Original Publish date October 7, 2021. https://weeklyview.net/2021/10/14/abraham-lincolns-first-ghost-story/

There are many ghost stories associated with Abraham Lincoln. Most revolve around his time in the White House, his assassination at Ford’s Theatre, and his death in the Petersen House across the street. But what was the first ghost story that Abraham Lincoln ever heard? Historian Louis A. Warren, whose 1959 book “Lincoln’s Youth. Indiana Years 1816-1830” is considered to be the definitive work on Lincoln’s early life in the state, does its best to answer that question.
In the fall of 1816, Thomas and Nancy Lincoln packed their belongings and their two children, Sarah, 9, and Abraham, 7, and left Kentucky bound for southern Indiana. Arriving at his 160-acre claim near the Little Pigeon Creek sometime between Thanksgiving and Christmas. Thomas moved his family into a hunter’s half-face camp consisting of three rough-hewn walls and a large fourteen-foot space where a fire was almost always kept burning. Lincoln’s earliest memories of this home were the sounds of wild panthers, wolves, and coyotes howling just beyond the opening.
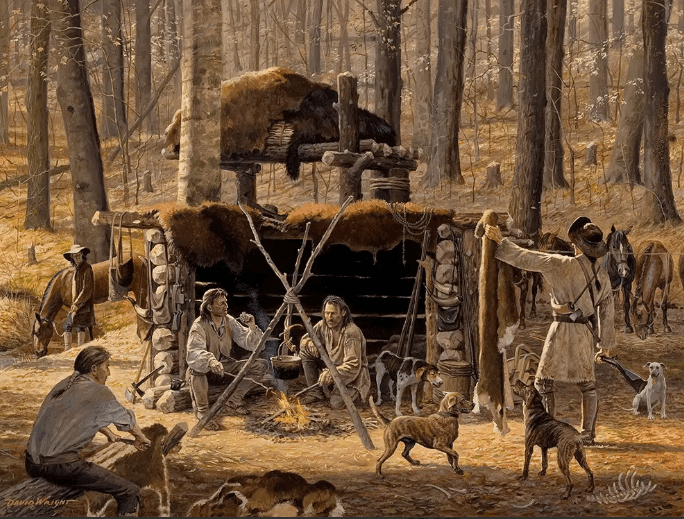
Once the chores were finished, Thomas would entertain his small family with tales of hunters, wild Indians, and ghosts. None of which was more frightening than the ghost of old Setteedown, mighty chief of the Shawnee tribe. The Shawnees were scattered throughout the region with their main settlement of about 100 wigwams located on the Ohio River near present-day Newburgh.

For the most part, the Indians were friendly and peaceful. Tradition recalls that Chief Setteedown (or Set-te-tah) and settler Athe Meeks were the exceptions to that rule. The Chief accused Meeks, a farmer and trapper, of robbing his traps and Meeks accused Setteedown of stealing his pigs. A feud developed between the two men that would ultimately leave both men dead.

The hatred became bitter and Setteedown decided to settle the matter once and for all. Early on the morning of April 14, 1812, Setteedown, his seventeen-year-old son and a warrior named Big Bones lay in wait outside the Meeks family cabin. The warriors were armed with rifles, knives, and tomahawks. When Atha, Jr. stepped out of the cabin to fetch water from a nearby spring, one of the Indians fired at him, wounding him in the knee and wrist.
In 2016, descendent Anthony Dale Meeks detailed the encounter in his family history. The Indians “crept up behind a fodder stack ten or twelve rods in front of the door and when my brother Athe (Jr.) got out of bed and passed out of the house and turned the corner with his back towards them, they all fired at him. One ball passed through his knee cap, another ball passed through his arm, about halfway from his elbow to his wrist. Another ball passed through the leg of his pants doing no injury.”
When Atha, Sr. heard the shots, he ran out of the cabin where Big Bones shot him as he exited the doorway. Margaret Meeks and another son dragged the dying man into the cabin before the Indians could scalp him. Atha, Sr. died without ever knowing what hit him. That 2016 account continues “Meanwhile father jumped out of bed, ran to the door to see what was up, and met an Indian right at the door who shot him right through the heart. He turned on his heels and tried to say something and fell dead under the edge of the bedstead.”

