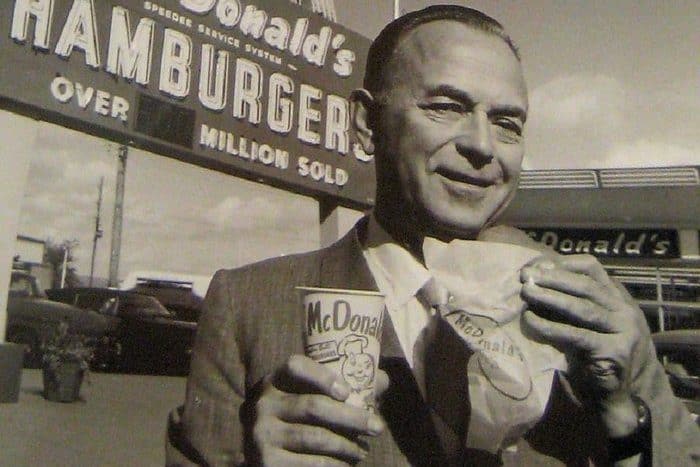






 By this time, Ray Kroc was relegated to the sidelines serving in a largely ceremonial role as McDonald’s “senior chairman”. Kroc had given up day-to-day operations of McDonald’s in 1974. Ironically, the same year he bought the San Diego Padres baseball team. The Padres were scheduled to move to Washington, D.C., after the 1973 season. Legend claims that the idea to buy the team formulated in Kroc’s mind while he was reading a newspaper on his private jet. Kroc, a life-long baseball fan who was once foiled in an attempt to buy his hometown Chicago Cubs, turned to his wife Joan and said: “I think I want to buy the San Diego Padres.” Her response: “Why would you want to buy a monastery?” Five years later, frustrated with the team’s performance and league restrictions, Kroc turned the team over to his son-in-law, Ballard Smith. “There’s more future in hamburgers than baseball,” Kroc said. Ray Kroc died on January 14, 1984 and the San Diego Padres won the N.L. pennant that same year (They lost in the World Series to the Detroit Tiger 4 games to 1).
By this time, Ray Kroc was relegated to the sidelines serving in a largely ceremonial role as McDonald’s “senior chairman”. Kroc had given up day-to-day operations of McDonald’s in 1974. Ironically, the same year he bought the San Diego Padres baseball team. The Padres were scheduled to move to Washington, D.C., after the 1973 season. Legend claims that the idea to buy the team formulated in Kroc’s mind while he was reading a newspaper on his private jet. Kroc, a life-long baseball fan who was once foiled in an attempt to buy his hometown Chicago Cubs, turned to his wife Joan and said: “I think I want to buy the San Diego Padres.” Her response: “Why would you want to buy a monastery?” Five years later, frustrated with the team’s performance and league restrictions, Kroc turned the team over to his son-in-law, Ballard Smith. “There’s more future in hamburgers than baseball,” Kroc said. Ray Kroc died on January 14, 1984 and the San Diego Padres won the N.L. pennant that same year (They lost in the World Series to the Detroit Tiger 4 games to 1).