Category: Assassinations
Osborn H. Oldroyd’s Greatest Fear.
Original Publish Date March 6, 2025.
https://weeklyview.net/2025/03/06/osborn-h-oldroyds-greatest-fear/
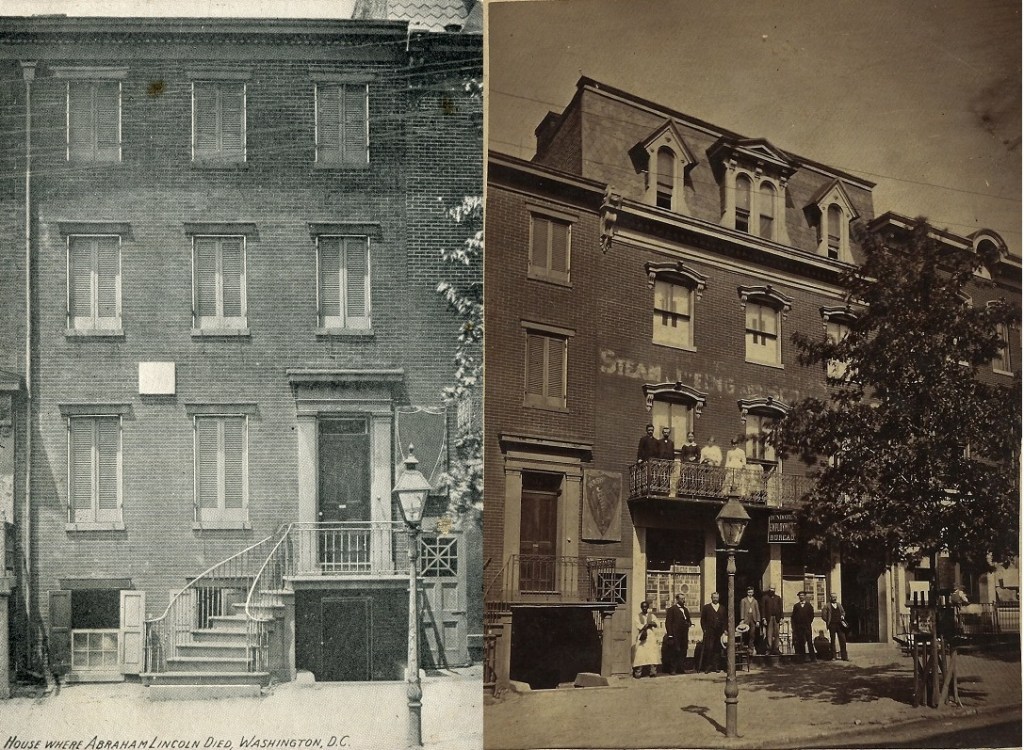

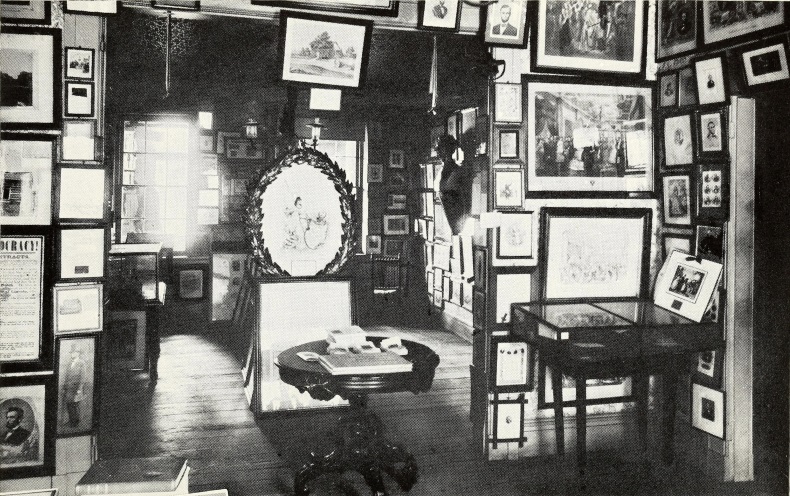
My wife and I recently traveled to Springfield, Illinois for a book release event (actually two books). One book on Springfield’s greatest living Lincoln historian, Dr. Wayne C. “Doc” Temple, and the other on my muse for the past fifteen years, Osborn H. Oldroyd. I have fairly worn out my family, friends, and readers with the exploits of Oldroyd over the years. He has been the subject of two of my books and a bevy of my articles. Oldroyd was the first great Lincoln collector. He exhibited his collection in Lincoln’s Springfield home and then in the House Where Lincoln Died in Washington DC from 1883 to 1926. Oldroyd’s collection survives and forms much of the objects in Ford’s Theatre today.

For this trip, we traveled up from the south to Springfield through parts of northwest Kentucky and southeast Missouri. What struck us most were the conditions of the small towns we drove through. Today many of these little burgs and boroughs are in sad shape, littered by once majestic brick buildings featuring the names of the merchants that built them above the doorways, eaves, and peaks of their frontispieces in a valiant last stand. Most had boarded-up windows and doors and some with ghost signs of products and services that disappeared generations ago.
They are tightly packed and many share common walls. We were amazed how many of them have caved-in or worse, burnt down. The caved-in buildings are the work of Father Time and Mother Nature, but the burnt ones look as if the fires were extinguished just recently. My wife deduces that these are likely the result of the many meth labs that blight these long-forgotten, empty buildings. Indeed, a little research reveals that these rural areas do lead the league in these hastily constructed, outlaw drug factories.
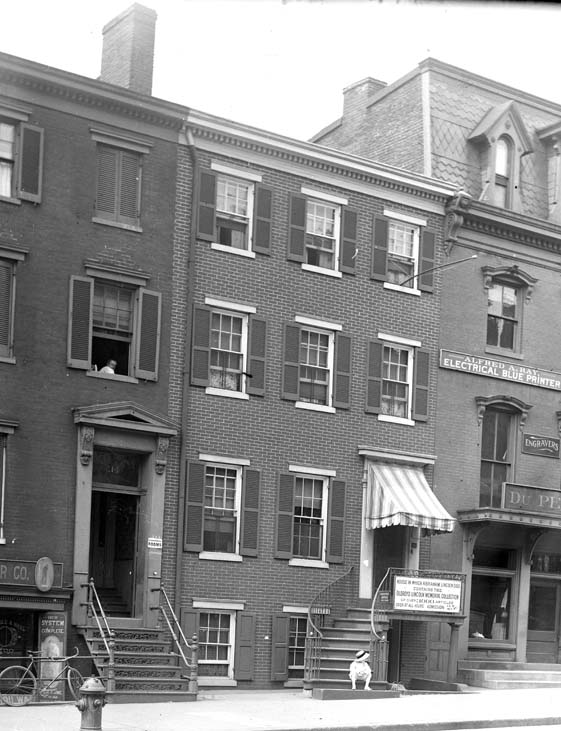

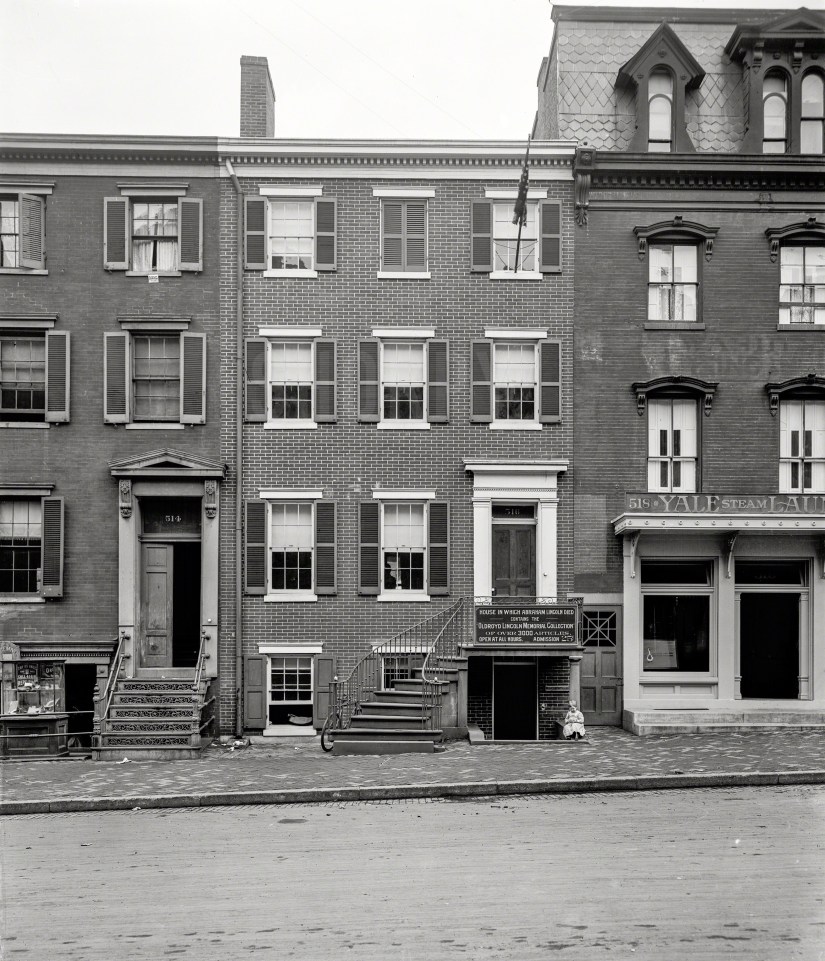
Of course, that got me thinking about Oldroyd’s museum. Oldroyd lobbied for decades to have his collection purchased by the U.S. government and preserved for future generations to explore. The Feds eventually purchased it in 1926 for $50,000 (around $900,000 today). For over half a century while assembling his collection, Oldroyd had one great fear: Fire. Visiting the House Where Lincoln Died today, the building remains unique in size and architecture compared to those around it. In Oldroyd’s day, smoking cigars, pipes, and cigarettes indoors was as prevalent as carrying cell phones and water bottles are today. The threat of fire was very real for Oldroyd.

The March 20, 1903, Huntington Indiana Weekly Herald ran an article titled “A Visit to the Lincoln Museum in Washington City.” After describing the relics in the collection, columnist H.S. Butler states, “It is hoped the next Congress will purchase this collection and care for it. Mr. Oldroyd is not a man of means such as would enable him to do all he would like, and it seems to me a little short of criminal to expose such valuable relics, impossible to replace, to the great risk of fire. I understand Congressman [Charles] Landis, of Indiana, is trying to get the collection stored in the new Congressional Library, in itself the handsomest structure, interiorly, in Washington. I hope that his brother, the congressman from the Eleventh District [Frederick Landis], will lend his influence to Senators [Charles] Fairbanks and [Albert] Beveridge to urge forward the same end.”