Setteedown and his son then ran to the wounded younger man and attacked him with their tomahawks. Meeks Jr. managed to fight his attackers off until his uncle William arrived from his adjacent cabin. William Meeks fired his rifle at the tribesmen, killing Big Bones and chasing the other two away.
Some accounts report that the attack on the Jr. Atha was more of a contest of humiliation than a duel to the death. Chief Setteedown and his son were toying with their prey like a cat with a mouse, throwing tomahawks and knives at the wounded young man from a close distance.

Among the Plains Indians, counting coup is the warrior tradition of winning prestige in battle by showing bravery in the face of an enemy. It involves shaming a captive with the ultimate goal being to persuade the enemy combatant to admit defeat, without having to kill him. In Native American Indian culture, any blow struck against the enemy counted as a coup. The most prestigious acts included touching an enemy warrior with a hand, bow, or coup stick and escaping unharmed; all without killing the enemy. The tradition of “counting coup”, if true in this instance, ultimately cost the great Chief his life. The gruesome practice allowed armed avengers to bring this “game” to an end by precipitating a hasty retreat.
Some eight hours later, a group of settlers arrived at Setteedown’s village seeking revenge. The vigilantes captured Setteedown, his wife, the son who participated in the attack, and two or three other children. The posse confined them in the cabin of Justice of the Peace Uriah Lamar near Grandview. They were guarded by three men, including the deceased brother William Meeks. Sometime during the night the old chief was shot and killed, presumably by Uncle William Meeks.

The remaining family members were banished from the region. Legend claims that they left a treasure behind buried somewhere near Cypress Creek and the Ohio River. Setteedown’s tribe disbanded and reportedly joined Tecumseh to fight in the War of 1812.
And what became of Chief Setteedown’s body? Author Louis Warren notes, “Setteedown was buried in his Indian blanket in a shallow grave close to the Lamar cabin. Mischievous boys were reported to have pushed sticks down through the soil until they pierced the old blanket. (thereby releasing his vengeful spirit) And for many years old Setteedown’s ghost was supposed to be visible at times in the vicinity.”

Local lore claims that old Chief Setteedown roamed the hills, dales, and waterways of Spencer and Warrick County looking for scalps to add to his war belt. Frontier children were warned that Setteedown’s playful spirit was a ruse with deadly intentions. Chief Setteedown was searching for souls to repopulate his lost tribe in the afterlife. In an age when children were often in charge of refilling the household water trough, gathering firewood, or collecting nuts and berries to supplement every meal, it is easy to imagine how ghost stories about bloodthirsty Indians may have sparked young Abe Lincoln’s imagination. The setteedown legend had every element that would have sparked a child’s imagination: Indians, murder and lost treasure.

The legend takes on added significance when it is remembered that Abraham Lincoln’s namesake grandfather was ambushed and killed by Indians. In May 1786, Abraham Lincoln, Sr. (his Kentucky tombstone lists his surname alternatively as “Linkhorn”) was putting in a crop of corn with his sons, Josiah, Mordecai, and Thomas, when they were attacked by a small war party. He was killed in the initial volley. In referring to his grandfather in a letter to Jesse Lincoln in 1854, Lincoln wrote that “the story of his death by the Indians, and of Uncle Mordecai, then fourteen years old, killing one of the Indians, is the legend more strongly than all others imprinted upon my mind and memory.”
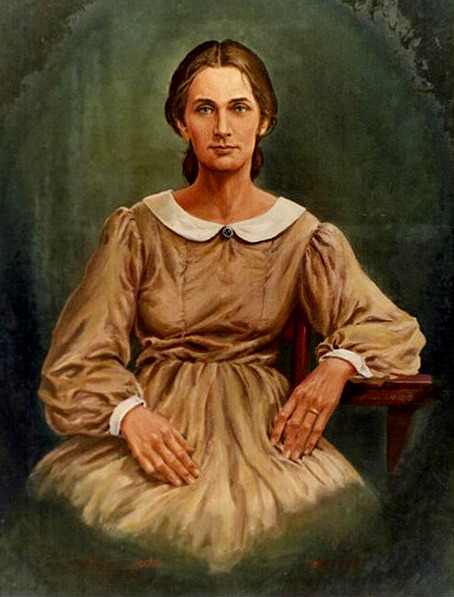