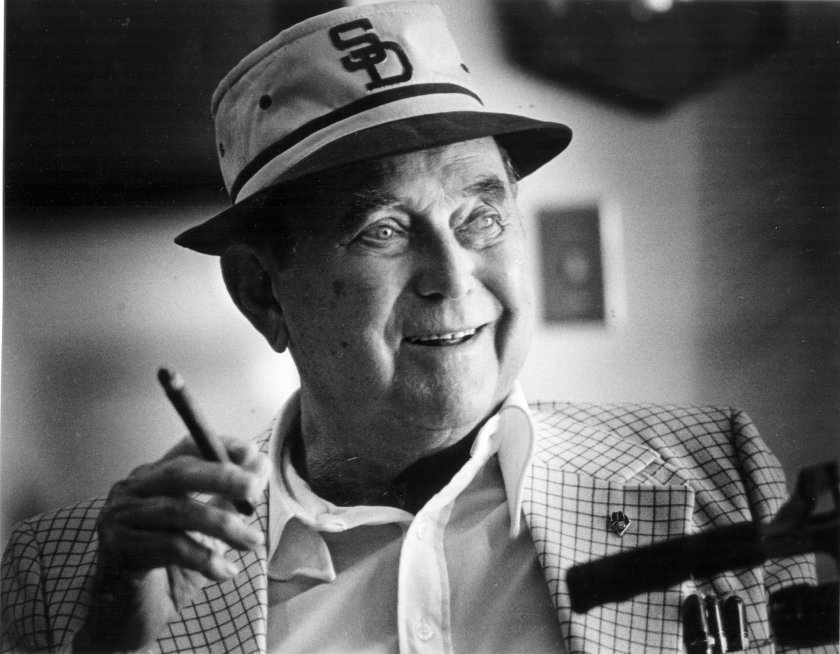 By the 1980s, Disney was a corporation that seemed to be creatively exhausted. The entertainment giant was seriously out of touch with what consumers wanted to buy, what moviegoers wanted to see. McDonald’s had introduced their wildly popular “Happy Meal” nationwide in 1979. Disney saw an opportunity for revival by proposing the idea of adding Disney toys and merchandising to Happy Meals. In 1987, the first Disney Happy Meal debuted, offering toys and prizes from familiar characters like Cinderella, The Sword In The Stone, Mickey Mouse, Aladdin, Simba, Finding Nemo, Jungle Book, 101 Dalmatians, The Lion King and other classics. For a time, changing food habits, mismanagement and failure to recognize trends, placed the Disney corporation in an exposed position. Rumors circulated that the Mouse was on the brink of being swallowed up by Mickey D’s.
By the 1980s, Disney was a corporation that seemed to be creatively exhausted. The entertainment giant was seriously out of touch with what consumers wanted to buy, what moviegoers wanted to see. McDonald’s had introduced their wildly popular “Happy Meal” nationwide in 1979. Disney saw an opportunity for revival by proposing the idea of adding Disney toys and merchandising to Happy Meals. In 1987, the first Disney Happy Meal debuted, offering toys and prizes from familiar characters like Cinderella, The Sword In The Stone, Mickey Mouse, Aladdin, Simba, Finding Nemo, Jungle Book, 101 Dalmatians, The Lion King and other classics. For a time, changing food habits, mismanagement and failure to recognize trends, placed the Disney corporation in an exposed position. Rumors circulated that the Mouse was on the brink of being swallowed up by Mickey D’s.
 Additionally, there once was a McDonald’s at downtown Disney (before it became Disney Springs). At the Magic Kingdom, visitors could munch on french fries at the Village Fire Shoppe. At Disney’s Hollywood Studios, McDonald’s sponsored Fairfax Fries at the Sunset Ranch March. Fairfax is a reference to the street where the famous Los Angeles Farmers Market (the inspiration for the Sunset Ranch Market) is located. At Epcot, on the World Showcase promenade, is the Refreshment Port where sometimes international cast members from Canada would bring Canadian Smarties (similar to M&Ms) for the food and beverage location to make a Smarties McFlurry. The exclusive contract with Disney did not allow McDonald’s to tie in with blockbuster movies such as the Star Wars franchise even though movie studios would have preferred the tie in since McDonald’s had a higher profile and market share.