Fifteen years later, the Topeka State Journal described an event that fueled Oldroyd’s concern. “May 21 [1918]-a few days ago the Negro cook in the kitchen of a dairy lunch spilled some fat on the fire and the resulting blaze was extinguished with some difficulty. The unique feature of this trifling accident was that, had the blaze gotten beyond control, it would probably have destroyed a neighboring house in which is the greatest collection in the world of relics, manuscripts, and books bearing upon the life and death of Abraham Lincoln…Sixty feet away from the room in which Lincoln died are three kitchens of restaurants and a hotel. More than one recent fire scare has caused alarm over the danger that threatens these relics.”

The February 11, 1922, Dearborn [Michigan] Independent reported, “A vagrant spark, a carelessly tossed cigarette or cigar stub, an exposed electric wire might at any time mean the destruction of the collection and the building which, of course, is itself a sacred bit of Lincolniana.” The January 21, 1924, Daily Advocate of Belleville, Ill. reported “The collection is contained in a small and overcrowded room of the house opposite Ford’s Theatre, with two restaurants across a narrow alleyway constituting a constant fire menace…it is likely that the U.S. Government will request that the Illinois Historical Society return the bed in which Lincoln died, that it may again be placed in the room it occupied on that fateful night and the entire setting restored.” Due to that unresolved fire threat the bed was never returned and is today on display at the Chicago History Museum. A 1924 Christmas day article in the Washington Standard 1924 described, “There are a number of restaurants in the block at the rear, and once an oil supply house did business close at hand. On two occasions there have been fires in the neighborhood.”

The July 6, 1926, Indianapolis News speculated, “The government will add to the collection the high silk hat Lincoln wore to the theatre that fatal night, the chair in which he sat in the presidential box, and the flag in which Booth’s foot caught. The flag now hangs in the treasury, while the hat and chair are in storage. These articles formerly were in the Oldroyd collection, but after a fire in the neighborhood some years ago, officials of the government took them back, fearing that they might be destroyed.” The February 18, 1927, Greenfield [Indiana] Reporter stated, “The plan proposed by Senator Watson, of Indiana, and Rep. Rathbone of Illinois, is to remodel the building to protect it against the danger of fire and the ravages of age. They would…place in it the famous Oldroyd collection of Lincoln relics.” Fire remained a nightmare for Oldroyd right up to the day he died on October 8, 1930.

Ironically, after that book signing I found myself browsing the bookstore. I found there a 2 1/2” x 4” business card from the New Lincoln Cafe in the adjoining building to the north of Oldroyd’s Museum (at 516 10th St. NW). Putting aside the fact that I have a personal affinity for old business cards, the item called out to me and made me wonder about the businesses that had been neighbors to this hallowed spot over the generations.

The card reads: “Chinese and American New Lincoln Cafe. Located at 518 10th St., N.W. Phone EX. 1468. We Specialize In Spaghetti-Home Made Fresh Daily. Your Favorite Mixed Drinks And Cocktails. President Lincoln Was Assassinated In Ford’s Theatre On Night Of April 14th, 1865, And Died Following Morning At Seven-Thirty.” A check of the records indicates that this restaurant remained next to the museum from the late 1930s to the early 1960s. This was just one of the businesses to call that space home over the generations.

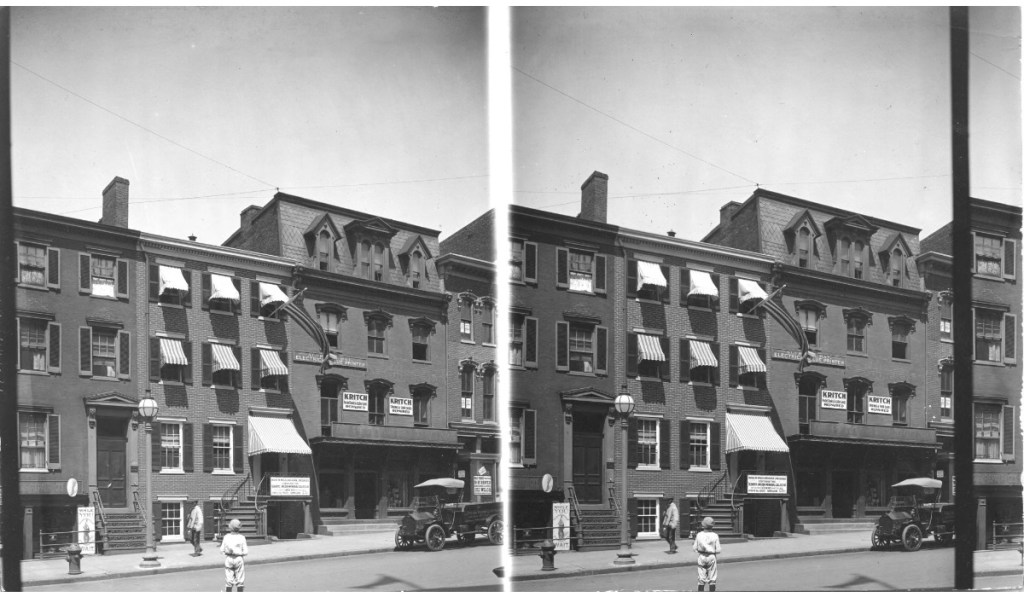
Located in the Penn Quarter section of DC, the building was built sometime between 1865 to 1873. It envelopes the entire north side and part of the northwest back of the HWLD. It is 4 stories tall and features 11,904 square feet of retail space. One of the earliest storefronts to appear there was Dundore’s Employment Bureau which served D.C. during the 1870-90s. Ironically, when Dundore’s moved three blocks south to 717 M Street NW, the agency regularly advertised jobs at businesses occupying their old address for generations to come. Above the Dundore agency was Mrs. A. Whiting’s Millinery, which created specialty hats for women. The Washington Evening Star touted Mrs. Whiting’s “Millinery Steam Dyeing and Scouring” business for their “Imported Hats and Bonnets”. A 3rd-floor hand-painted sign on the bricks of the building advertising Whiting’s remained for years after the business vacated the premises, creating a “ghost sign” visible for many years as it slowly faded from view.
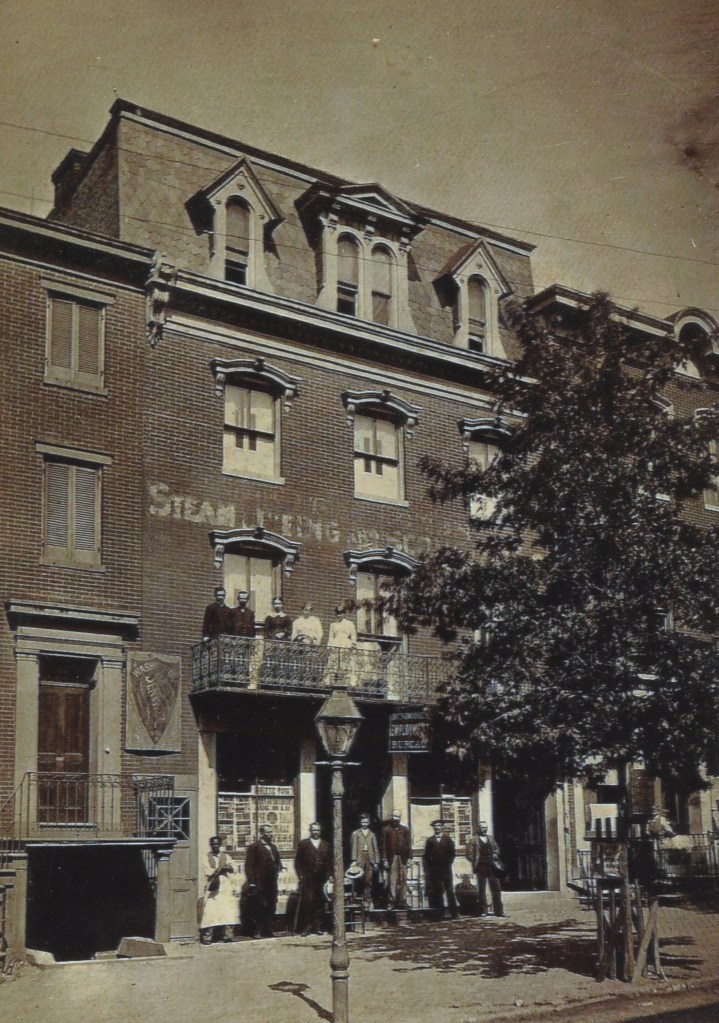

The Forsyth Cafe seems to have been the first bistro to pop up next to the Oldroyd Museum. In late February/March 1885 (in the leadup to Grover Cleveland’s first Presidential Inauguration), DC’s Critic and Record newspaper’s ad for the cafe decries, “Yes, One Dollar is cheap for the Inauguration supper, but what about those excellent meals at the Forsythe Cafe for 15 Cents?” The Forsyth continued to advertise their meals from 15 to 50 cents but by late 1886, they were gone, replaced by the Logan Cafe. The Logan offered 15 and 25-cent breakfasts, “Big” 10-cent lunches, and elaborate 4-course dinners of Roast beef, stuffed veal, lamb stew, & oysters. Proprietor W.E. Logan’s claim to fame was “the best coffee to be had in the city, made in French-drip Glass-Lined Urn” and “Special Dining Rooms for Ladies-Polite waiters in attendance” and his menus warned “No Liquors” served.