Although life was generally good for the Lincoln family during their first couple of years in Indiana, like most pioneer families they experienced their share of tragedy. In October 1818, when Abraham was nine years old, his mother, Nancy Hanks Lincoln, died of “milk sickness”. The milk sickness ensued after a person consumed the contaminated milk of a cow infected with the toxin from the white snakeroot plant ( or Ageratina altissima). Nancy had gone to nurse and comfort her ill neighbors and became herself a victim of the dreaded disease.

Thomas and Abraham whipsawed Hoosier Forrest logs into coffin planks, and young Abe whittled wooden pegs with his own hands, pausing only briefly to wipe the tears away that were flowing down his cheeks. Ultimately, Abe’s hand-carved pegs fastened the boards together into the coffin for his beloved mother. She was buried on a wooded hill south of the cabin. For young Abraham, it was a tragic blow. His mother had been a guiding force in his life, encouraging him to read and explore the world through books.

His feelings for her were still strong some 40 years later when he said, “All that I am or hope to be, I owe to my angel mother.” Lincoln’s fatalistic countenance, his famous bouts with melancholy, and his overall sad-faced demeanor could easily be traced back to those “growing-up” days in Southern Indiana. It is easy to imagine that, although terrifying to most children, the Setteedown ghost story was welcome entertainment to the hard reality of life on the Hoosier frontier for young Abe Lincoln.