Additionally, there once was a McDonald’s at downtown Disney (before it became Disney Springs). At the Magic Kingdom, visitors could munch on french fries at the Village Fire Shoppe. At Disney’s Hollywood Studios, McDonald’s sponsored Fairfax Fries at the Sunset Ranch March. Fairfax is a reference to the street where the famous Los Angeles Farmers Market (the inspiration for the Sunset Ranch Market) is located. At Epcot, on the World Showcase promenade, is the Refreshment Port where sometimes international cast members from Canada would bring Canadian Smarties (similar to M&Ms) for the food and beverage location to make a Smarties McFlurry. The exclusive contract with Disney did not allow McDonald’s to tie in with blockbuster movies such as the Star Wars franchise even though movie studios would have preferred the tie in since McDonald’s had a higher profile and market share.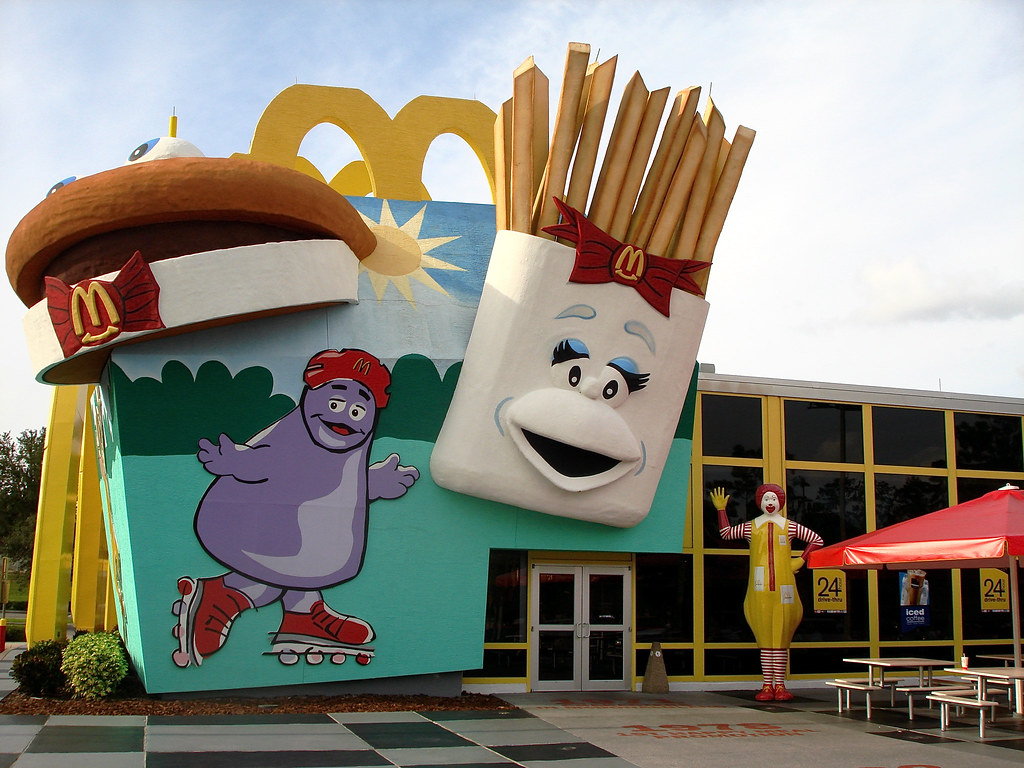
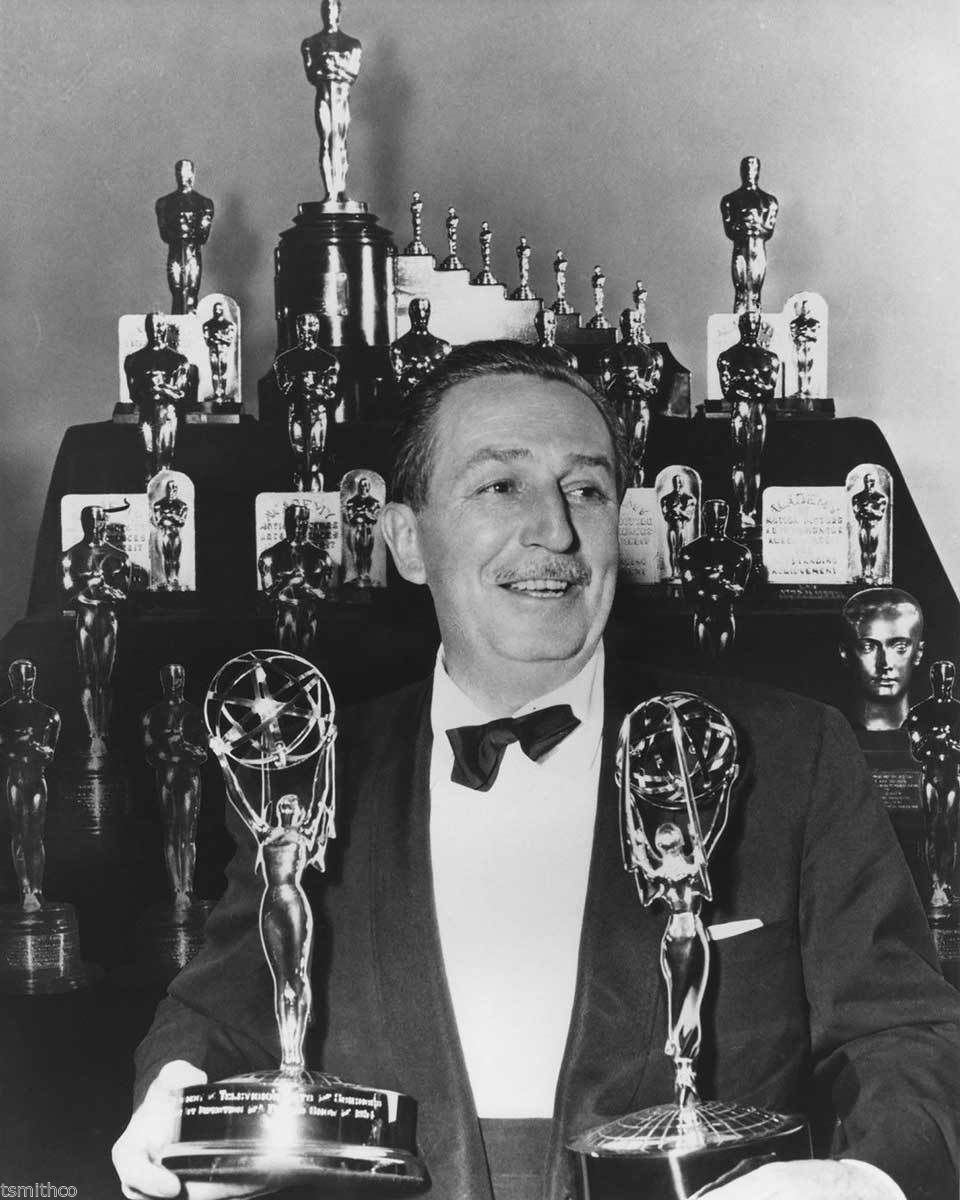 During his lifetime, Walt Disney received 59 Academy Award nominations, including 22 awards: both totals are records. Walt Disney’s net worth was equal to roughly $1 billion at the time of his death in 1966 (after adjusting for inflation). At the time of his death, Disney’s various assets were worth $100-$150 million in 1966 dollars which is the same as $750 million-$1.1 billion today. By the time of Kroc’s death in 1984, his net worth was $600 million. That’s the same as $1.4 billion after adjusting for inflation. One can only imagine how the pop culture landscape might have changed back in 1955 if those two former ambulance corps buddies had formed a partnership. But wait, would that make it Mickey D’s Mouse?
During his lifetime, Walt Disney received 59 Academy Award nominations, including 22 awards: both totals are records. Walt Disney’s net worth was equal to roughly $1 billion at the time of his death in 1966 (after adjusting for inflation). At the time of his death, Disney’s various assets were worth $100-$150 million in 1966 dollars which is the same as $750 million-$1.1 billion today. By the time of Kroc’s death in 1984, his net worth was $600 million. That’s the same as $1.4 billion after adjusting for inflation. One can only imagine how the pop culture landscape might have changed back in 1955 if those two former ambulance corps buddies had formed a partnership. But wait, would that make it Mickey D’s Mouse?