The June 4, 1887, Critic and Record reported on a “friendly scuffle” at the Logan between two “colored” employees when cook Charles Sail tripped waiter William Butler who hit his head on the edge of a table and died the next morning at Freedman’s Hospital. The men were described as best friends and the death was deemed an accident. By late 1887, the Logan disappears from the newspapers. From 1897 to 1897, the building was home to the Yale Laundry. The Jan. 7, 1897, DC Times Herald reported on an event that likely added to Oldroyd’s anxiety. The article, titled “Laundry is Looted” details a break-in next door to the museum during which a couple of safecrackers got away with $85 cash including an 1883 $5 gold piece.
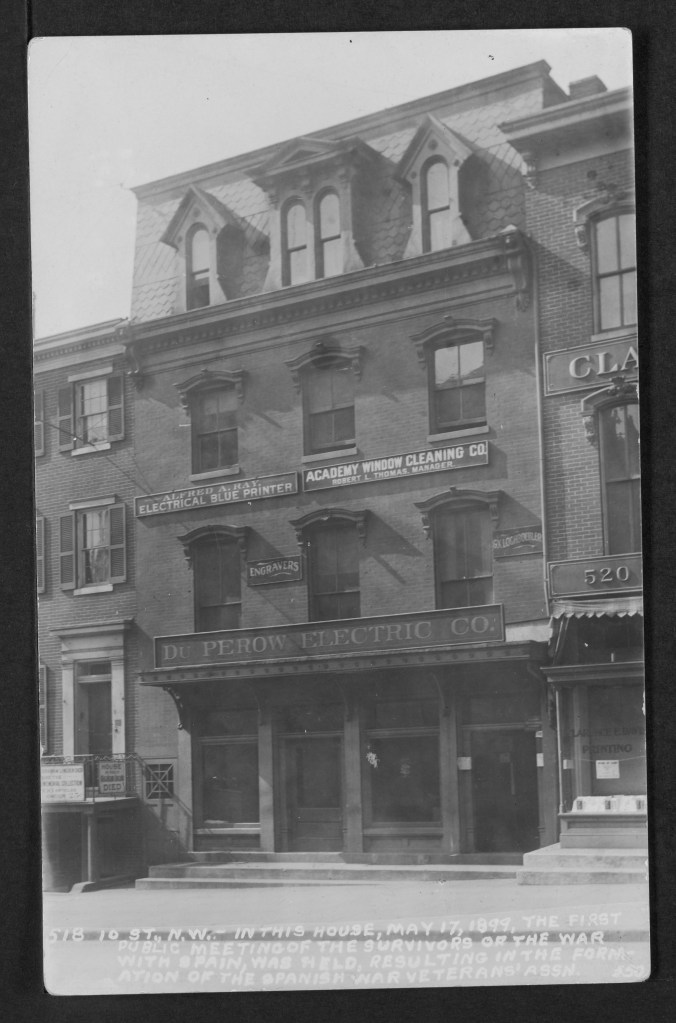


A real photo postcard in the collection of the District of Columbia Public Library pictures the building during Yale Laundry’s tenure captioned, “In this house the first public meeting of the survivors of the war with Spain, was held on May 17, 1899, resulting in the formation of the Spanish War Veterans’ Association.” The Dec. 1, 1900, Washington Star notes the addition of Harry Clemons Miller’s “Teacher of Piano” Studio and by 1903, the “Yale Steam Laundry” appeared in the DC newspapers at the address.
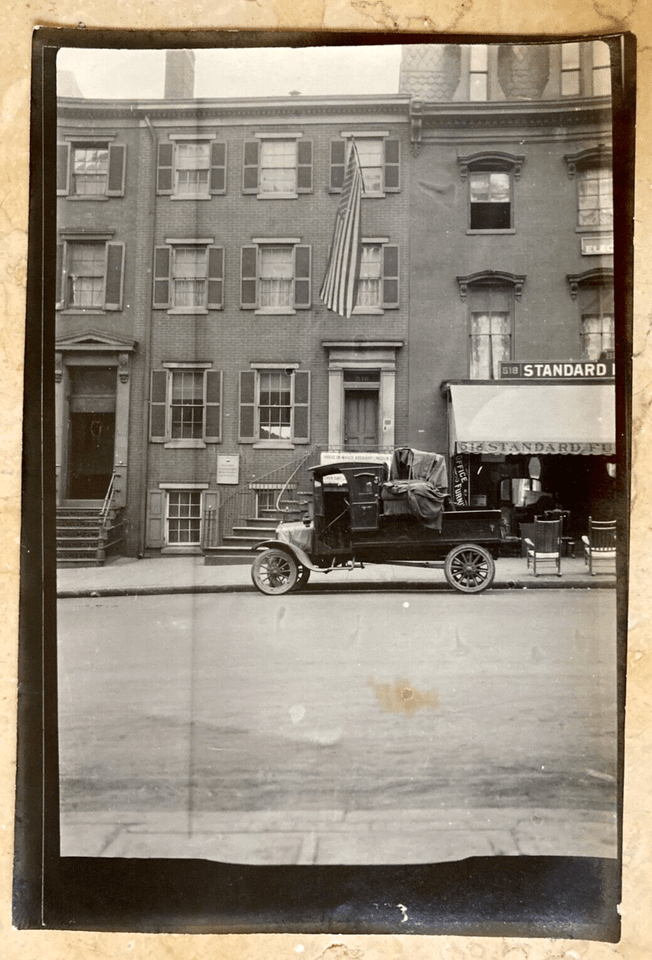
In 1909, Du Perow Electric Co. (AKA as “Du Pe”) and partner Alfred A. Ray “Electrical Blueprints” occupied the building. A window cleaning company occupied room # 9 and a leather goods store was located there during this same period. By 1912, the storefront was occupied by the Standard Furniture Co. At least one photo survives presenting an amusing scene of a furniture truck blocking the entrance to Oldroyd’s museum. Amusing to the viewer today but most assuredly not to the museum curator back in the day. Eventually, the restaurants, bars, and cafes that worried Oldroyd began to come and go, among them, the Lincoln Cafe & Cocktail Lounge, whose sign was dominated by the words “Beer Wine.” It appears that during the 1920-50s, a Pontiac, DeSoto, Plymouth Motor Car dealer known as “News & Company” kept an office in the building, with the car lot and gas station across the street.
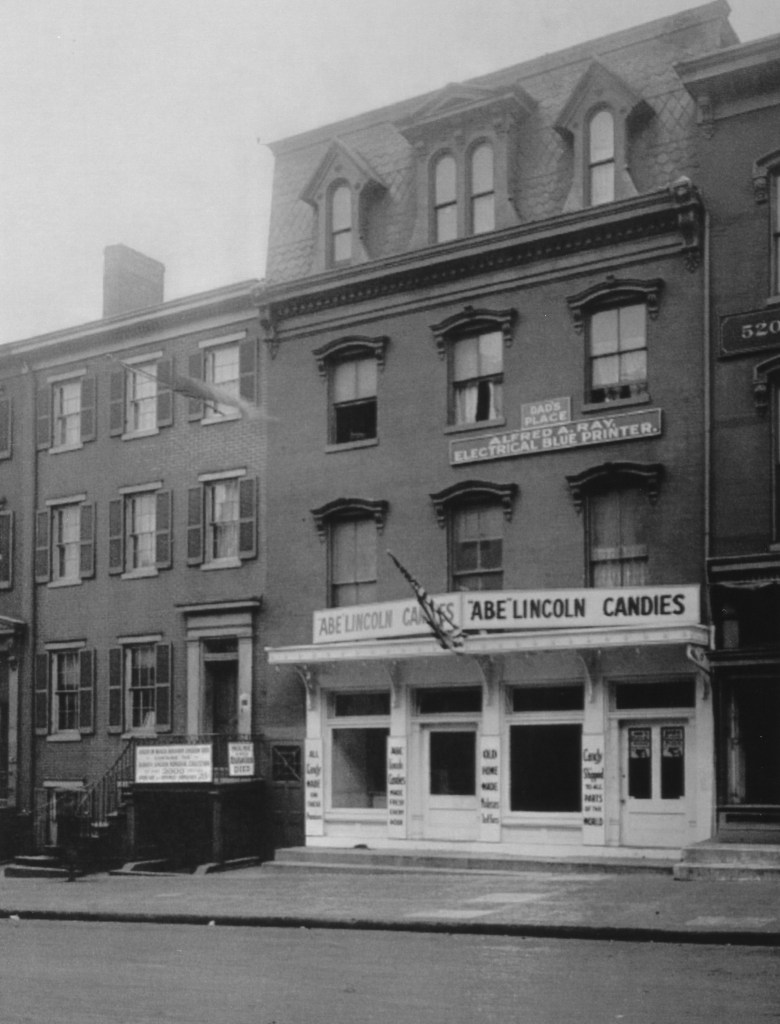


Old-timers remember a long-term tenant known as “Abe Lincoln Candies” that occupied the space from the 1950-70s. Other recent tenants included Abe’s Cafe & Gift Shop, Bistro d’Oc and Wine Bar, Jemal’s 10th Street Bistro, Mike Baker’s 10th St Grill, and the I Love DC gift store, and last year, The Inauguration-Make America Great Again Store, who one Yelp reviewer complained was crowded with outdated, sketchy clothing and that “they make u give them a good review before they give u a refund kinda scummy.”
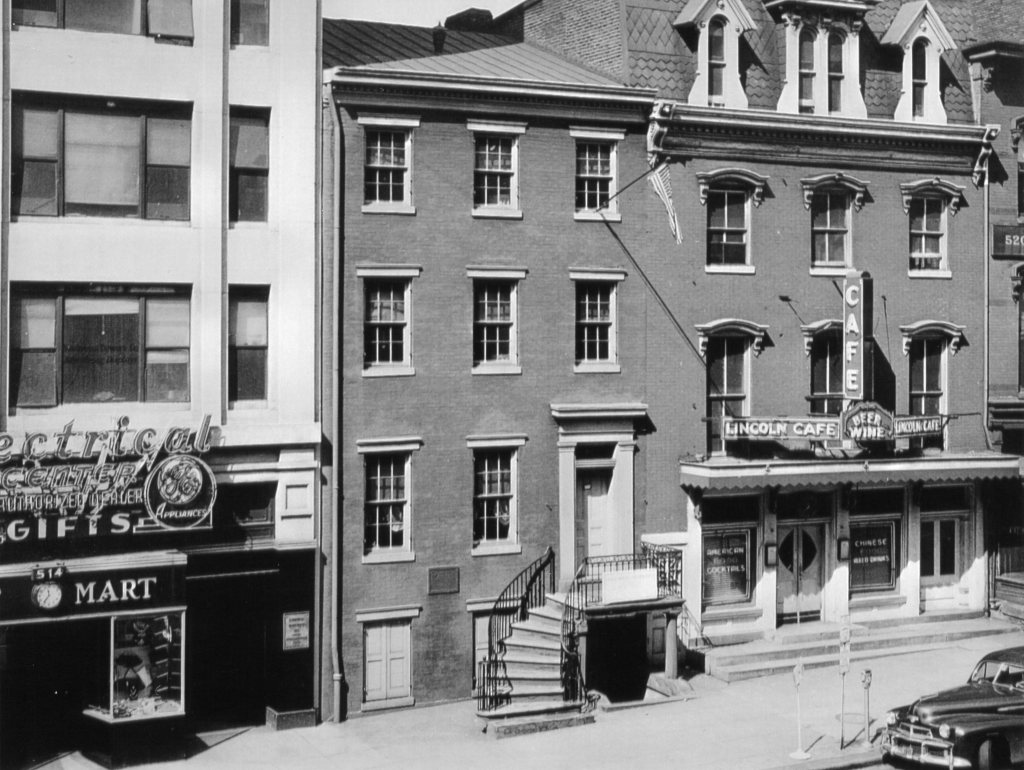

As for the building on the opposite side of Oldroyd’s museum at 514 Tenth St. NW, it remained a residence until 1922 when a $55,000, 10-story concrete & steel building with steam heat and a flat slag roof was built. Designed by architect Charles Gregg and built by Joseph Gant, the sky-scraper, known as the Lincoln Building, dwarfed the Oldroyd Museum. It was home to several businesses, including the Electrical Center (selling General Electric TVs, radios, and appliances) and the Garrison Toy & Novelty Co, its modern construction alleviated any concern of fire.