 Eventually it was Abraham’s turn to hitch his old mare to the gristmill’s arm. As he tediously walked his horse round and round, he grew impatient at having wasted most of the morning already. He began to apply a hickory switch to the beast’s behind while shouting, “Git up, you old hussy; git up, you old hussy” to keep his horse moving at an accelerated pace. This tactic worked for a short time until the horse had had enough and, just as his young master clucked out the words “Git up”, the horse kicked backwards and hit the boy in the head with a rear hoof. Lincoln was knocked off his feet and into the air, landing some distance away where he came to rest bruised and bloodied. Noah Gordon rushed to the aid of the unconscious young man. Realizing the seriousness of the situation, Gordon picked the boy up and brought him in to his house, placing him on a nearby bed.
Eventually it was Abraham’s turn to hitch his old mare to the gristmill’s arm. As he tediously walked his horse round and round, he grew impatient at having wasted most of the morning already. He began to apply a hickory switch to the beast’s behind while shouting, “Git up, you old hussy; git up, you old hussy” to keep his horse moving at an accelerated pace. This tactic worked for a short time until the horse had had enough and, just as his young master clucked out the words “Git up”, the horse kicked backwards and hit the boy in the head with a rear hoof. Lincoln was knocked off his feet and into the air, landing some distance away where he came to rest bruised and bloodied. Noah Gordon rushed to the aid of the unconscious young man. Realizing the seriousness of the situation, Gordon picked the boy up and brought him in to his house, placing him on a nearby bed. Meanwhile, Dave Turnham, who had come to the mill with Abraham, ran the two miles to get Abraham’s father. Thomas Lincoln rushed to his wagon and lit out to the scene. The elder Lincoln, seeing his son’s grave condition, hauled the injured boy home and put him to bed where the young man remained prone and unconscious all night. Neighbors from the small, close knit community, including mill owner Noah Gordon, gathered at the Lincoln cabin believing Thomas Lincoln’s boy was close to death. The next morning one witness jumped from their seat, pointed and shouted, “Look he’s coming straight back from the dead!” Abraham was shaking and jerking from head to toe when he opened his eyes and finished his cadence from the day before by shouting “You old hussy”.
Meanwhile, Dave Turnham, who had come to the mill with Abraham, ran the two miles to get Abraham’s father. Thomas Lincoln rushed to his wagon and lit out to the scene. The elder Lincoln, seeing his son’s grave condition, hauled the injured boy home and put him to bed where the young man remained prone and unconscious all night. Neighbors from the small, close knit community, including mill owner Noah Gordon, gathered at the Lincoln cabin believing Thomas Lincoln’s boy was close to death. The next morning one witness jumped from their seat, pointed and shouted, “Look he’s coming straight back from the dead!” Abraham was shaking and jerking from head to toe when he opened his eyes and finished his cadence from the day before by shouting “You old hussy”. Lincoln’s contemporaries noticed that at times his left eye drifted upward independently of his right eye, a condition doctors diagnosed as “strabismus” but more derisively known as “Lazy Eye”. The resulting affliction results in the eyes failure to properly align with each other when looking straight ahead, particularly when trying to focus on an object. As proof, experts point to the best surviving evidence; two life masks of Lincoln. One a beardless portrait made in April of 1860 and the other, a bearded image made in February of 1865. Laser scans of both masks reveal an unusual degree of facial asymmetry. In short, the left side of Lincoln’s face was much smaller than the right, resulting in the double diagnosis of “hemifacial microsomia” compounded by “strabismus”. The defects join a long list of posthumously diagnosed ailments including smallpox, heart disease, bi-polar disorder and depression that doctors claimed afflicted Lincoln.
Lincoln’s contemporaries noticed that at times his left eye drifted upward independently of his right eye, a condition doctors diagnosed as “strabismus” but more derisively known as “Lazy Eye”. The resulting affliction results in the eyes failure to properly align with each other when looking straight ahead, particularly when trying to focus on an object. As proof, experts point to the best surviving evidence; two life masks of Lincoln. One a beardless portrait made in April of 1860 and the other, a bearded image made in February of 1865. Laser scans of both masks reveal an unusual degree of facial asymmetry. In short, the left side of Lincoln’s face was much smaller than the right, resulting in the double diagnosis of “hemifacial microsomia” compounded by “strabismus”. The defects join a long list of posthumously diagnosed ailments including smallpox, heart disease, bi-polar disorder and depression that doctors claimed afflicted Lincoln.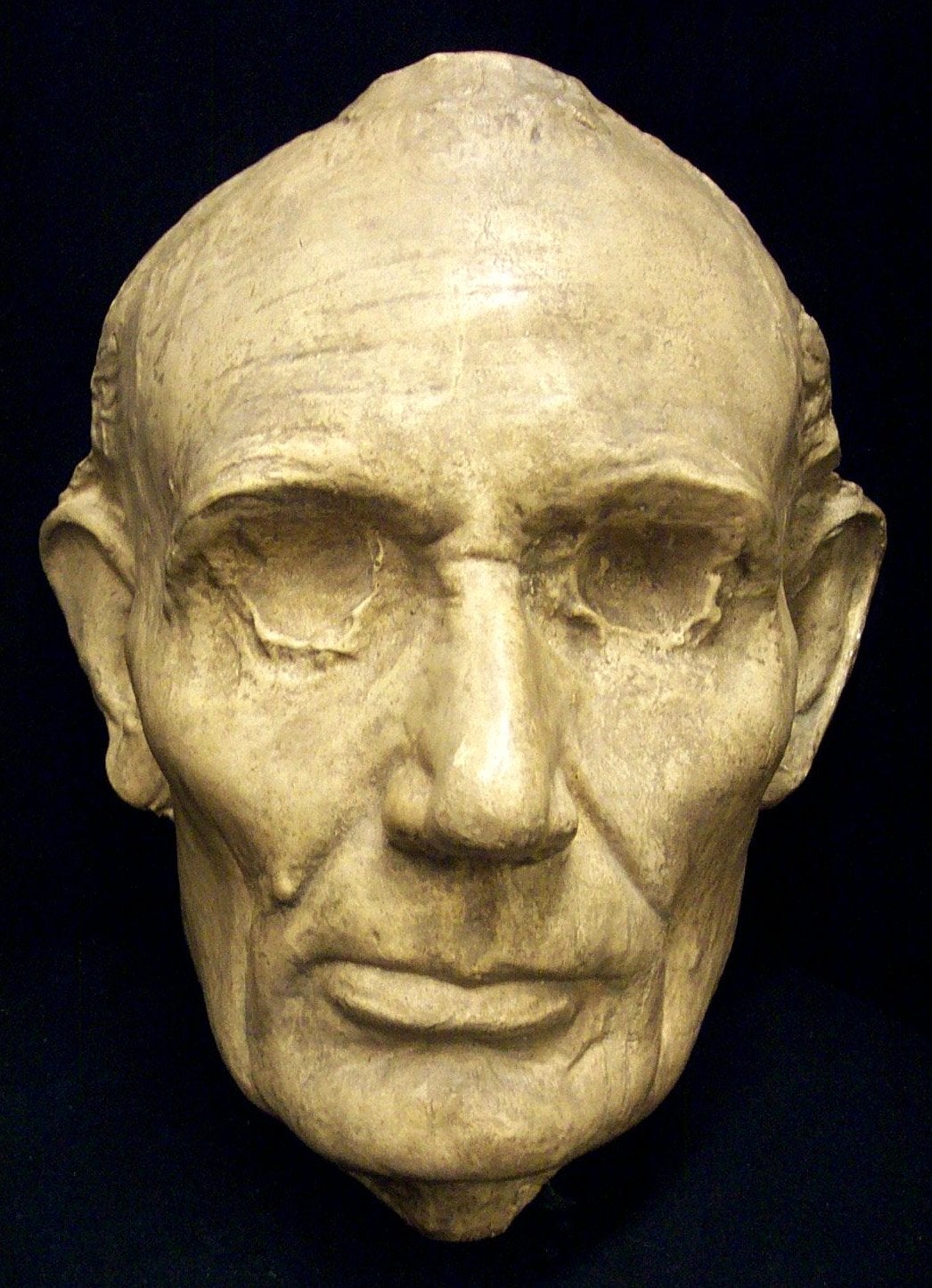 According to a cadre of modern day medical historians, Gardner’s photo is worth a thousand words. Although modern neurologists admit that a positive diagnosis would require a complete examination of the living Lincoln, photographic evidence strongly supports their theory. The mule kick to the forehead undoubtedly fractured the skull at the point of impact, the size and depth of the depression attesting to the incident’s severity. In addition, the nerves behind the left eye were damaged by the violent snapping of the head and neck backward. That whiplash also caused several small hemorrhages in the brainstem resulting in the permanent ocular and facial effects and was likely responsible for Lincoln’s high pitched, rasping voice.
According to a cadre of modern day medical historians, Gardner’s photo is worth a thousand words. Although modern neurologists admit that a positive diagnosis would require a complete examination of the living Lincoln, photographic evidence strongly supports their theory. The mule kick to the forehead undoubtedly fractured the skull at the point of impact, the size and depth of the depression attesting to the incident’s severity. In addition, the nerves behind the left eye were damaged by the violent snapping of the head and neck backward. That whiplash also caused several small hemorrhages in the brainstem resulting in the permanent ocular and facial effects and was likely responsible for Lincoln’s high pitched, rasping voice. Yet another after effect of that boyhood mulekick was noticed by Josiah Crawford, a neighbor from Gentryville, Ind. who employed the boy Lincoln, loaned him books for study. Gentry liked to playfully needle the young railsplitter about the way he “stuck out” his lower lip while in deep concentration. When 35-year-old Lincoln returned to to make a speech in southern Indiana in 1844 for Henry Clay, Crawford noticed Abe’s lower lip still protruded abnormally. When Crawford asked what books he consulted before making the speech, Lincoln replied humorously, “I haven’t any. Sticking out my lip is all I need.”
Yet another after effect of that boyhood mulekick was noticed by Josiah Crawford, a neighbor from Gentryville, Ind. who employed the boy Lincoln, loaned him books for study. Gentry liked to playfully needle the young railsplitter about the way he “stuck out” his lower lip while in deep concentration. When 35-year-old Lincoln returned to to make a speech in southern Indiana in 1844 for Henry Clay, Crawford noticed Abe’s lower lip still protruded abnormally. When Crawford asked what books he consulted before making the speech, Lincoln replied humorously, “I haven’t any. Sticking out my lip is all I need.”