It must be noted that many great collections of Lincolniana fell victim to fire in the century and a half after Lincoln’s death. The Great Chicago Fire of 1871 consumed many Lincoln objects, documents, and personal furniture that had been removed from the Springfield home after the President’s departure to Washington DC. On June 15, 1906, Major William Harrison Lambert (1842-1912), recipient of the Congressional Medal of Honor and one of the Lincoln “Big Five” collectors, lost much of his collection in a fire at his West Johnson St. home in Germantown, Pa. Among the items lost were a bookcase, table, and chair from Lincoln’s Springfield law office and the chairs from Lincoln’s White House library. The threat of fire was a constant waking nightmare in Oldroyd’s life. While he did his best to control what went on inside his museum, he had no control over what happened outside. His life’s work of collecting precious Lincoln objects, over 3,500 at last count, could be gone in the flash of a pan.
ADDITIONAL IMAGES.








The Gun That Killed Vincent Van Gogh?
Original Publish Date February 15, 2024.
https://weeklyview.net/2024/02/15/the-gun-that-killed-vincent-van-gogh/

I have spent the past 12 years on a quest. A quest to discover a little-known Lincoln collector turned museum curator named Osborn H. Oldroyd. I have written about Oldroyd many times and, sometimes, the mere mention of his name elicits groans from family and friends whom I’ve forced to share my obsession, whether they want to or not. No worries, I’m not going down that road again today. I simply mention him regarding another of my early obsessions: artist Vincent van Gogh. I know, I know, Oldroyd to Van Gogh? Evel Knievel couldn’t have made that jump. Stay with me now.

A few years back, a Paris auction house (Auction Art–Rémy Le Fur) sold the gun that Van Gogh allegedly killed himself with for approximately $182,000 to an unidentified Belgian buyer. The hammer price was almost triple the auction estimate of $44,800 to $67,000 and presumably included the buyer’s premium. Like everything in Van Gogh’s life, the sale was not without controversy. And, like many of the objects in Oldroyd’s collection (for his collection was his life), the provenance of the firearm is the sticking point. If authentic, the auction house’s description of it as “the most famous weapon in the history of art” would be unchallenged. However, let’s examine the event, the discovery, and its ultimate disposition and see what you think.

As a kid, I spent most of my free time in the library. Like many my age, my first instinct was to discover a much-wished-for connection to some (or any) historical event. I pored through the annual book of Guinness World Records looking for some record (any record) that I could conceivably break. I never found one. Then I tried to prove a genealogical link to anyone of note . . . Please be Lincoln . . . Please be Lincoln. It was not Lincoln. I was descended from a long line of boringly average people. The last hope was a connection to someone/something according to my birthday (July 30th). I found two: Jimmy Hoffa disappeared and Vincent van Gogh was buried. Oh sure, Henry Ford was born, Jamestown was founded, but not much else. So I clung to the Van Gogh square. He’s been a windmill for me to tilt at ever since.

There are so many mysteries surrounding Vincent van Gogh. Was he crazy? Was a visual problem responsible for his unique painting style? Why did his paintings, all acknowledged masterpieces, not sell until after he died? And perhaps most of all, did he REALLY kill himself? Well, he did famously cut off an ear after an argument with fellow artist Paul Gauguin and famously presented it to a prostitute in a nearby brothel. And he was confined to insane asylums more than once in his lifetime. But that gun may fuel the biggest Van Gogh mystery of them all.


Arthur Ravoux’s Inn in Auvers-sur-Oise in France today (at left) & in Van Gogh’s time.
In May of 1890, after one of those asylum stays, Van Gogh moved into Arthur Ravoux’s Inn in Auvers-sur-Oise in France. While living in room number five there, he turned out an average of a painting a day, despite his increasingly unstable mental state. The common theory is that on Sunday, July 27th, 1890, Van Gogh ventured from his château hideaway to a nearby wheat field in the village of Auvers-sur-Oise and shot himself in the chest. The gunshot did not kill him immediately, instead, Van Gogh lost consciousness and, after waking up and in seeming defiance of his mortal injuries, left his easel against a haystack before stumbling back to his modest attic room, lit only by a small skylight, in the Ravoux Inn. He died two days later, his beloved brother Theo by his side.
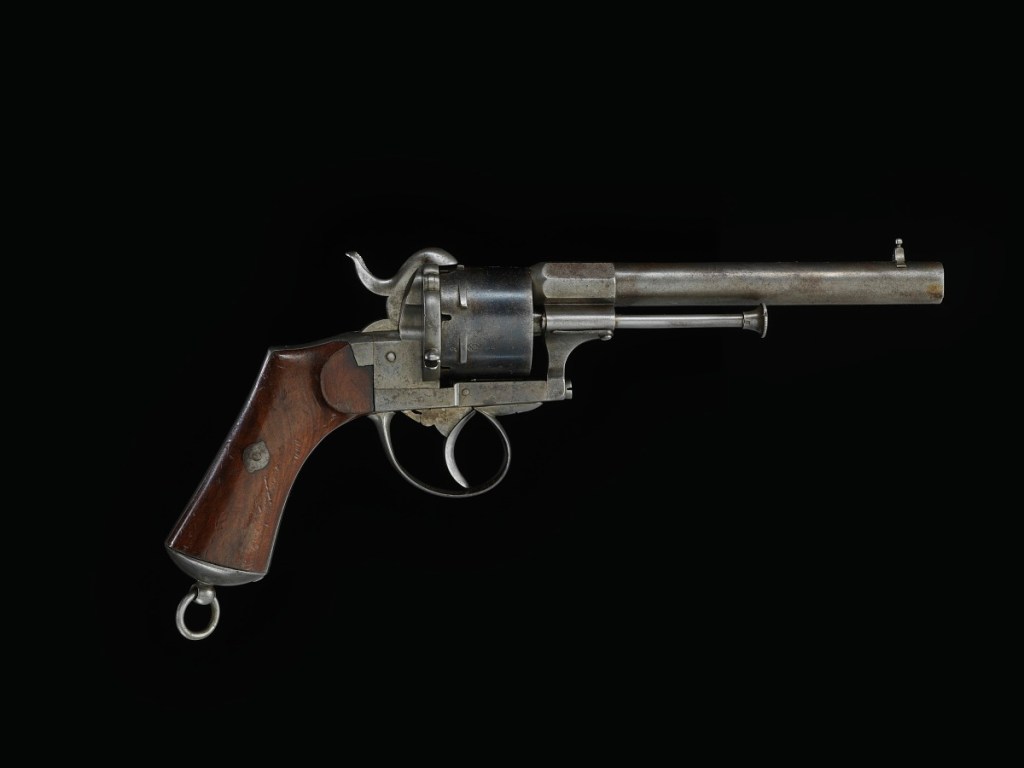

According to the auction house, while admitting that it could never be 100% certain that it was the actual gun used by the artist to take his life, circumstantial evidence certainly points to that conclusion. According to museum officials, the rusted skeletal frame of the 7mm Lefaucheux revolver was “discovered where Van Gogh shot it; its caliber is the same as the bullet retrieved from the artist’s body as described by the doctor at the time; (and) scientific studies demonstrate that the gun had stayed in the ground since the 1890s.” Devil’s advocate: Lefaucheux pinfire revolvers were inexpensive and plentiful in the late 19th century. They can be found everywhere all over the world, so finding one in a field under a random tree in France may not constitute proof experts require for authentication. While stories like that may have worked in Oldroyd’s day, it certainly does not live up to modern curatorial standards. However, it does pique one’s imagination.

The story goes that a local farmer found the gun in 1965 after plowing up the very spot in the field where tradition states the artist shot himself in the stomach in July of 1890. The farmer presented the weapon to the owners of an inn in the village, and it was passed down through their family before it was given to the auction consignor’s mother, who put it up for auction. Also weighing in the gun’s favor is the fact that it is a low-power gun, which explains why the gun didn’t kill Vincent instantly. For those subscribing to the theory that Van Gogh did not shoot himself, the auction house explains that even if his death was caused by hoodlums with a grudge against him or after two young boys playing with a gun “accidentally pressed the trigger and wounded Van Gogh by mistake” the gun could still be the weapon responsible for his death. In 2016, the Van Gogh Museum in Amsterdam exhibited the gun as part of the show “On the Verge of Insanity, Van Gogh and His Illness.”

Regardless, Vincent’s myth is so complicated, his art so unattainable to all but the ultra-rich, the thought of owning the pistol that killed him may strike some as irresistible. Imagine owning the ultimate instrument of tortured artistic doom, carried into an otherwise unremarkable wheat field in northern France in late July of 1890 by a man tortured with night terrors and “overwhelmed by boredom and grief.” Did the nightmares of mental illness finally prove too much to bear? Is this the final instrument of self-martyrdom? I’ll leave that for you, the reader, to decide. Shortly before his death, on July 2, writing to his brother Theo, Vincent commented: “I myself am also trying to do as well as I can, but I will not conceal from you that I hardly dare count on always being in good health. And if my disease returns, you would forgive me. I still love art and life very much…” Eight days later, Vincent wrote Theo in French, “Je me sens – raté” (I feel failed), and added: “And the prospect grows darker, I see no happy future at all.” Before his death at 1:30 in the morning, Vincent’s last words to his brother were remembered as “La tristesse durera toujours” (The sadness will last forever).

On the afternoon of July 30th, Van Gogh’s body was laid out in his attic room, surrounded by his final canvases and masses of yellow flowers including dahlias and sunflowers. His easel, folding stool, and paintbrushes were placed before the coffin. Van Gogh’s last retreat at the Auberge Ravoux has remained intact since his death, as according to legend a room where a suicide took place must never again be rented out. Legend states that the room remained sealed up for almost a century for fear of bad luck. The room is unfurnished, except for a chair. However, like Oldroyd’s museum in the House Where Lincoln Died in Washington D.C., Van Gogh’s spirit can be felt there, permeating the very floors, joists, ceiling, and walls where he passed.

Charlotte Corday
Original publish date July 18, 2024. https://weeklyview.net/2024/07/18/charlotte-corday/

This 24-hour news cycle world can be exhausting. As I write this article, we stand at 120 days and counting until our next Presidential election. We are constantly reminded that this will be the most important election in the history of our country and that the end of Democracy is on the line. Since I spend most of my time buried in history of one sort or another, a phrase from the ancients runs on a loop in my head; “What has been will be again, what has been done will be done again; there is nothing new under the sun.” My idiomatic paraphrase is a Biblical verse: Ecclesiastes 1:9, “The thing that hath been, it is that which shall be; and that which is done is that which shall be done: and there is no new thing under the sun.”
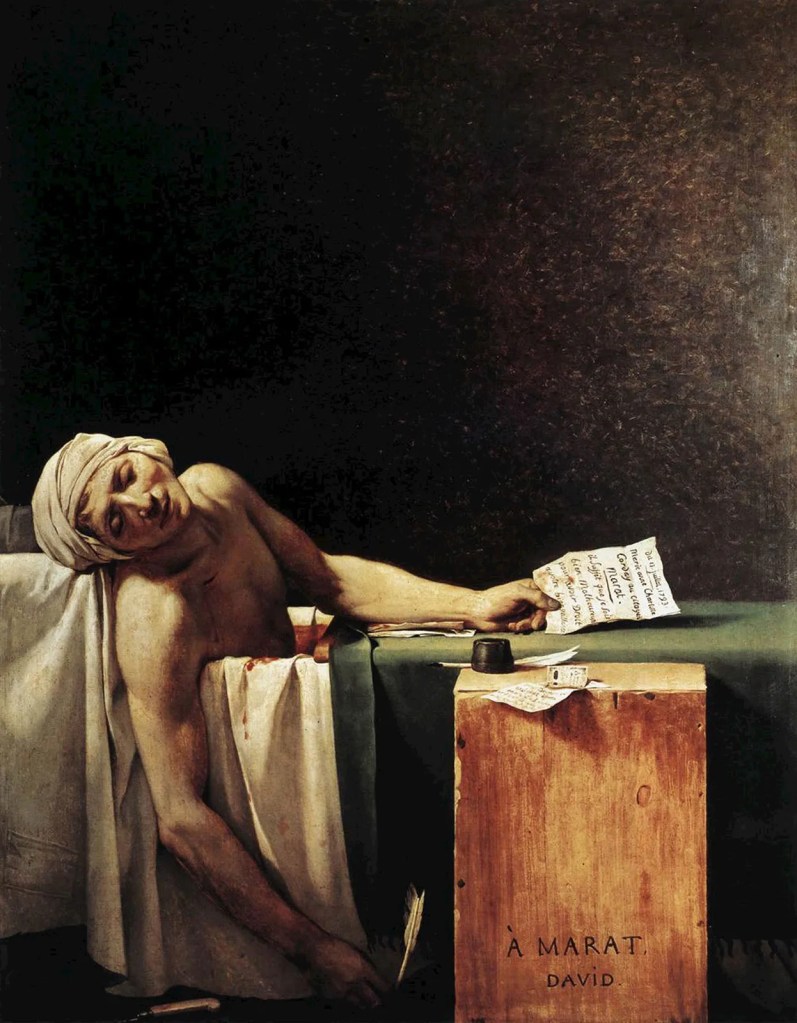
This is the story of Charlotte Corday. It is complicated, shocking, and gory, and does not end well. Her act is immortalized in one of the most famous images from the French Revolution: The Death of Marat, a 1793 painting by Jacques-Louis David. The painting depicts Jean-Paul Marat lying dead in his bathtub after his assassination by Corday on July 13, 1793. It is considered a masterpiece of the highest order and the first modernist work to express just how bad politics can be. The original painting is at the Royal Museum of Fine Arts of Belgium with a replica on display at the Louvre.

Marie-Anne Charlotte de Corday d’Armont (July 27, 1768 – 17 July 1793) was born to an aristocratic family in Normandy, France. Corday held Marat responsible for the September Massacres of 1792, a series of executions of prisoners in Paris during the French Revolution. Over 1600 people, most of whom were non-violent political prisoners, were dragged from their cells and killed by guillotine at the hands of the “Committee of Surveillance of the Commune” led by the Montagnards, who advocated a more radical approach to the revolution. As The French Revolution radicalized further and headed towards terror, Corday began to sympathize with the Girondins. The Girondins supported democratic reforms and a strong legislative branch at the expense of much weaker executive and judiciary branches. She regarded the Girondins as a movement that would ultimately save France and that the Revolution was in jeopardy due to the radical course taken by Marat and the Montagnards.

On July 13, 1793, Corday traveled to Paris to assassinate Marat. He was not hard to find. Marat was suffering from a debilitating skin disease that left him nearly constantly confined to a bathtub to ease his suffering. Marat had always been a sickly man whom contemporaries described as “short in stature, deformed in person, and hideous in face.” The nature of his skin disease has been debated for centuries, some claimed it was syphilis, though most experts have identified it as “Dermatitis herpetiformis” a chronic, intensely itchy, blistering skin manifestation commonly known as celiac disease, a rash affecting about 10 percent of the population. Marat’s condition, which he had been suffering from for three years, was exacerbated by extreme weight loss, emaciation, and diminished strength. Marat stewed in a soup of various minerals and medicines with a bandana soaked in vinegar wrapped around his head. Marat sat upon a linen sheet for modesty, with the dry corners covering his back and bare shoulders, a board straddled the tub from rim to rim which served as a writing desk.

Corday is described on her passport as “five feet and one inch…curly auburn hair, eyes gray, forehead high, mouth medium size, chin dimpled, and an oval face”. Based solely on her appearance, Corday was the unlikeliest of assassins. On July 9, 1793, Corday arrived in Paris and took a room at the Hôtel de Providence. She bought a kitchen knife with a 6-inch blade. During the next few days, she wrote a detailed manifesto explaining her motives for assassinating Marat. At noon on July 13, she arrived at Marat’s home claiming to know about a planned Girondist uprising but was turned away. She returned that evening and was admitted. Their interview lasted fifteen minutes. From his bathtub, Marat wrote down the names of the Girondins as Corday crept ever closer to him. As he busily wrote out the list, Marat said, “Their heads will fall within a fortnight.”

Now within striking distance, Corday pulled the knife from her corset and plunged it deep into his chest, just under his right clavicle, opening the brachiocephalic artery, close to the heart. Marat, still clutching the list of names, slumped into the tub as he called out his last words: “Aidez-moi, ma chère amie!” (“Help me, my dear friend!”). The wound was fatal. In response to Marat’s cries, his wife Simonne Evrard, and two others rushed into the room and seized Corday. Two neighbors, a military surgeon and a dentist, attempted to revive Marat to no avail. Officials arrived to interrogate Corday and to calm a hysterical crowd who appeared ready to lynch her.


Corday’s manifesto claimed: “I have avenged many innocent victims, I have prevented many other disasters. The people, one day disillusioned, will rejoice in being delivered from a tyrant…I rejoice in my fate, the cause is good…I alone conceived the plan and executed it. Crime is shame, not the scaffold!” Corday credited her single-blow knifing of Marat not to skill or practice but to luck. Arrested on the spot, she was tried and convicted by the Revolutionary Tribunal and sentenced to death by guillotine on the Place de la Révolution. On July 17, 1793, four days after Marat was killed, Corday was led to the guillotine via the tumbril, an open cart used to transport its load of condemned prisoners to the guillotine amid the shouts and jeers of bystanders. Corday stood calmly facing the crowd, suddenly, the heavens opened the thousands of curious on-lookers were drenched by a sudden summer rainfall. Corday never flinched.
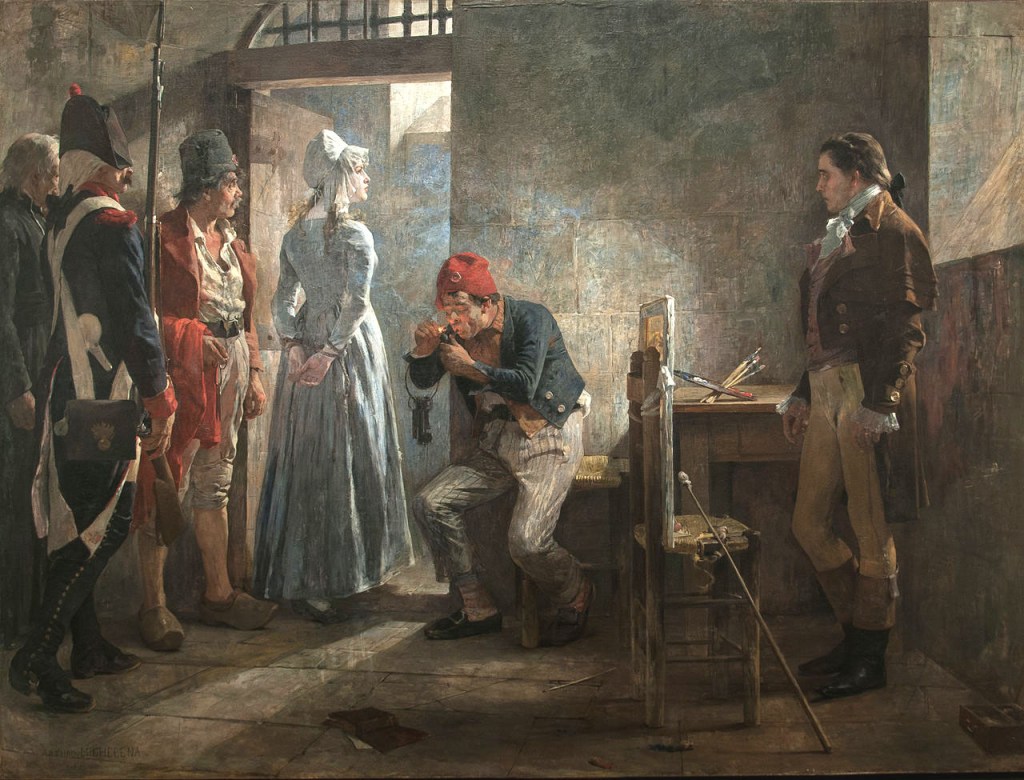



Corday strode confidently to the guillotine, curtseyed to the crowd, leaned against the Bascule, and was lowered face down horizontally, her head placed into the Lunette. The Declic (handle) was pulled by the hooded executioner, releasing the heavy Mouton (weight) and blade from the crossbar. A silent swish swept the crowd as Corday’s head tumbled into the basket below. The Bascule, a sort of table, was hinged to make it easier to push the headless body into a larger side basket immediately after the execution. Moments after Corday’s decapitation, a carpenter named Legros leaped from the crowd and lifted her head from the basket. He turned towards the crowd and slapped it on the cheek. Horrified witnesses reported an expression of “unequivocal indignation” on her face when her cheek was slapped and that “Charlotte Corday’s severed head blushed under the executioner’s slap.” Ever since, the incident has fueled the suggestion that victims of the guillotine retain consciousness for a short while after decapitation. For that offense, Legros the carpenter was imprisoned for three months. To make matters worse, believing that there had to be a man sharing her bed who masterminded the assassination plan, officials had her body autopsied after her death to determine if she was a virgin. To their dismay, their non-scientific examination revealed that she was a virgin. Her body was buried in the Madeleine Cemetery, alongside the decapitated corpses of of King Louis XVI, Queen Marie Antoinette, and three thousand other guillotine victims. Legend claims that Corday’s skull was saved and passed from Parisian to Parisian (friend and foe alike) for generations after her execution.

Corday’s crime did not have the expected outcome and Marat’s assassination did not stop the reign of Terror. Instead, Marat became a martyr. Although the killing of Marat was considered vile, there is no doubt that the murder changed the political role and position of women during the French Revolution. Corday’s action aided in restructuring the private versus public role of women in society at the time. The idea of women as second-class citizens was challenged, and Corday was considered a hero. As the revolution progressed, the Girondins became progressively more opposed to the radical, violent views of the Montagnards espoused by Marat, Robespierre, and others.

However, Corday’s critics quickly elevated Marat to the level of the immortals. His heart was embalmed separately and placed in an urn on an altar erected to his memory. His remains were transferred to the Panthéon where his near messianic role in the Revolution was gaslighted in a eulogy delivered by the Marquis de Sade, who compared Marat to Jesus Christ and idealized him as a man who loved only the people of France. Marat was transformed into a quasi-saint, his bust often replacing crucifixes in the churches of Paris. After the ousting of Maximilien Robespierre a year later, Marat’s reputation plummeted. His busts were knocked off their pedestals, carried away, and dragged through the streets by local children to the chants of ‘Marat, voilà ton Panthéon!’ (Marat, here is your Panthéon) before being dumped into the sewers. The few remaining statues of Marat were melted down during the Nazi occupation of Paris in World War II. Strangely, he continued to be held in high regard in the Soviet Union with many citizens, streets, and even a battleship sharing the name Marat.

Europeans remain split on the legacy of Corday. Some place her alongside Joan of Arc, the patron saint of France, who died 350 years prior, and others dismiss her as an idealistic radical. Corday lives on in popular memory through numerous works of art, poetry, plays, and literature including works by Percy Bysshe Shelley and Oscar Wilde, and her story is referenced variously in Rebecca of Sunnybrook Farm and Les Misérables. Marat’s wife peddled his bathtub to the highest bidder but not very successfully. Reportedly, interested parties included Madame Tussaud’s wax museum and P.T. Barnum, but it ultimately landed in the Musée Grévin, a Paris wax museum, where it remains today. The tub is in the shape of an old-fashioned high-buttoned shoe with a copper lining. However, the most tangible reminder of Marat’s death is Jacques-Louis David’s painting. David was not only the painter but also the man who organized Marat’s funeral. Marat’s disorder accelerated decomposition, making any realistic depiction of the scene impossible. The result was that David’s work beautified the skin that in reality had been discolored and scabbed from his chronic skin disease. The resulting painting was widely criticized as glorifying Marat’s death.

As for Corday’s reputation, history recalls her as the “Angel of Assassination” and lauds her as an early pioneer in the annals of women’s rights. After the assassination of Abraham Lincoln, the April 29, 1865, Harper’s Weekly mentioned Corday in a series of articles analyzing the assassination as the “one assassin whom history mentions with toleration and even applause”, but goes on to conclude that her assassination of Marat was a mistake in that she became Marat’s last victim rather than vindicating his thousands of victims. Proving that violence in the interest of “small d” democracy is, was, and always will be, futile and unacceptable.
George Alfred Townsend and The War Correspondent Memorial Arch.
Original publish date April 11, 2024. https://weeklyview.net/2024/04/11/george-alfred-townsend-and-the-war-correspondent-memorial-arch/

Next week will witness another sad passing in American history: the 159th anniversary of the assassination of Abraham Lincoln. Because I live with this date dancing around in my head more than most, I want to share my experience (and admiration) for a peripheral character in that tragedy: George Alfred Townsend. Born in Georgetown, Delaware on January 30, 1841, Townsend was one of the youngest war correspondents during the American Civil War. Soon after graduation from high school (with a Bachelor of Arts) in 1860, Townsend began his career as a news editor with The Philadelphia Inquirer. In 1861, he moved to the Philadelphia Press as city editor. As the war broke out, he worked for the New York Herald as a war correspondent in Philadelphia.
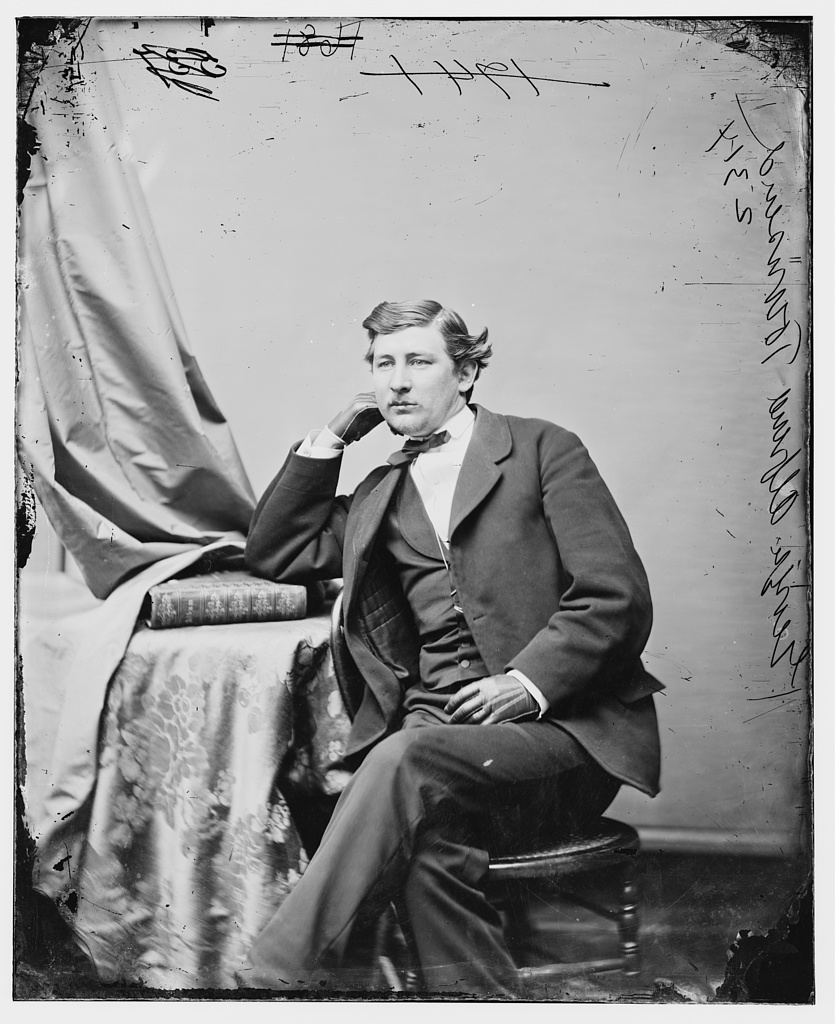

By April 1862, George got his big break when General George McClellan rode through Philadelphia on his way to Washington. That fortuitous meeting would propel young Townsend to exclusive access to many of the Civil War’s greatest battles. One of America’s first nationally syndicated columnists, Townsend used the pen name “Gath” for his newspaper columns. Gath was an acronym of his initials with the addition of an “H” at the end. Friends and contemporaries like Mark Twain, Bret Harte, and Noah Brooks, claimed the “H” stood for “Heaven” while wags and rivals claimed it stood for “Hell.” Gath himself was inspired by the biblical passage uttered by David after the death of King Saul in II Samuel 1:20, “Tell it not in Gath, publish it not in the streets of Askalon.”

While Townsend won accolades for his work covering the war, it was his coverage of the Lincoln assassination that he is best remembered for. His detailed columns (which he called “letters”) about the tragedy were filed between April 17 – May 17 and would later be published as The Life, Crime and Capture of John Wilkes Booth. Published in 1865, Townsend’s book offers a full sketch of the assassin, the conspiracy, the pursuit, trial, and execution of his accomplices. As a lifelong student of Lincoln, I have read countless books, articles, letters, and various accounts centered on his life. It was in George Alfred Townsend’s “letters” that I found my holy Grail. Townsend’s description of Lincoln in his coffin made me feel as if I were standing there myself. His description of Lincoln’s office left me awestruck and wishful. In my opinion, it would be hard to find a more worthy example of Victorian journalism than these excerpts from Gath’s “letters”.
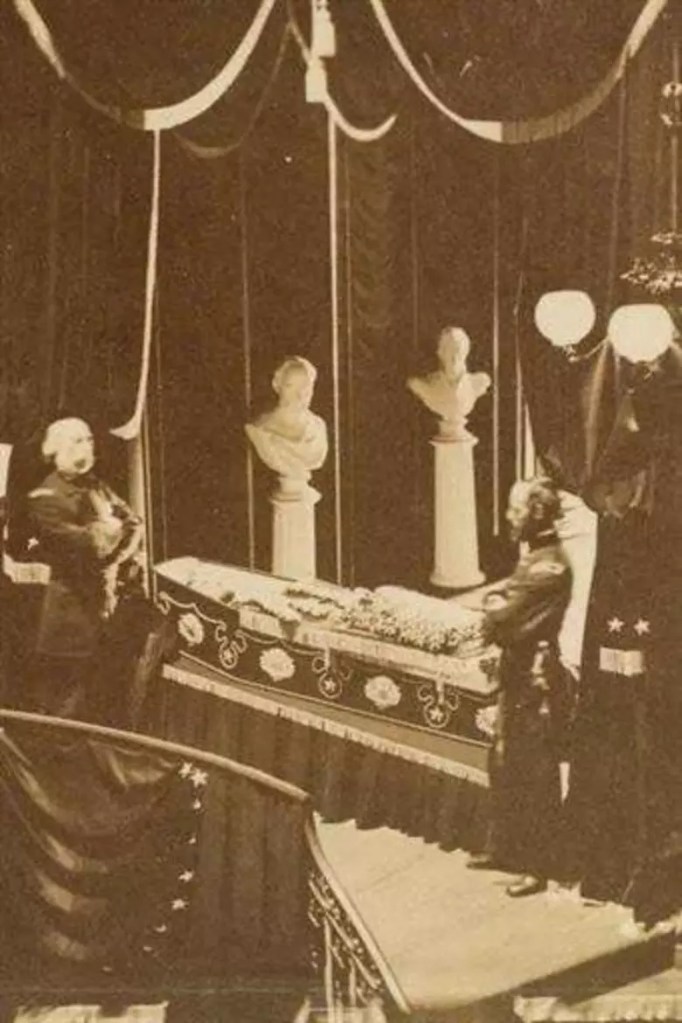
“Deeply ensconced in the white satin stuffing of his coffin, the President lies like one asleep. Death has fastened into his frozen face all the character and idiosyncrasy of life. He has not changed one line of his grave, grotesque countenance, nor smoothed out a single feature. The hue is rather bloodless and leaden; but he was always a sallow. The dark eyebrows seem abruptly arched; the beard, which will grow no more, is shaved close, save the tuft at the short small chin. The mouth is shut, like that of one who had put the foot down firm, and so are the eyes, which look as calm as slumber. The collar is short and awkward, turned over the stiff elastic cravat, and whatever energy or humor or tender gravity marked the living face is hardened into its pulseless outline. No corpse in the world is better prepared according to appearances. The white satin around it reflects sufficient light upon the face to show us that death is really there; but there are sweet roses and early magnolias, and the balmiest of lilies strewn around, as if the flowers had begun to bloom even upon his coffin. Looking on interruptedly! for there is no pressure, and henceforward the place will be thronged with gazers who will take from the site its suggestiveness and respect. Three years ago, when little Willie Lincoln died, Doctors Brown and Alexander, the embalmers or injectors, prepared his body so handsomely that the President had it twice disinterred to look upon it. The same men, in the same way, have made perpetual these beloved lineaments. There is now no blood in the body; it was drained by the jugular vein and sacredly preserved, and through a cutting on the inside of the thigh the empty blood vessels were charged with the chemical preparation which soon hardened to the consistence of stone. The long and bony body is now hard and stiff, so that beyond its present position it cannot be moved any more than the arms or legs of a statue. It has undergone many changes. The scalp has been removed, the brain taken out, the chest opened and the blood emptied. All that we see of Abraham Lincoln, so cunningly contemplated in his splendid coffin, is a mere shell, an effigy, a sculpture. He lies in sleep, but it is the sleep of marble. All that made the flesh vital, sentiment, and affectionate is gone forever.”

On May 14, 1865, the day Abraham Lincoln’s body was placed on the funeral train to leave Washington DC forever, Townsend visited the White House. Mary Lincoln still resided there with her beloved son Tad, too distraught to leave the White House. “I am sitting in the President’s office. He was here very lately, but he will not return to dispossess me of the high-backed chair he filled so long, nor resume his daily work at the table where I am writing. There are here only Major Hay (Salem Indiana’s John Hay, Lincoln’s private secretary) and the friend who accompanies me. A bright-faced boy runs in and out, darkly attired, so that his fob chain of gold is the only relief to his mourning garb. This is little Tad, the pet of the White House. That great death, with which the world rings, has made upon him only the light impression which all things make upon childhood. He will live to be a man pointed out everywhere, for his father’s sake; and as folks look at him, the tableau of the murder will seem to encircle him.”
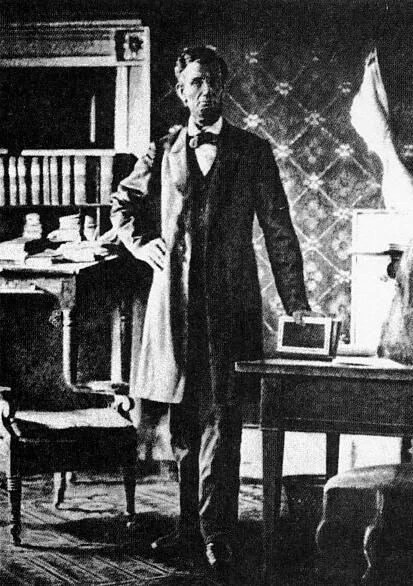

Townsend further describes Lincoln’s office, just as he left it. “The room is long and high, and so thickly hung with maps that the color of the wall cannot be discerned. The President’s table at which I am seated adjoins a window at the farthest corner; and to the left of my chair as I reclined in it, there is a large table before an empty grate, around which there are many chairs, where the cabinet used to assemble. The carpet is trodden thin, and the brilliance of its dyes is lost. The furniture is of the formal cabinet class, stately and semi-comfortable; there are bookcases sprinkled with the sparse library of a country lawyer, but lately plethoric, like the thin body which has departed in its coffin. Outside of this room, there is an office, where his secretaries sat – a room more narrow but as long – and opposite this adjacent office, a second door, directly behind Mr. Lincoln’s chair leads by a private passage to his family quarters. I am glad to sit here in his chair, where he has spent so often, – in the atmosphere of the household he purified, and the site of the green grass and the blue river he hallowed by gazing upon, in the very center of the nation he preserved for the people, and close the list of bloodied deeds, of desperate fights of swift expiations, of renowned obsequies of which I have written, by indicting at his table the goodness of his life and the eternity of his memory.”
“They are taking away Mr. Lincoln’s private effects, to deposit them wheresoever his family may abide, and the emptiness of the place, on this sunny Sunday, revives that feeling of desolation from which the land has scarce recovered. I rise from my seat and examine the maps; they are from the coast survey and engineer departments, and exhibit all the contested grounds of the war: there are pencil lines upon them where someone has traced the route of armies, and planned the strategic circumferences of campaigns. Was it the dead President who so followed the March of Empire, and dotted the sites of shock and overthrow? So, in the half-gloomy, half-grand apartment, roamed the tall and wrinkled figure whom the country had summoned from his plain home into mighty history, with the geography of the Republic drawn into a narrow compass so that he might lay his great brown hand upon it everywhere. And walking to and fro, to and fro, to measure the destinies of arms, he often stopped, with his thoughtful eyes upon the carpet, to ask if his life were real and he were the arbiter of so tremendous issues, or whether it was not all a fever-dream, snatched from his sofa in the routine office of the Prairie state.”

“I see some books on the table; perhaps they have lain there undisturbed since the reader’s dimming eyes grew nerveless. A parliamentary manual, a thesaurus, and two books of humor, “Orpheus C. Kerr,” and “Artemis Ward.” These last were read by Mr. Lincoln in the pauses of his hard day’s labor. Their tenure here bears out the popular verdict of his partiality for a good joke; and, through the window, from the seat of Mr. Lincoln, I see across the grassy grounds of the capitol, the broken shaft of the Washington Monument, the long bridge and the fort-tipped Heights of Arlington, reaching down to the shining riverside. These scenes he looked at often to catch some freshness of leaf and water, and often raised the sash to let the world rush in where only the nation abided, and hence on that awful night, he departed early, to forget this room and its close applications in the abandon of the theater. I wonder if it were the least of Booth’s crimes to slay this public servant and the stolen hour of recreation he enjoyed but seldom. We worked his life out here, and killed him when he asked a holiday.”

As one of the most successful journalists of his day, Townsend accumulated a tidy fortune. He used much of that fortune to build a 100-acre baronial estate near Crampton’s Gap, South Mountain, Maryland known as “Gapland”. The Civil War Battle of Crampton’s Gap was fought as part of the Battle of South Mountain on September 14, 1862, and resulted in 1,400 combined casualties. Tactically the battle resulted in a Union victory because they broke the Confederate line and drove through the gap. Strategically, the Confederates were successful in stalling the Union advance and were able to protect the rear. Gath literally bought the battlefield upon which he built his estate. The estate was composed of several buildings, including Gapland Hall, Gapland Lodge, the Den and Library Building, and a brick mausoleum (notable for its inscription of “Good Night Gath” above the entrance).
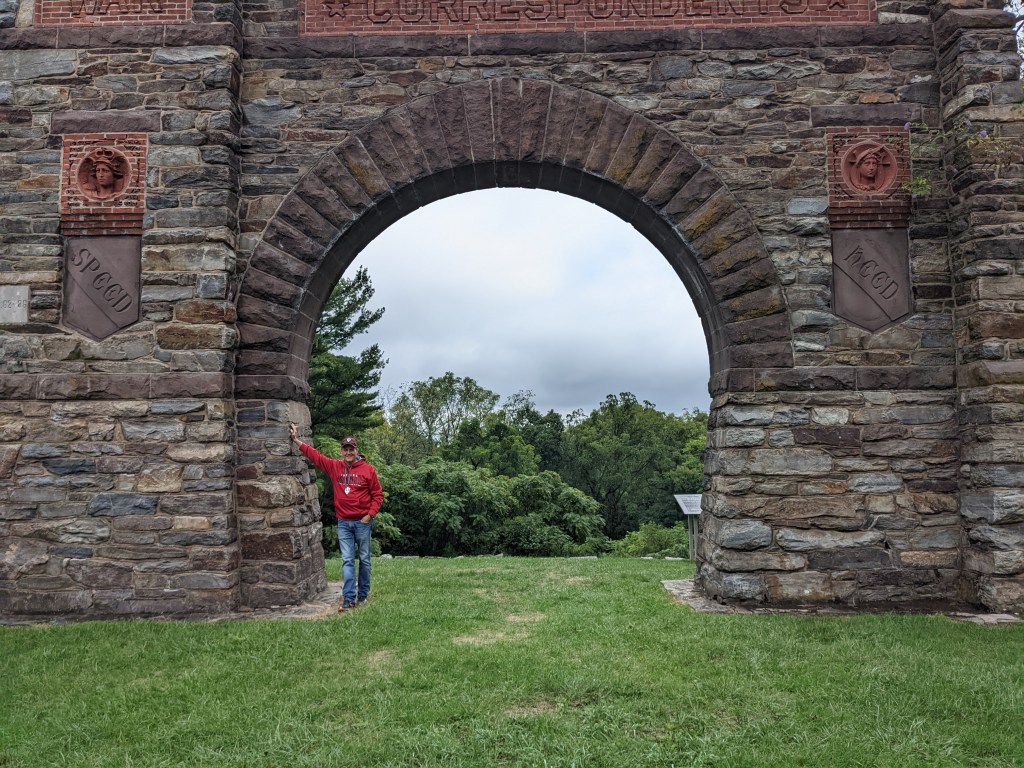

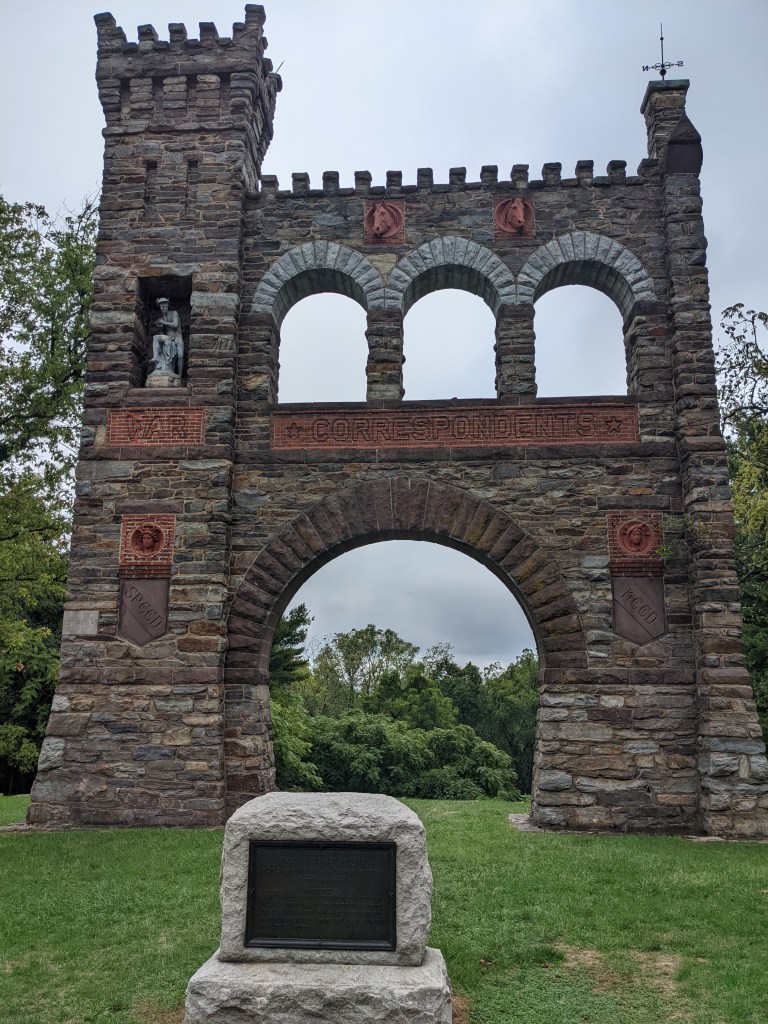
In 1896, Townsend built a monument to war correspondents to memorialize the contributions of his colleagues North and South. Dedicated in 1896, The War Correspondent Memorial Arch is 50 feet high and 40 feet wide and is the only monument in the world dedicated solely to war correspondents. Not only does the arch stand on Townsend’s original estate (operated by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources), it also rests smack dab in the middle of the Appalachian National Scenic Trail. Furthermore, the woods surrounding Gapland and the nearby town of Burkittsville were the setting for the 1999 horror film Blair Witch Project.
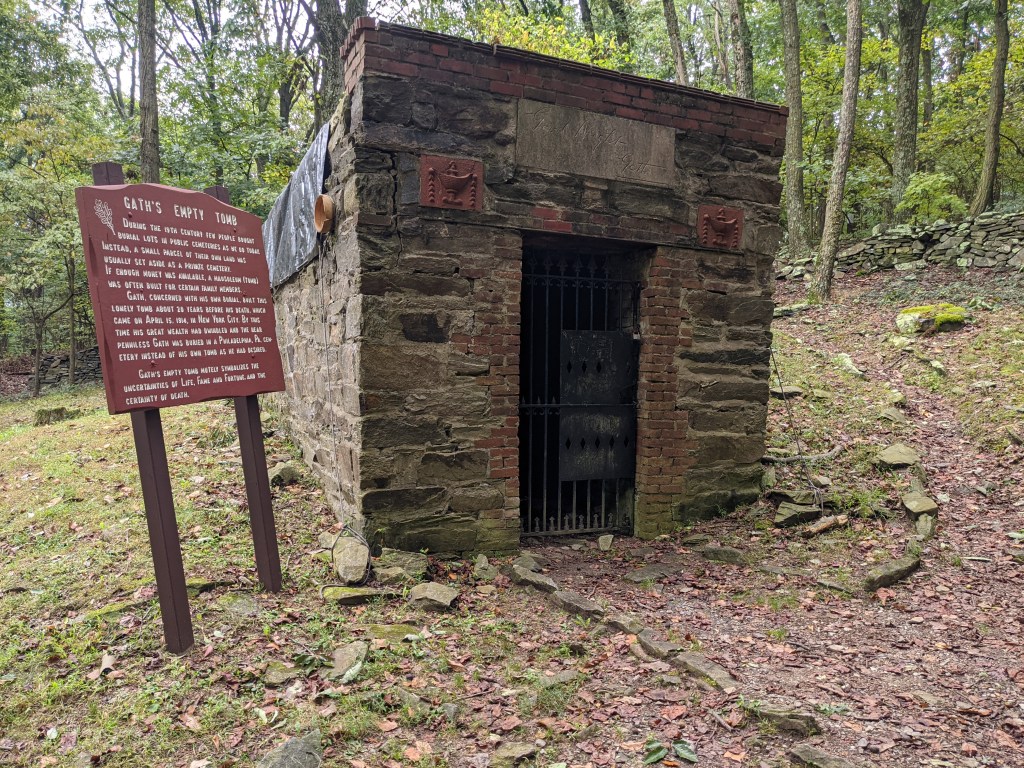

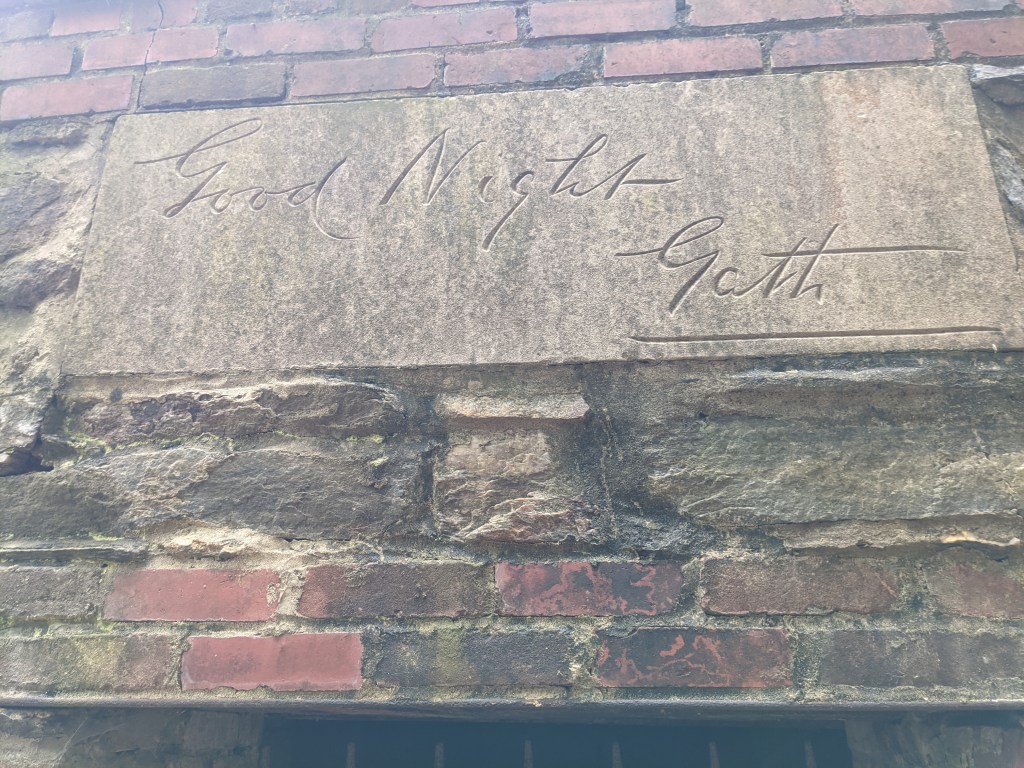
Last September, I traveled to the Catoctin Mountains to visit Townsend’s estate not far from the Antietam battlefield. Townsend’s Gapland estate is now known as Gathland State Park. Several buildings still stand, including Gapland Hall (which is the park headquarters) and the mausoleum, while other buildings are mere shadows of their former self. Townsend left Gapland in 1911 and died in New York City three years later on April 15, 1914. The 49th anniversary of Abraham Lincoln’s death. He was buried at Laurel Hill Cemetery in Philadelphia.
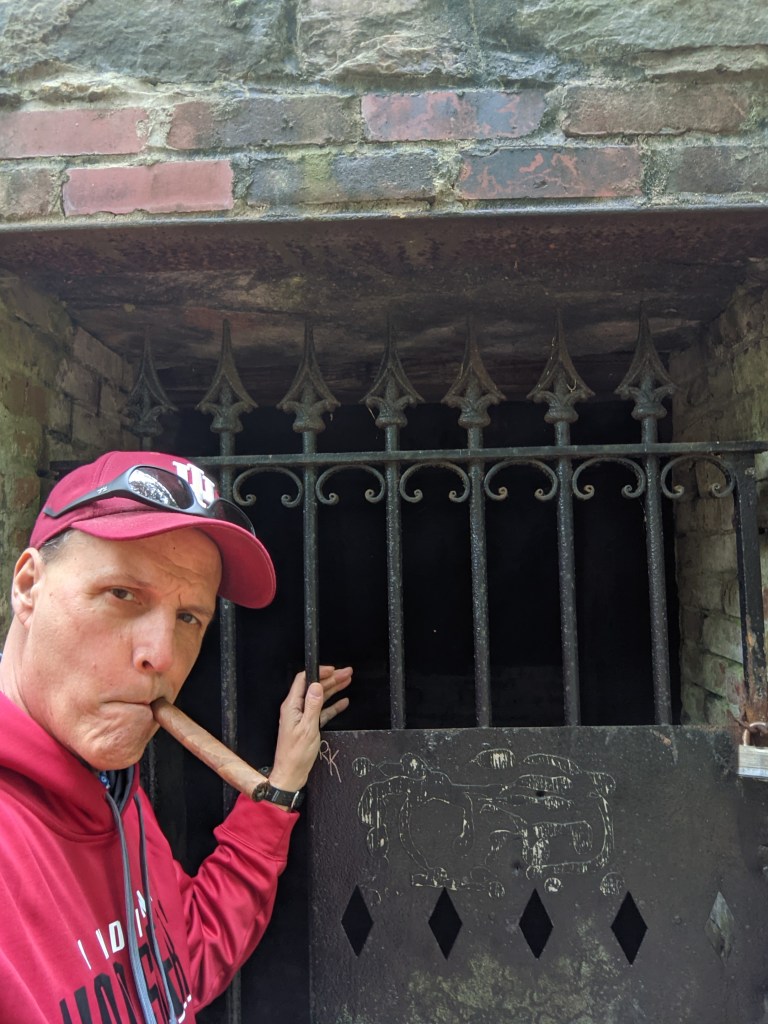

His brick mausoleum, fronted by an ominous-looking iron gate causing it to look more like a jail cell than a tomb, stands empty, its roof slowly caving in. Although the object of my quest was The War Correspondent Memorial Arch, I could not help but spend most of my time seated beneath that empty tomb smoking a cigar. While the hale and hearty hikers pausing briefly at the foot of the Appalachian Trail might not have appreciated my vice, as I stared at the epitaph above the iron gate above Townsend’s unused tomb, George Alfred Townsend would understand. Good Night Gath.

